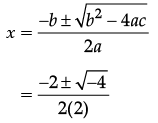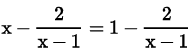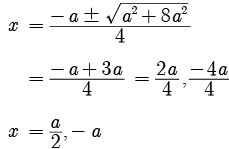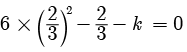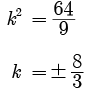Q1:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself:Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): The degree of quadratic equation is always 2. Hence, x2 – 1 = 0 is pure quadratic equation.
Reason (R): An equation of the form ax2 + c = 0 is known as pure quadratic equation.
Explanation
An equation that can be expressed in the form ax2 + c = 0, where a and c are real numbers and a = 0 is a pure quadratic equation. Or the quadratic equation having only second degree variable is called a pure quadratic equation.
Report a problem
Q2:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): The product of two successive positive integral multiples of 5 is 300, then the two numbers are 15 and 20.
Reason (R): The product of two consecutive integrals is a multiple of 2.
Explanation
15 and 20 are the correct two successive positive integral multiples whose product is 300. So, this Assertion is true.
The reason is also true as n(n+1) is divisible by 2 always for all natural number n.
Therefore, Both A and R are true and R is not correct explanation for A.
Report a problem
Q3:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): In the expression: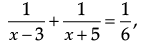 x can’t have values 3 and – 5
x can’t have values 3 and – 5
Reason (R): If discriminant D = b2 – 4ac > 0 then the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are real and unequal.
Explanation
In the expression:
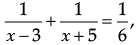
we can’t have values of 3 and – 5
As we will get 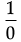 forms in the expression which has no solution.
forms in the expression which has no solution.
So, the assertion is correct.
D = b2 – 4ac > 0 then the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are real and unequal. The reason perfectly explains the roots of the equation whose D > 0. But it doesn’t explains the assertion.
Therefore, Both A and R are true and R is not correct explanation for A.
Report a problem
Q4:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): The equation 8x2 + 3kx + 2 = 0 has equal roots than the value of k is ± 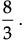
Reason (R): The equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has equal roots if D = b2 – 4ac = 0.
Explanation
Reason perfectly explains the nature of roots when D = 0 for any quadratic equation.
Let us apply the reason on the equation,
8x2 + 3kx + 2 = 0
D = b2 – 4ac = 0
⇒ (3k)2 – 4(8) (2) = 0
⇒ 9k2 – 64 = 0
⇒ 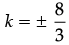
Report a problem
Q5:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself:Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Values of x are a for the quadratic equation 2x2 + ax – a2 = 0.
Reason (R): For a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, the roots are given by
x = (-b ± √(b2 - 4ac)) / 2a.
Explanation
The Reason (R) statement correctly states the quadratic formula for roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, which is:
x = (-b ± √(b2 - 4ac)) / 2a.
Let us apply this formula to the equation 2x2 + ax – a2 = 0:
Here, a = 2, b = a, and c = -a2.
Roots are:
x = (-a ± √(a2 - 4 × 2 × (-a2))) / (2 × 2)
= (-a ± √(a2 + 8a2)) / 4
= (-a ± √(9a2)) / 4
= (-a ± 3a) / 4
Therefore the roots are:
(-a + 3a) / 4 = 2a / 4 = a / 2
and
(-a - 3a) / 4 = -4a / 4 = -a
So the roots are x = a/2 and x = -a, which means the assertion that values of x are a is incorrect.
Hence, Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Report a problem
Q6:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Sum of ages of two friends is 20 years. Four years ago, the product of their ages in years was 48. Then the difference between their ages is 16.
Reason (R): For quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0,
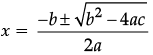
Explanation
Present age of 1
st friend = x years
Present age of 2nd friend = 20 – x years
4 years ago, age of 1st friend = x – 4
Age of 2nd friend = 16 – x years
According to the question,
(x – 4)(16 – x) = 48
⇒ 16 x – x2 – 48 + 4x = 48
⇒ x2 – 20x + 112 = 0
⇒ D = b2 – 4ac = (–20)2 – 4(1)(112) = – 48
Roots of the equation would be imaginary which is not possible for ages.
Hence, the situation is wrong.
Therefore, A is false but R is true.
Report a problem
Q7:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): The roots of the quadratic equation x2 + 2x + 2 = 0 are imaginary.
Reason (B): If discriminant D = b2 – 4ac < 0="" then="" the="" roots="" of="" the="" quadratic="" equation="" />2 + bx + c = 0 are imaginary.
Explanation
Let us apply the reason on the equation,
x2 + 2x + 2 = 0
D = b2 – 4ac = (2)2 – 4(1)(2) = 4 – 8 = – 4
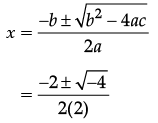
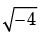 is unreal.
is unreal.
No real value is possible in this case.
Therefore, Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation for A.
Report a problem
Q8:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): If we solve the equation of the form 9(x+2) – 6.(3)(x+1) + 1 = 0, then x = – 2.
Reason (R): The equation of the form x2a + xb + b = 0 can’t be solved by quadratic formula.
Explanation
9
(x+2) – 6.(3)
(x+1) + 1 = 0
9x.92 – 6.3x.31 + 1 = 0
Or 81(3x)2 – 18.3x + 1 = 0
Let 3x = y So the equation becomes, 81y2 – 18y + 1 = 0 Which is a quadratic equation and its zeroes are 1/9, 1/9
Which contradicts the reason.
Therefore, A is true but R is false
Report a problem
Q9:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): The equation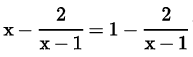 has no root.
has no root.
Reason (R): x - 1 ≠ 0, then only above equation is defined.
Explanation
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
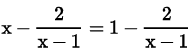
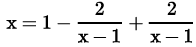
x = 1
However at x = 1 the expression 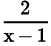 is not defined.
is not defined.
Hence the above equation has no real roots.
Report a problem
Q10:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : The equation x2 + 3x+1 = (x - 2)2 is a quadratic equation.
Reason : Any equation of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0 where a ≠ 0 , is called a quadratic equation.
Explanation
We have, x
2 + 3x + 1 = (x - 2)
2 = x
2 - 4x + 4
⇒ x2 + 3x + 1 = x2 - 4x + 4
⇒ 7x - 3 = 0 ,
it is not of the form ax2 + 6x + c = 0
So, A is incorrect but R is correct.
Report a problem
Q11:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : The values of x are 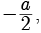 a for a quadratic equation 2x2 +ax- a2 =0 .
a for a quadratic equation 2x2 +ax- a2 =0 .
Reason : For quadratic equation ax2 + bx+ c = 0
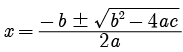
Explanation
2x
2 +ax- a
2 = 0
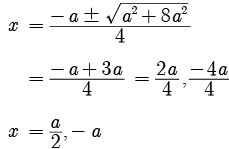
So, A is incorrect but R is correct.
Report a problem
Q12:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : The value of k = 2 , if one root of the quadratic equation 6x2 -x- k = 0 is ⅔
Reason : The quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 a has two roots.
Explanation
As one root is 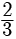 x =
x = 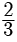
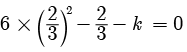
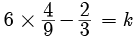
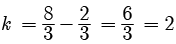
k = 2
So, both A and R are correct but R does not explain A.
Report a problem
Q13:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself:DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : If roots of the equation x2 - bx + c = 0 are two consecutive integers, then b2 - 4c =1
Reason : If a, b, c are odd integer then the roots of the equation 4abc x2 + (b2 - 4ac)x - b = 0 are real and distinct.
Explanation
Assertion : Given equation
x2 - bx + c = 0
Let α,β be two roots such that
|α, - β|2 = 1
(α + β)2 - 4αβ = 1
b2 - 4c = 1
Reason : Given equation
4abc x2 + (b2- 4ac) x - b = 0
D = (b2 - 4ac)2 + 16ab2 c
D = (b2 - 4ac)2 > 0
Hence roots are real and unequal.
Report a problem
Q14:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 , has two distinct real roots, if b2 - 4ac >0 .
Reason : A quadratic equation can never be solved by using method of completing the squares.
Explanation
If a = 0, it becomes linear equation.
If b2 − 4ac = 0, then there will be real and equal roots.
If b2 − 4ac < 0,="" then="" the="" roots="" will="" be="" />
Only if b2 − 4ac > 0, we will get two real distinct roots.
Report a problem
Q15:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : 4x2 -12x+9 =0 has repeated roots.
Reason : The quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 have repeated roots if discriminant D > 0 .
Explanation
Assertion 4x
2 - 12x + 9 = 0
D = b2 - 4ac
= (- 12)2 - 4(4)(9)
= 144 - 144 = 0
Roots are repeated.
Report a problem
Q16:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : (2x - l)2 - 4x2 + 5 = 0 is not a quadratic equation.
Reason : x = 0, 3 are the roots of the equation 2x2 -60x = 0.
Explanation
Assertion and Reason both are true statements. But Reason is not the correct explanation.
Assertion (2x - 1)2 - 4x2 + 5 = 0
- 4x + 6 = 0
Reason 2X2 - 6x = 0
2x(x - 3) = 0
x = 0
and x = 3
Report a problem
Q17:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : The equation 8x2 + 23kx+0 = has equal roots then the value of k is 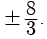
Reason : The equation ax2 + bx+ c = 0 has equal roots if D =b2 - 4ac =0
Explanation
8x2 + 3kx + 2 = 0
Discriminant, D = b2 - 4ac
D = (3k)2 - 4 x 8 x 2 = 9k2 - 64
For equal roots, D = 0
9k2 - 64 = 0
9k2 = 64
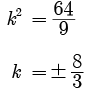
So, A and R both are correct and R explains A.
Report a problem
Q18:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : The roots of the quadratic equation x2 + 2x+2 = 0 are imaginary.
Reason : If discriminant D =b2 - 4ac <0 then="" the="" roots="" of="" quadratic="" equation="">2 + bx+ c = 0 are imaginary.
Explanation
x
2 + 2x + 2 = 0
Discriminant, D = b2 - 4ac
= (2)2 - 4 x 1 x 2
= 4 - 8 = - < />
Roots are imaginary.
So, both A and R are correct and R explains A.
Report a problem
Q19:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Try yourself: DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : The equation 9x2 + 34kx + 4 = 0 has equal roots for k = + 4 .
Reason : If discriminant ‘D’ of a quadratic equation is equal to zero then the roots of equation are real and equal.
Explanation
Assertion 9x2 + 43kx + 4 = 0
D = b2 - 4ac
= (3k)2 - 4(9)(4)
= 9k2 - 144
For equal roots D = 0
9k2 = 144
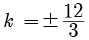
k = ± 4
Report a problem
Q20:
Question for Assertion & Reason Type Questions: Quadratic Equations
Explanation
Assertion says sum and product of roots are 3/2 and 5/2, respectively.
But we just found:
-
Sum = 35/2, not 3/2
-
Product = 0, not 5/2
So, Assertion is false
Reason states:
So, Reason is true
Final Answer: (d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Report a problem
![]() x can’t have values 3 and – 5
x can’t have values 3 and – 5![]()
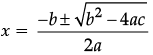
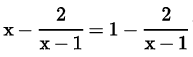 has no root.
has no root.![]() a for a quadratic equation 2x2 +ax- a2 =0 .
a for a quadratic equation 2x2 +ax- a2 =0 .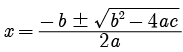
![]()
![]() and
and![]() respectively.
respectively.![]() and product of roots
and product of roots ![]()