Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - Life Processes
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the blanks
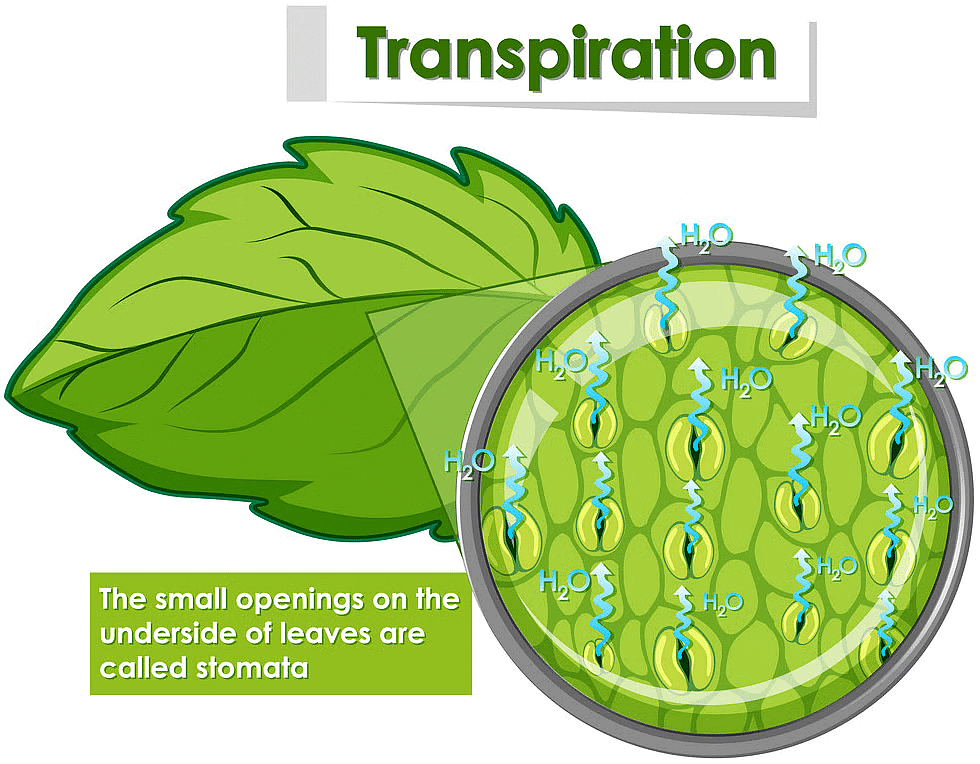
Q1: Plants get rid of excess water by ........................
Ans: Plants get rid of excess water by transpiration.
Transpiration is the process where:
- Water evaporates from plant leaves.
- This helps maintain water balance.
- It cools the plant and aids nutrient uptake.
Overall, transpiration is essential for plant health and growth.
Q2: ........................ and water are produced as wastes during respiration by plants.
Ans: CO2 and water are produced as wastes during respiration by plants.
Q3: ........................ is produced as a waste during photosynthesis.
Ans: Oxygen is produced as a waste during photosynthesis.
Q4: The gaseous wastes of respiration and photosynthesis in plants are removed through the .................... in leaves and ....................... in stem and released to the air.
Ans: The gaseous wastes of respiration and photosynthesis in plants are removed through the stomata in leaves and lenticels in the stem, then released into the air.
Q5: The plants excrete CO2 produced as a waste during .................. process in night time.
Ans: The plants excrete CO2 produced as a waste during the respiration process at night.
Q6: Gums and resins are the ...................... products of plant.
Ans: Gums and resins are the waste products of plants.
Q7: The phenomenon of removal of waste products from the body is known as ......................
Ans: The phenomenon of the removal of waste products from the body is known as excretion.
Q8: Leaves of ...................... contain essential oils.
Ans: Leaves of tulsi and lemon contain essential oils.
Q9: ...................... are found in stem of conifers as waste product.
Ans: Resins are found in the stems of conifers as a waste product.
Q10: Aquatic plants lose most of their metabolic wastes by ...................... process.
Ans: Aquatic plants lose most of their metabolic wastes through the process of diffusion.
Match the Column
Match the items of Column A with items of Column B.
Ans:
A - (ii)
B - (iv)
C - (iii)
D - (i)
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Define nutrition.
Ans: Nutrition is the process by which organisms consume food and use its nutrients to support their bodily functions.
- It involves taking in food through eating.
- Nutrients from food are essential for growth, energy, and overall health.
- Proper nutrition helps maintain bodily functions and prevents diseases.

Q2: Name the enzymes present in the stomach.
Ans: Pepsin is the main enzyme found in the stomach. It plays a crucial role in the digestive process by breaking down proteins into smaller peptides.
- Pepsin: The primary enzyme for protein digestion.
- Gastric lipase: Helps digest fats.
- Renin: Assists in digesting milk proteins, primarily in infants.
These enzymes work together to ensure effective digestion in the stomach.
Q3: Which part of the body secretes bile? Where is bile stored?
Ans: Bile is secreted exclusively by the liver and is stored in the gall bladder.
Q4: Define peristalsis.
Ans: Peristalsis is the process by which food is moved through the digestive tract. It involves:
- Wave-like muscle contractions that push food along.
- Sequential contractions that occur in the oesophagus, stomach, and intestines.
- Essential for proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
This coordinated movement ensures that food is processed efficiently at each stage of digestion.
Q5: What is the emulsification of fat?
Ans: Emulsification is the process of breaking down large fat globules into smaller ones, making them soluble in water.
Q6: Name the enzyme present in human saliva. What type of food material is digested by this enzyme?
Ans: The enzyme present in human saliva is ptyaline, also known as salivary amylase. This enzyme plays a key role in the digestion of:
Starch
Ptyaline begins the process of starch digestion in the mouth.
Q7: Define assimilation.
Ans: Assimilation refers to the process of the body or any biological system absorbing and digesting food or nutrients.
Q8: Name the most common method of ingestion in Amoeba.
Ans: Phagocytosis is the primary method of ingestion in Amoeba.
Q9: Why is the food vacuole of Amoeba called a temporary stomach?
Ans: In amoeba, the food vacuole acts as a temporary stomach because:
- It forms when the amoeba engulfs food.
- After digestion, the vacuole dissolves.
- A new food vacuole is created for each meal.
This cycle of formation and disappearance is why it is referred to as a 'temporary stomach'.
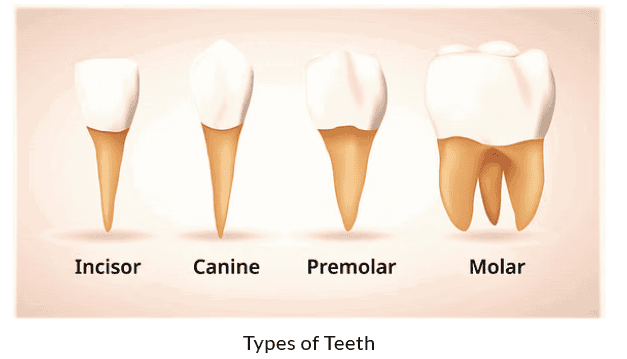
Q10: Name different types of teeth present in man.
Ans: Different types of teeth present in man:
- Eight incisors: Four in the upper jaw and four in the lower jaw, designed for cutting food.
- Four canines: Pointy teeth located next to the incisors, used for tearing food.
- Eight premolars: Found next to the canines, these teeth are used for grinding food.
- Twelve molars: Located at the back of the jaw, next to the premolars, these teeth also include four wisdom teeth.
Q11: Which part of the alimentary canal is adapted for complete digestion and absorption of food?
Ans: The small intestine is specifically adapted for the complete digestion and absorption of food. It plays a crucial role in the digestive process due to the following features:
- Surface area: It has a large surface area, enhanced by villi and microvilli, which maximises nutrient absorption.
- Digestive enzymes: It secretes various enzymes that break down food into smaller nutrients.
- Length: Its length allows sufficient time for digestion and absorption to occur.
- Muscle contractions: Peristaltic movements help mix and propel food along the canal.
These adaptations make the small intestine essential for effective digestion and nutrient uptake.
Q12: Explain the importance of xylem in plants.
Ans: Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to all parts of the plant.
- It provides structural support to the plant.
- It plays a critical role in maintaining water balance and nutrient distribution.
Q13: Name the largest gland of the human body.
Ans: The liver is the largest gland in the human body.
Q14: Name the protein-digesting enzymes present in the pancreatic juice of man.
Ans: Trypsin is a key protein-digesting enzyme found in human pancreatic juice.
- It helps break down proteins into smaller peptides.
- Produced in an inactive form called trypsinogen.
- Activated in the small intestine for digestion.
Q15: What are the end-products of fat digestion?
Ans: Fats are digested primarily in the small intestine. During digestion, one triglyceride molecule is broken down into:
- Three fatty acid molecules
- One glycerol molecule
The liver produces bile, which aids in the digestion of fats and some vitamins.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe various modes of nutrition.
Ans: Nutrition is mainly divided into two categories:
Autotrophic mode of nutrition:
- Phototrophic: Organisms prepare their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Example: Green plants.
- Chemotrophic: Organisms create their own food using chemicals like nitrate, hydrogen sulphate, iron, and sulphur. Example: Bacteria.
Heterotrophic mode of nutrition:
- Holozoic: Animals consume solid food, involving five digestion stages: ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion. Example: Humans.
- Saprophytic: Organisms feed on dead and decaying organic matter, breaking down complex food into simpler forms before ingestion. Example: Decomposers.
- Parasitic: Organisms obtain nutrients from other living organisms. The parasite lives inside a host organism and derives nutrients from it. Example: Tapeworm.
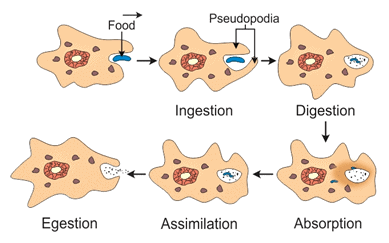
Q2: Mention various steps of nutrition in Amoeba.
Ans: Amoeba exhibits a type of nutrition known as holozoic nutrition, which involves the ingestion of solid or liquid food. The steps involved in this process are as follows:
- Ingestion: The amoeba surrounds and takes in food through its cell membrane.
- Digestion: Enzymes break down the food within food vacuoles.
- Absorption: Nutrients from the digested food are absorbed into the cytoplasm.
- Assimilation: The absorbed nutrients are incorporated into the amoeba's cells for energy and growth.
- Egestion: Undigested material is expelled from the cell.
Q3: Draw the position of salivary glands in the mouth.
Ans:
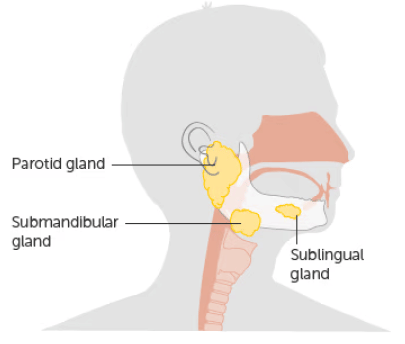
Q4: What is the role of hydrochloric acid in our stomach?
Ans: Hydrochloric acid plays a crucial role in the stomach by:
- Creating an acidic environment in the stomach.
- Killing harmful microbes that enter with food.
- Providing the right conditions for the enzyme pepsin to digest food.
Q5: State two functions of the large intestine of man.
Ans: The large intestine has two main functions:
- It stores waste food materials until they are eliminated.
- It reabsorbs water and salts that remain after digestion.
Q6: What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Ans: All living organisms are composed of cells and exhibit specific characteristics that indicate life. These include:
- Visible movement: Such as walking, breathing, or growing.
- Invisible processes: Movements that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- Life processes: Essential functions like respiration, nutrition, and reproduction.
The presence of these life processes is a key criterion to determine if something is alive.
Q7: What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Ans:
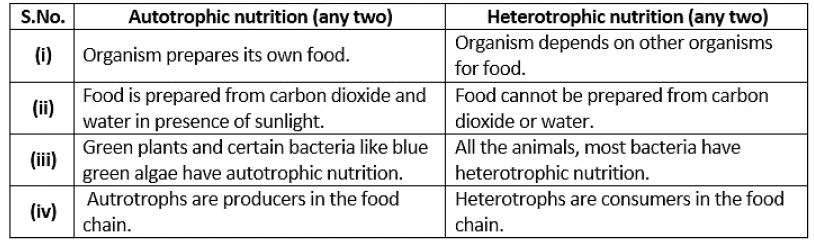
Q8: How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
Ans: The small intestine is designed to absorb digested food efficiently due to the following features:
- Large Surface Area: The inner walls of the small intestine have numerous finger-like projections called villi and microvilli, which significantly increase the surface area for absorption.
- Thin Walls: The walls of the villi are thin, allowing easy diffusion of nutrients into the bloodstream.
- Rich Blood Supply: Each villus contains a network of blood capillaries and a lymph vessel (lacteal) to transport absorbed nutrients like glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids to the rest of the body.
- Length of the Intestine: Its long length ensures sufficient time for complete digestion and absorption of food.
These adaptations make the small intestine highly efficient in absorbing digested food.
Q9: What is the difference between ingestion and egestion?
Ans:
- Ingestion: Taking in complex organic food by the organism is called ingestion.
- Egestion: The elimination of undigested waste and food materials from the body is called egestion.
Q10: How can dental caries be prevented?
Ans: Dental caries can be prevented by following these key practices:
- Avoiding acidic foods and drinks that can harm tooth enamel.
- Maintaining a regular dental hygiene routine, including brushing twice a day.
- Flossing daily to remove food particles and plaque between teeth.
- Regular visits to the dentist for check-ups and cleanings.
By implementing these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of dental caries.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - Life Processes
| 1. What are the main life processes essential for living organisms? |  |
| 2. How do organisms obtain nutrition, and why is it important? |  |
| 3. What is the role of respiration in living organisms? |  |
| 4. How do living organisms carry out excretion, and why is it necessary? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of reproduction in life processes? |  |
















