Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Metals and Non-metals
Q1: Define the following terms
(i) Mineral
(ii) Ore
(iii) Gangue.
Ans:
(i) Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances found in the Earth's crust, composed of elements or compounds. (ii) Ores are minerals from which metals can be profitably extracted.
(ii) Ores are minerals from which metals can be profitably extracted.
(iii) Gangue refers to the unwanted impurities such as sand, rock, and other non-metallic substances present in an ore.
Q2:
(a) Due to which property of metals is metallic foils prepared?
(b) Write uses of aluminium foils.
Ans:
(a) Metallic foils are prepared, making use of the malleable property of metals.
(b) Aluminium foils are used for:
(i) Wrapping chocolates and foodstuff.
(ii) To prepare hydrogen.
Q3: Give reasons for the following
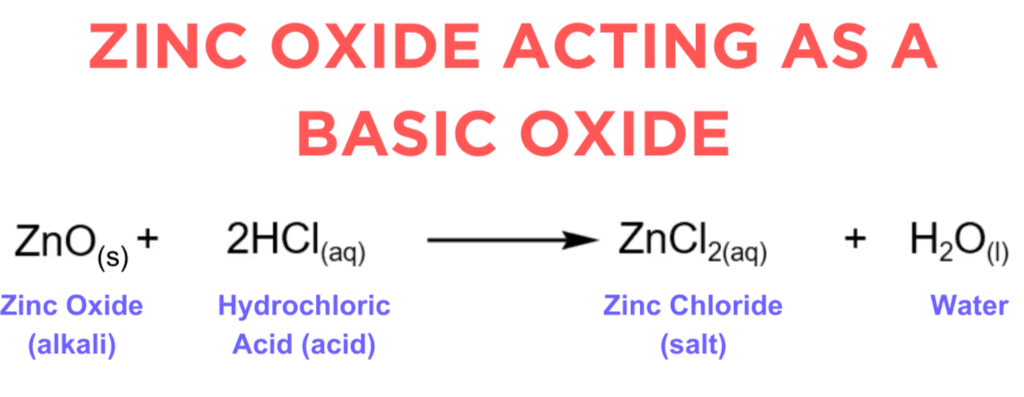
(i) Zinc oxide is considered an amphoteric oxide.
(ii) Non-metals in general do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
(iii) Metals conduct electricity.
Ans:
(i) Zinc oxide is considered amphoteric because it exhibits both acidic and basic properties, reacting with both acids and bases.
 (ii) Non-metals do not react with acids because they lack free electrons to donate, unlike metals.
(ii) Non-metals do not react with acids because they lack free electrons to donate, unlike metals.
(iii) Metals conduct electricity due to the presence of free electrons, which move easily through the metal, allowing the flow of electric current.
Q4: Explain the process of electrolytic refining of impure copper (Cu). Describe how this process helps in obtaining pure copper and write the balanced chemical equation for the electrolytic refining of impure copper.
Ans: Electrolytic refining is a process used to purify metals obtained from ore or other sources. In the case of impure copper, this process involves the use of electrolysis to remove impurities and obtain pure copper.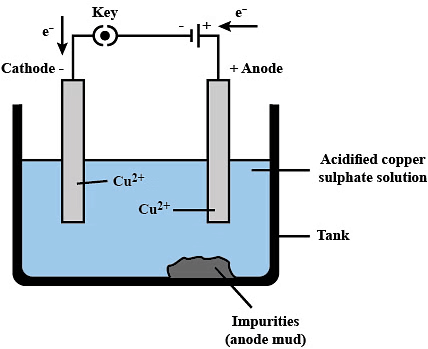 Process of Electrolytic Refining: Impure copper is used as the anode, while a thin sheet of pure copper serves as the cathode. Both are immersed in an electrolyte solution containing copper sulfate (CuSO₄) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
Process of Electrolytic Refining: Impure copper is used as the anode, while a thin sheet of pure copper serves as the cathode. Both are immersed in an electrolyte solution containing copper sulfate (CuSO₄) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
- Anode → Impure copper
- Cathode → Pure copper sheet
- Electrolyte → Copper sulfate (CuSO₄) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
Steps:
- An electric current passes through the electrolyte, dissolving the impure copper from the anode.
- Copper ions (Cu²⁺) move to the cathode, where they gain electrons and deposit as pure copper.
- Impurities settle at the bottom as anode mud.
Balanced Chemical Equation for Electrolytic Refining of Copper:
- At Anode: Cu → Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻
- At Cathode: Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
The overall process ensures that impurities from the anode settle at the bottom as anode mud or dissolve into the electrolyte. The pure copper deposited at the cathode is collected, resulting in the purification of copper.
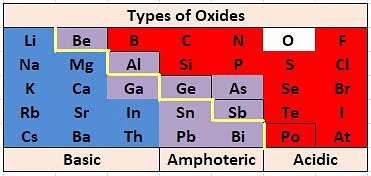
Q5: Identify the following oxides with basic and amphoteric oxides.
(i) ZnO (ii) Na2O (iii) CaO (iv) Al2O3 (v) MgO
Ans:
Basic oxides: MgO; Na2O; CaO
Amphoteric oxides: Al2O3 ; ZnO
(i) Na, K, and Ca metals form hydrides by combination with hydrogen gas, but most other metals do not.
(ii) Aluminium easily combines with oxygen but still, it can be used for making kitchen utensils.
Ans: (i) In the reactivity series, Na, K, and Ca are placed higher up, indicating they are more reactive and can easily form hydrides by reacting with hydrogen. Most other metals are lower in the series, meaning they are less reactive and do not readily form hydrides with hydrogen.
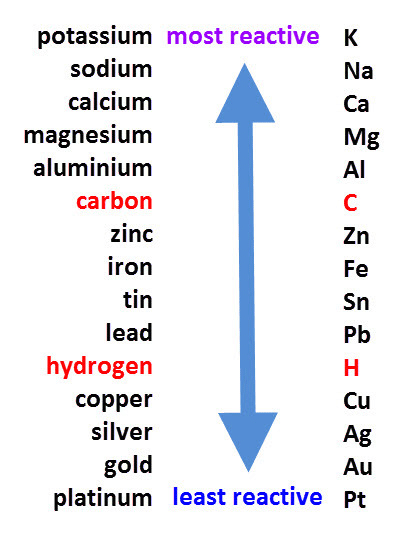 Reactivity Series(ii) Aluminum easily reacts with oxygen to form a thin, stable layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) on its surface. This oxide layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing further oxidation and corrosion. Because of this protective coating, aluminum utensils remain durable and safe for use in the kitchen, even when exposed to air, moisture, or food substances.
Reactivity Series(ii) Aluminum easily reacts with oxygen to form a thin, stable layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) on its surface. This oxide layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing further oxidation and corrosion. Because of this protective coating, aluminum utensils remain durable and safe for use in the kitchen, even when exposed to air, moisture, or food substances.Q7: (i) Among iron and aluminium which rusts easily?
(ii) What are the conditions, necessary for rusting of iron?
Ans:
(i) Among iron and aluminium, iron rusts easily. Aluminium forms Al2O3 which prevents further rusting. That is why iron pipes are wrapped with aluminium metal to prevent rusting of iron.
(ii) Conditions necessary for rusting:
- Presence of oxygen (air)
- Presence of water (moisture)
Q8: What property of hydrogen is observed in the following experiments?
(i) Pop sound is heard when a burning splint is introduced at the mouth of hydrogen-filled jar.
(iii) When black cupric oxide is heated in a stream of hydrogen, reddish colour is obtained.
Ans:
(i) Pop sound is due to the combustible property of hydrogen. Hydrogen burns with oxygen at the mouth of the hydrogen filled jar.
(iii) When black cupric oxide (CuO) is heated in a stream of hydrogen, it undergoes a reduction reaction. The hydrogen acts as a reducing agent and reduces the copper(II) oxide to metallic copper, which has a reddish color:
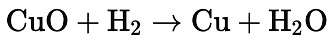
Q9: Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when
(i) Cinnabar is heated in air.
(ii) Calcium metal reacts with water.
Ans:
(i) Cinnabar is heated in air
2HgS + 3O2 (g) → 2HgO (s) +2SO2
(ii) Calcium metal reacts with water.
Ca(s) + 2H2O(I) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g).
Q10: Why do some metals like Na, K, Ca, Mg not occur in nature as free elements?
Ans: Metals like Na, K, etc (alkali metals) and Ca, Mg, etc (alkaline earth metals) are very reactive and hence they react with atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and also with other non-metals like sulphur present in the earth’s crust to form compounds like oxides, carbonates, sulphides, sulphates and chlorides. So they do not occur in a free state but are found in the form of the above compounds.
Q11: Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when:
(i) Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder.
(ii) Steam is passed over hot iron.
Ans:
(i) Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminum powder.
3MnO2(s) + 4AI(s) → 3Mn(I) + 2Al2O3
(ii) Steam is passed over hot iron.
3Fe(s) + 4H2O → Fe3O4 (s) + 4H2
Q12: Explain the term "amphoteric oxides" and provide examples. Describe the reaction of an amphoteric oxide with an acid and a base. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) with sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Ans: Amphoteric oxides are oxides that can exhibit both acidic and basic properties. They can react with both acids and bases to form salts and water.
- Examples of Amphoteric Oxides: Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) and zinc oxide (ZnO) are examples of amphoteric oxides.
- Reaction with Acid: Amphoteric oxides react with acids to form salts and water. For example, aluminum oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce aluminum chloride and water.
Balanced Chemical Equation for Reaction with Acid:
Al₂O₃ + 6HCl → 2AlCl₃ + 3H₂O - Reaction with Base: Amphoteric oxides also react with bases to form salts and water. For instance, aluminum oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce sodium aluminate and water.
Balanced Chemical Equation for Reaction with Base:
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + 2H2O
Ans: Metals like Na, Ca, Mg, Al etc, which are high up in the activity series are electropositive elements and possess a high affinity for oxygen. So their oxides are very much stable and cannot be reduced with common reducing agents like carbon. So carbon reduction process cannot be applied to prepare these metals. They can only be prepared by electrolytic reduction of their fused chlorides or oxides.
(a) What is the chemical composition of the green coating?
(b) Why do copper vessels form such a green coating?
(c) What is the name of the phenomenon, responsible for the green coating?
(d) Copper vessels are best cleaned with tamarind or lemon juice, but not with soap. Why?
 Ans:
Ans: (a) Green coloured coating on copper is due to the formation of basic copper carbonate, CuCO3.Cu(OH)2.
(b) Copper forms a green coating of basic copper carbonate as it reacts with water, atmospheric oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
(c) Corrosion phenomenon is responsible for the formation of basic copper carbonate (green).
(d) Since basic copper carbonate is basic in nature, it can be removed by tartaric acid present in tamarind or citric acid, present in lemon. Soap is basic in nature. So copper vessels are best cleaned with tamarind or lemon.
Q15: Give reasons for the following
(i) the blue colour of crystalline copper sulphate
(ii) Carbon is not used for making aluminium from aluminium oxide.
(iii) For making hydrogen by reaction with hydrochloric acid, granulated zinc is preferred to a block of zinc.
Ans:
(i) Blue colour of crystalline copper sulphate is due to five water molecules of hydration in CuSO4 5H2O.
(ii) Carbon has less affinity for oxygen than Aluminium and hence it cannot eliminate oxygen from Aluminium oxide.
(iii) Zinc granules are preferred to a block of zinc because it offers a large surface area for the reaction with the acid.
Galvanisation | Alloying |
1. It is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting. | 1. It is the process of combining two or more metals or a metal and a non-mental. |
2. It is done through electrolysis. | 2. It is done by heating the primary metal and adding other elements in definite proportions and then cooling it down to room temperature. |
3. The properties of inner metal are not changed. | 3. The properties like strength, conductivity etc. are changed. |
Q17: Describe an activity to find out the conditions under which iron rusts.
Ans: Procedure:
(i) Take three test tubes and put clean nails in each of the three tubes. Label them as A, B and C.
(ii) Pour some water in test tube A and cork it.
(iii) In tube B, pour some boiled distilled water along with some turpentine oil and cork it.
(iv) In test tube C, add some anhydrous calcium chloride and cork it.
(v) Look these test tubes properly and keep them undisturbed for a few day
Observation: Only in test tube A, iron nails get rusted since the nails in this test tube are exposed to both air and water.
Conclusion: Both air and water are required for rusting of iron.
Q18: (a) Define corrosion.
(b) What is corrosion of iron called?
(c) How will you recognise the corrosion of silver?
(d) Why corrosion of iron is a serious problem?
(e) How can we prevent corrosion of iron?
Ans:(a) The process of slowly eating up of metals due to their conversion into oxides, carbonates, sulphides, etc., by the action of atmospheric gases and moisture is called corrosion.
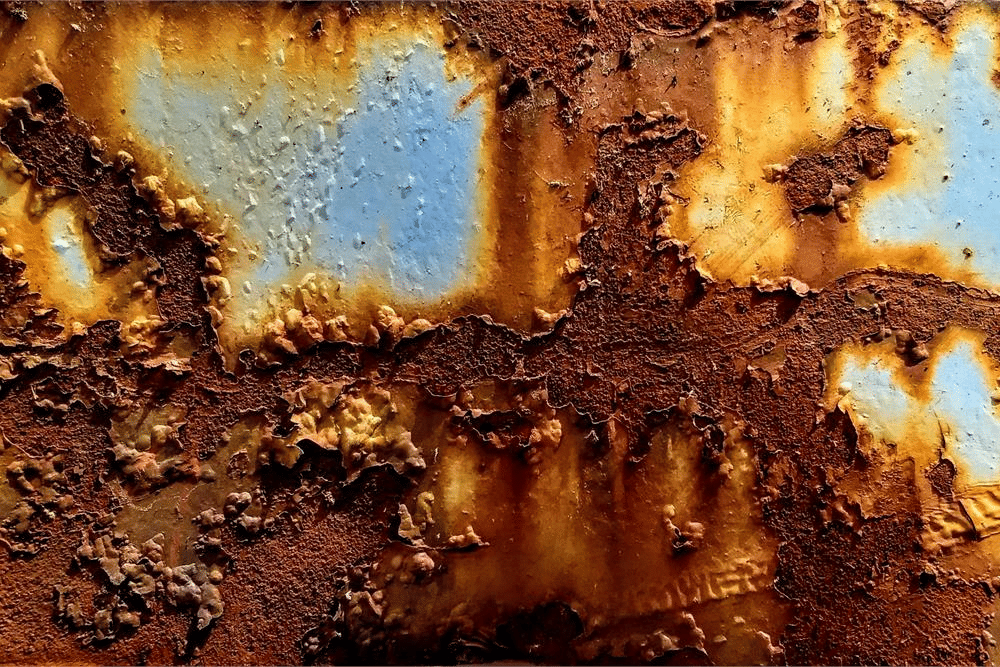 Corrosion(b) The corrosion of iron is called rusting.
Corrosion(b) The corrosion of iron is called rusting.
(c) Silver articles become black after sometime when exposed to air. This is due to formation of a coating of black silver sulphide (Ag2S) on its surface by the action of H2S gas present in the air.
(d) Corrosion of iron is a serious problem. Every year large amount of money is spent to replace damaged iron articles. Corrosion causes damage to car bodies, bridges and iron railings, ships and to all objects made of metals specially those of iron.
(e) Corrosion of iron is prevented by coating it with a layer of oil. The reason being that the layer of oil does not allow air and water to react the surface of iron. Corrosion of iron can also be prevented by painting, greasing, galvanising, anodising, electroplating or making alloys.
Q19: An ore on treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid produces brisk effervescence. Name the type of ore with one example. What steps will be required to obtain metal from the enriched ore? Also write the chemical equations for the reactions involved in the process.
Ans: The ore on treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid produces brisk effervescence hence, it must be a carbonate ore. Calamine (ZnCO3) is an important carbonate ore of zinc.
Steps required to obtain metal from the enriched carbonate Are:
(a) Conversion of the carbonate ore into metal oxide : This is done by calcination (for carbonate ores).
Calcination is the process of heating the ore strongly in the absence or limited supply of air. The zinc carbonate on heating decomposes to form zinc oxide as shown :
(b) Reduction of the metal oxide to metal: As zinc is moderately reactive, zinc oxide cannot be reduced by heating alone. Hence, it is reduced to zinc by using a reducing agent such as carbon.
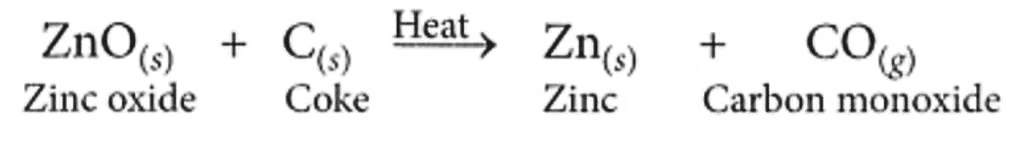
Q20: (i) Write down the electronic configuration
of magnesium and oxygen.
(ii) Give two general properties of the compound formed by combination of magnesium and oxygen.
(iii) Show the formation of this compound by the transfer of electrons.
Ans: (i) Atomic number of magnesium (Mg) = 12
∴ Its electronic configuration = 2, 8, 2
Atomic number of oxygen = 8
Electronic configuration of oxygen = 2, 6
(ii) Magnesium (Mg) reacts with oxygen (O2) to form magnesium oxide (MgO).
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Properties of MgO are :
(a) It involves ionic bonding.
(b) It has high melting point due to strong electrostatic forces of attraction between Mg2+ and O2- ions.
(iii) In the formation of magnesium oxide, two electrons are transferred from magnesium atom to oxygen atom as represented :
Add Content FAQs
Add Questions
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Metals and Non-metals
| 1. What are the main differences between metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. How do metals and non-metals react with oxygen? |  |
| 3. What are some common uses of metals and non-metals in daily life? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the reactivity series of metals? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the properties of ionic compounds formed by metals and non-metals? |  |






















