Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Previous Year Questions - Life Processes
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Secretion of less saliva in mouth will affect the conversion of: (1 Mark)
(a) Proteins into amino acids
(b) Fats into fatty acids and glycerol
(c) Starch into simple sugars
(d) Sugars into alcohol
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Starch into simple sugars
Saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase which breaks down starch (complex carbohydrate) into simple sugar. If less saliva is secreted, this conversion is affected.
Q2: The breakdown of glucose has taken the following pathway: (1 Mark)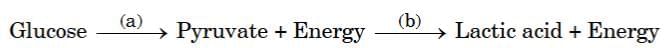
The sites 'a' and 'b' respectively are:
(a) Mitochondria and Oxygen deficient muscle cells
(b) Cytoplasm and Oxygen rich muscle cells
(c) Cytoplasm and Yeast cells
(d) Cytoplasm and Oxygen deficient muscle cells
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Cytoplasm and Oxygen deficient muscle cells
Glucose breaks down to pyruvate in the cytoplasm. In lack of oxygen, pyruvate changes to lactic acid in muscle cells, causing cramps.
Q3: The opening and closing of stomata is regulated by: (1 Mark)
(a) CO₂ concentration in stomata
(b) Temperature in guard cells
(c) O₂ concentration in stomata
(d) Amount of water in guard cells
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Amount of water in guard cells
The opening and closing of the stomatal pore is a function of the guard cells. The guard cells swell when water flows into them, causing the stomatal pore to open. Similarly the pore closes if the guard cells shrink.
Q4: One-cell thick blood vessels are known as: (1 Mark)
(a) Alveoli
(b) Capillaries
(c) Arteries
(d) Veins
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Capillaries
Capillaries: These are the smallest blood vessels, with walls one cell thick, allowing efficient exchange of gases (O₂, CO₂), nutrients, and wastes between blood and tissues. Their thin walls and small diameter maximize surface area for diffusion, connecting arteries and veins in the circulatory system.
Other Options:
- Alveoli: Air sacs in lungs for gas exchange, not blood vessels.
- Arteries: Thick-walled to withstand high pressure, carrying blood away from the heart.
- Veins: Thinner walls than arteries but thicker than capillaries, returning blood to the heart.
Q5: The essential element used in the synthesis of proteins is: (1 Mark)
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Iron
(d) Magnesium
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Nitrogen
Nitrogen is an essential element used in the synthesis of proteins and other compounds. This is taken up in the form of inorganic nitrates or nitrites. Or it is taken up as organic compounds which have been prepared by bacteria from atmospheric nitrogen.
Other Options:
- Phosphorus: Essential for DNA, RNA, and ATP, not directly for proteins.
- Iron: Involved in hemoglobin and enzyme function, not protein synthesis.
- Magnesium: Part of chlorophyll and enzyme activation, not a direct component of proteins.
Q6: Select TRUE statements about lymph from the following: (1 Mark)
A. Lymph vessels carry lymph through the body and finally open into larger arteries.
B. Lymph contains some amount of plasma, proteins, and blood cells.
C. Lymph contains some amount of plasma, proteins, and red blood cells.
D. Lymph vessels carry lymph through the body and finally open into larger veins.
The true statements are:
(a) A and B
(b) B and D
(c) A and C
(d) C and D
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) B and D
Lymph Composition and Flow: Lymph is a fluid derived from blood plasma, containing plasma, proteins, and white blood cells, but not red blood cells. Lymph vessels collect lymph from tissues and return it to the bloodstream via larger veins.
Statement Analysis:
- A: False. Lymph vessels drain into veins, not arteries.
- B: True. Lymph contains plasma, proteins, and white blood cells.
- C: False. Lymph lacks red blood cells, which remain in blood vessels.
- D: True. Lymph vessels merge with veins to return lymph to circulation.
Q7: Select the correct option from the following statements about the functioning of the human heart: (1 Mark)
(a) Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body and sends it to pulmonary veins.
(b) Left atrium sends oxygenated blood to right ventricle which pumps it to different parts of the body.
(c) Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and sends it to the right ventricle.
(d) Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary arteries and sends it to the left ventricle.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and sends it to the right ventricle.
Heart Function: The heart has four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle. It operates via double circulation.
Correct Statement (c):
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava and passes it to the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation via pulmonary arteries.
Other Options:
- A: Incorrect. The right atrium sends deoxygenated blood to the right ventricle, not pulmonary veins (which carry oxygenated blood to the left atrium).
- B: Incorrect. The left atrium sends oxygenated blood to the left ventricle, not the right ventricle, which handles deoxygenated blood.
- D: Incorrect. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins, not arteries.
Q8: Parasitic mode of nutrition is observed in: (1 Mark)
(a) Bryophyllum
(b) Hibiscus
(c) Cuscuta
(d) Helianthus
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Cuscuta
Parasitic Nutrition: The organism derives nutrients by living on or in a host, harming it. Cuscuta (dodder) is a parasitic plant that lacks chlorophyll and absorbs nutrients from host plants via haustoria.
Other Options:
- Bryophyllum: Autotrophic, performs photosynthesis.
- Hibiscus: Autotrophic, uses chlorophyll for food production.
- Helianthus (Sunflower): Autotrophic, photosynthetic.
Q9: Question consist of two statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below: (1 Mark)
Assertion (a): In large animals, oxygen can reach different parts of the animal's body easily.
Reason (R): Respiratory pigments take up oxygen from the air and carry it to body tissues.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) A is false, but R is true.
- Assertion (a): False. In large animals, oxygen cannot reach all body parts easily by diffusion alone due to their size and complexity. They rely on a circulatory system with respiratory pigments to transport oxygen.
- Reason (R): True. Respiratory pigments (e.g., hemoglobin in humans) bind oxygen in the lungs and transport it via blood to tissues, releasing it where needed.
- Why R does not explain A: R correctly describes oxygen transport but does not support the false claim that oxygen reaches tissues easily without a transport system.
Q10: Question consist of two statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below: (1 Mark)
Assertion (a): Xylem tissue moves water and minerals obtained from the soil by the roots.
Reason (R): Xylem tissue is found only in the roots of a plant.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) A is true, but R is false.
Assertion (a): True. Xylem tissue transports water and dissolved minerals from roots to leaves and other parts via transpiration pull and capillary action.
Reason (R): False. Xylem is not limited to roots; it is present throughout the plant (roots, stems, leaves) as part of the vascular bundle, facilitating water transport.
Q11: Which one of the following is not an excretory product in plants? (1 Mark)
(a) CO₂
(b) Starch
(c) Resins and gums
(d) Dead cells
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Starch
Plant Excretion: Plants excrete waste products like CO₂ (from respiration), resins, gums, and dead cells (e.g., bark shedding) through processes like diffusion or secretion.
Starch: Not an excretory product; it is a storage carbohydrate produced during photosynthesis and stored in roots, tubers, or seeds.
Q12: The basic filtration unit of the excretory system in human beings is: (1 Mark)
(a) Nephron
(b) Urethra
(c) Neuron
(d) Urinary bladder
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Nephron
Nephron Role: The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering blood, reabsorbing essential substances, and forming urine. Each kidney contains about a million nephrons.
Other Options:
- Urethra: Transports urine out of the body, not a filtration unit.
- Neuron: Nerve cell, unrelated to excretion.
- Urinary bladder: Stores urine, not involved in filtration.
Significance: Nephrons ensure removal of nitrogenous wastes while maintaining water and electrolyte balance.
Q13: In human alimentary canal, the digestive juice secreted by the gastric glands are: (1 Mark)
(a) Bile, Trypsin, Pepsin
(b) Hydrochloric acid, Pepsin, Mucus
(c) Lipase, Bile, Mucus
(d) Salivary amylase, Pepsin, Bile
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Hydrochloric acid, Pepsin, Mucus
Gastric Glands Secretions:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl): Creates an acidic environment (pH 1.5–3.5) to activate pepsin and kill pathogens.
- Pepsin: Digests proteins into peptides (activated from pepsinogen by HCl).
- Mucus: Protects the stomach lining from acid and pepsin damage.
Other Options:
- Bile: Secreted by the liver, stored in the gallbladder, acts in the small intestine.
- Trypsin, Lipase: Secreted by the pancreas, not gastric glands.
- Salivary amylase: Secreted in saliva, not stomach.
Q14: Listed below are the steps of nutrition in Amoeba. Select the correct sequence of these steps: (1 Mark)
(i) Diffusion of simple nutrients into cytoplasm
(ii) Food vacuole formation
(iii) Formation of finger-like temporary extensions of cell surface
(iv) Complex substances broken to simpler ones
(v) Undigested material thrown out of the cell surface
(a) (iv), (i), (ii), (iii), (v)
(b) (iii), (iv), (i), (v)
(c) (ii), (i), (iv), (v), (iii)
(d) (iii), (iv), (i), (ii), (v)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) (ii), (i), (iv), (v), (iii)
Nutrition in Amoeba: Amoeba feeds, with the following sequence:
(ii) Food vacuole formation: Amoeba engulfs food (e.g., algae) by forming pseudopodia, creating a food vacuole.
(i) Diffusion of simple nutrients into cytoplasm: Digestive enzymes in the vacuole break down food, and nutrients diffuse into the cytoplasm.
(iv) Complex substances broken to simpler ones: Enzymes digest complex molecules (e.g., proteins) into simpler ones (e.g., amino acids).
(v) Undigested material thrown out of the cell surface: Waste is expelled via exocytosis.
(iii) Formation of pseudopodia: Occurs first to capture food, but listed last in the correct sequence as it initiates the process.
Correct Sequence: (ii), (i), (iv), (v), (iii) reflects the logical flow, though pseudopodia formation (iii) precedes vacuole formation (ii) in reality.
Q15: In aerobic respiration, the steps are: breakdown of glucose to pyruvate and its further conversion to carbon dioxide. Both processes respectively occur in: (1 Mark)
(a) Vacuole and Cytoplasm
(b) Chloroplast and Mitochondria
(c) Mitochondria and Cytoplasm
(d) Cytoplasm and Mitochondria
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Cytoplasm and Mitochondria
Aerobic Respiration Steps:
Glucose to Pyruvate (Glycolysis): Occurs in the cytoplasm, breaking glucose into two pyruvate molecules.
Pyruvate to CO₂: Occurs in the mitochondria, where pyruvate is oxidized to CO₂.
Other Options:
- Vacuole: Not involved in respiration; stores substances.
- Chloroplast: Site of photosynthesis, not respiration.
Q16: (a) Besides minimising the loss of blood, why is it essential to plug any leak in a blood vessel? Name the component of blood which helps in this process and state how this component performs this function. (2 Marks)
OR
(b) (i) The transport system in plants is relatively slower than in animals. Give reasons.
(ii) State the role of phloem in the transport of materials in plants. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Need to Plug Leaks: Besides minimising the loss of blood, it is essential to plug any leak in a blood vessel to prevent the entry of harmful substances into the body and to maintain the transportation of food and oxygen. The component of blood which helps in this process is platelets. Platelets release factors which help in clotting the blood at the site of injury.
OR
(b) (i) Slower Plant Transport: The transport system in plants is relatively slower than in animals because plants do not have a heart to pump substances, and the movement relies on processes like diffusion and transpiration which are slower. In animals, blood is pumped by the heart for faster transport.
(ii) Role of Phloem: Transports food (sugars, amino acids) produced in leaves (via photosynthesis) to other parts (roots, fruits) for growth, storage, or metabolism.
Q17: State the main function of arteries. Why do they have thick and elastic walls? (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Main Function: Arteries carry oxygenated blood (except pulmonary arteries) from the heart to body tissues.
- Reason for Thick Walls: Arteries have thick, elastic, muscular walls to withstand high pressure from heart pumping and maintain blood flow through elasticity.
Q18: "Plants use a variety of techniques to get rid of waste material." Justify this statement giving any four ways. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Plants excrete wastes through:
- Diffusion of Gases: CO₂ (from respiration) and excess O₂ (from photosynthesis) are released via stomata.
- Shedding of Parts: Dead cells, leaves, or bark are shed (e.g., leaf fall in deciduous plants).
- Secretion of Resins/Gums: Wastes like resins or gums are secreted through specialized cells, often as defense.
- Storage in Vacuoles: Wastes are stored in vacuoles or old leaves, later shed.
Q19: Based on the characteristics of the processes given in the brackets in each case, differentiate between the following:
(a) Products of breakdown of pyruvate in aerobic and anaerobic respiration in human beings (product(s) of the processes)
(b) Respiration and photosynthesis in plants (gas released)
(c) Respiration in terrestrial animals and fishes (organs involved) (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) In aerobic respiration, which happens in the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is broken down in the mitochondria into carbon dioxide and water, releasing a large amount of energy (used to form ATP). In anaerobic respiration, which occurs in the absence of oxygen (e.g., in muscle cells during heavy exercise), pyruvate is converted in the cytoplasm into lactic acid, releasing a small amount of energy and causing muscle cramps.
(b) In respiration, plants break down glucose to release energy, producing carbon dioxide as a by-product, which is released through stomata, especially at night. In photosynthesis, plants use carbon dioxide and water with sunlight and chlorophyll to produce carbohydrates, releasing oxygen as a by-product during the day.
(c) Terrestrial animals, like humans, use lungs for respiration, where oxygen from the air is absorbed, and carbon dioxide is released through alveoli. Fishes use gills to extract dissolved oxygen from water and release carbon dioxide, requiring faster breathing due to lower oxygen levels in water compared to air.
Q20: (a) Enlist any two nitrogenous waste products removed from the blood of human kidney.
(b) Name the capillary cluster formed by the branch of renal artery in the Bowman's capsule.
(c) Depict in the form of a flow chart the path of the urine formed in each kidney until it is finally passed out through the urethra. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) Two nitrogenous waste products removed by the human kidney are urea and uric acid.
(b) The capillary cluster formed by the branch of the renal artery in the Bowman's capsule is called the glomerulus.
(c) Path of urine: Kidney (Urine formed in nephrons: Filtration in glomerulus → Reabsorption in tubules) → Ureter → Urinary bladder → Urethra → Excreted out of the body.
Q21: Why is blood circulation in vertebrates known as "double circulation"? Trace its path in the form of a flow chart. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
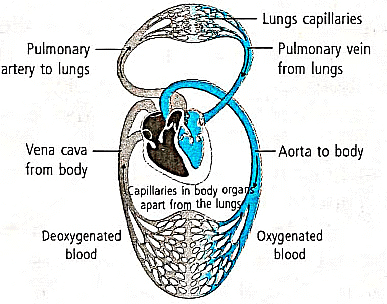
Ans: Blood circulation in vertebrates, like humans, is called double circulation because blood passes through the heart twice in one complete cycle: once for pulmonary circulation (to the lungs for oxygenation) and once for systemic circulation (to the rest of the body). This keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separate, ensuring efficient oxygen supply.
Flow chart: Deoxygenated blood from body → Vena cava → Right atrium → Right ventricle → Pulmonary artery → Lungs (oxygenation) → Pulmonary vein (oxygenated blood) → Left atrium → Left ventricle → Aorta → Body tissues → Back to vena cava.
Q20: What is the first step of cellular respiration? In which part of the cell does it occur? Write the equation for the process of breakdown of glucose in a human cell: (3 Marks)
(i) in the presence of oxygen
(ii) due to lack of oxygen
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
The first step of cellular respiration is the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, called glycolysis. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
(i) In the presence of oxygen (aerobic respiration): C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP)
(ii) Due to lack of oxygen (anaerobic respiration): C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2 C₃H₆O₃ (Lactic acid) + Energy (ATP)
Q21: Name the blood vessel that brings (i) oxygenated blood (ii) deoxygenated blood, to the human heart. Also name that chamber of the heart which receives deoxygenated blood and state how deoxygenated blood from this chamber is sent to lungs for oxygenation. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Oxygenated blood is brought to the heart by the pulmonary vein.
(ii) Deoxygenated blood is brought to the heart by the vena cava.
The chamber that receives deoxygenated blood is the right atrium. From the right atrium, deoxygenated blood flows into the right ventricle through a valve. The right ventricle contracts, pumping the blood through the pulmonary artery to the lungs for oxygenation.
Q22: (a) (i) "The length of the small intestine in various animals depends on the food they eat." Justify the statement.
(ii) Discuss the role of the pancreas and bile juice in the digestion of food in human beings.
(iii) How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food? (5 Marks)
OR
(b) (i) State the role of rings of cartilage present in the throat.
(ii) Discuss the role of the ribs and diaphragm when air is taken in during the breathing cycle.
(iii) Why do we get muscle cramps during heavy exercise? Explain. (5 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) The length of the small intestine varies depending on the diet. Herbivores, like cows, have a longer small intestine because grass contains cellulose, which is hard to digest and requires more time for breakdown. Carnivores, like tigers, have a shorter small intestine since meat is easier to digest. Omnivores, like humans, have a medium-length small intestine suited for a mixed diet.
(ii) The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice into the small intestine, containing enzymes like trypsin (digests proteins into amino acids), lipase (breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol), and amylase (converts carbohydrates into sugars). Bile juice, from the liver, emulsifies fats into smaller droplets for easier digestion by lipase and makes the intestinal environment alkaline for pancreatic enzymes to work.
(iii) The small intestine has finger-like projections called villi on its inner lining, which increase the surface area for absorption. Villi have thin walls (one cell thick) and blood vessels that absorb digested nutrients (like glucose and amino acids) and transport them to body cells. Fats are absorbed by lymph vessels (lacteals) in the villi.
OR
(i) Rings of cartilage in the throat (trachea) keep the air passage open by preventing it from collapsing during breathing, ensuring smooth airflow to the lungs.
(ii) During inhalation, ribs move upward and outward due to intercostal muscle contraction, and the diaphragm contracts and flattens, enlarging the chest cavity. This reduces pressure in the lungs, allowing air to be sucked in.
(iii) Muscle cramps during heavy exercise occur due to anaerobic respiration in muscle cells when oxygen is insufficient. Glucose breaks down into pyruvate, which is converted to lactic acid, causing fatigue and cramps due to its accumulation.
Q23: The following question are Source-based/Case-based questions. Read the case carefully and answer the question that follow.
The maintenance functions of all living organisms must go on even when they are not doing anything particular. Even when we are just sitting in a class or even asleep, this maintenance job has to go on. These maintenance processes require energy to prevent damage and break-down of cells and tissues, which is obtained by the individual organism from the food prepared by the autotrophs, called producers.
(a) Name and define the process by which green plants prepare food. (1 Mark)
(b) Write chemical equation involved in the above process. (1 Mark)
(c) (i) State in proper sequence the events that occur in synthesis of food by desert plants. (2 Marks)
OR
(c) (ii) Explain giving reasons what happens to the rate at which the green plants will prepare food: (2 Marks)
(I) during cloudy weather, and
(II) when stomata get blocked due to dust.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) The process by which green plants prepare food is called photosynthesis. It is the process where plants use carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and chlorophyll to produce carbohydrates (stored energy) and release oxygen.
(b) Chemical equation for photosynthesis: 6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ (Glucose) + 6O₂
(c) (i) Events in food synthesis by desert plants:
- Stomata open at night to take in carbon dioxide.
- Carbon dioxide is stored as an intermediate organic acid.
- During the day, chlorophyll absorbs sunlight energy.
- The stored acid releases carbon dioxide, which is converted into carbohydrates using light energy.
OR
(c) (ii) (I) During cloudy weather, the rate of photosynthesis decreases because sunlight is less intense. Sunlight provides the energy needed to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates, so reduced light slows the process.
(II) When stomata are blocked by dust, the rate of photosynthesis decreases because carbon dioxide cannot enter the leaves efficiently. Stomata are the entry points for CO₂, and blockage limits this raw material, reducing food production.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: A stomata closes when: (1 Mark) (2024)
(i) It needs carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
(ii) It does not need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
(iii) water flows out of the guard cells.
(iv) water flows into the guard cells.
The correct reason(s) in this process is/are:
(a) (i) only
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Stomata are small openings on the surface of leaves that allow gases to enter and exit the plant. They close when the plant doesn't need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis (which is when it's not producing food) and when water flows out of the guard cells (which helps the plant conserve water). Therefore, the correct answers are (ii) and (iii).
Q2: State one role of each of the following in the human digestive system: (2 Marks) (2024)
(i) Hydrochloric acid
(ii) Villi
(iii) Anal Sphincter
(iv) Lipase
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Hydrochloric acid: Creates an acidic environment that helps enzymes work and kills harmful microorganisms.
(ii) Villi: Increases the surface area of the intestine, enhancing the absorption of nutrients.
(iii) Anal Sphincter: Controls the release of waste from the body through the anus.
(iv) Lipase: Breaks down fats into smaller molecules, aiding in their digestion.
Q3: (i) Why is respiratory pigment needed in multicellular organisms with large body sizes? (3 Marks) (2024)
(ii) Give reasons for the following:
(a) Rings of cartilage are present in the throat.
(b) Lungs always contain a residual volume of air.
(c) The diaphragm flattens and ribs are lifted up when we breathe in.
(d) Walls of alveoli contain an extensive network of blood vessels.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) In large animals, diffusion alone cannot deliver enough oxygen throughout the body. Instead, respiratory pigments are essential because they:
- Absorb oxygen from the air in the lungs.
- Transport oxygen to tissues that need it.
- Release oxygen where it is required.
In humans, the main respiratory pigment is haemoglobin, found in red blood cells, which has a strong affinity for oxygen. Carbon dioxide is mostly carried in a dissolved form in the blood.
(ii) Reasons:
(a) Rings of cartilage in the throat prevent the air passage from collapsing.
(b) Lungs retain a residual volume of air to allow time for oxygen absorption and carbon dioxide release.
(c) When we breathe in, the diaphragm flattens and the ribs lift, making the chest cavity larger, which draws air into the lungs.
(d) The walls of alveoli contain many blood vessels to facilitate gas exchange.
Q4: Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true about human heart? (1 Mark) (CBSE 2024)
(A) Right atrium receives oxygenated blood from lungs through pulmonary artery.
(B) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to left ventricle which sends it to various parts of the body.
(C) Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood through vena cava from upper and lower body.
(D) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to aorta which sends it to different parts of the body.
(a) (A)
(b) (A) and (D)
(c) (B) and (C)
(d) (B) and (D)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- (A) is incorrect because the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the vena cava, not oxygenated blood from the lungs. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs, not to the right atrium.
- (B) is correct because the left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to the left ventricle, which then pumps it to various parts of the body through the aorta.
- (C) is correct because the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood through the vena cava from the upper and lower parts of the body.
- (D) is incorrect because it is the left ventricle, not the left atrium, that transfers oxygenated blood to the aorta, which then sends it to different parts of the body.
Therefore, the correct answer is (c) (B) and (C).
Q5: Photosynthesis takes place in the leaves and the food prepared by it reaches other parts of the plants. Name the process involved and explain it. (1 Mark) (2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The process is translocation.
- It involves the movement of food, mainly sugars like sucrose, from the leaves (where photosynthesis occurs) to other parts of the plant through the phloem.
- This ensures all parts of the plant receive nutrients for growth, storage, and energy.
Q6: Which of the following statement (s) is (are) true about human heart? (1 Mark) (2024)
(A) Right atrium receives oxygenated blood from lungs through pulmonary artery.
(B) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to left ventricle which sends it to various parts of the body.
(C) Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body through vena cava.
(D) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to aorta which sends it to different parts of the body.
(a) (B) only
(b) (A) and (D)
(c) (B) and (C)
(d) (B) and (D)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The correct statements about the human heart are (B) and (C). The left atrium does transfer oxygenated blood to the left ventricle, which then pumps it to the body. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the vena cava, while (A) is incorrect because the right atrium actually receives deoxygenated blood, not oxygenated, and (D) is misleading as the left atrium transfers blood to the left ventricle, not directly to the aorta.
Q7: Case/Source based questions. (4 & 5 Marks) (CBSE 2024)
Human digestive system is a tube running from mouth to anus. Its main function is to breakdown complex molecules present in the food which cannot be absorbed as such into smaller molecules. These molecules are absorbed across the walls of the tube and the absorbed food reaches each and every cell of the body where it is utilised for obtaining energy.
(a) Name the glands present in the buccal cavity and write the components of food on which the secretion of these glands act upon.
(b) Two organs have a sphincter muscle at their exit. Name them.
(c) What will happen if:
(i) mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands.
(ii) Villi are absent in the small intestine.
OR
(c) “Bile juice does not contain any enzyme, yet it has important roles in digestion.” Justify the statement.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Salivary glands; Starch / Carbohydrate
(b) Stomach, Anus
(c) The consequences of specific conditions are:
(i) If mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands, the inner lining of the stomach will be unprotected from acid, leading to potential damage.
(ii) If villi are absent in the small intestine, the absorption of digested food will be significantly reduced.
OR
(c) Emulsification of fats.
Acidic medium has to be made alkaline for the pancreatic enzymes to act.
Q8: In human beings, when the process of digestion is completed, the (i) proteins, (ii) carbohydrates, and (iii) fats are respectively finally converted into: (1 Mark) (CBSE 2024)
(a) (i) Amino acids, (ii) glucose and (iii) fatty acids
(b) (i) Amino acids, (ii) glucose, (iii) fatty acids and glycerol
(c) (i) Glucose, (ii) fatty acids and glycerol, (iii) amino acids
(d) (i) Sugars, (ii) amino acids, (iii) fatty acids and glycerol
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
During digestion in humans:
- Proteins are broken down into amino acids.
- Carbohydrates are converted into glucose.
- Fats are transformed into fatty acids and glycerol.
The correct answer is (b) as it accurately describes the final products of these macronutrients after digestion.
Q9: We need to water the soil in plants on a regular basis. But it ultimately reaches the leaves of the plant. Explain how this takes place. (1 Mark) (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Water reaches the leaves through the xylem.
- Roots absorb water from the soil by osmosis.
- Water moves upward through the xylem due to transpiration pull, capillary action, and cohesion of water molecules.
This ensures water supply to the leaves for photosynthesis and other processes.
Q10: The process in which transport of soluble products of photosynthesis takes place in plants is known as: (1 Mark) (CBSE 2024)
(a) Transpiration
(b) Evaporation
(c) Conduction
(d) Translocation
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The process of transporting soluble products of photosynthesis in plants is called translocation. This involves:
- Moving substances like sugars from the leaves, where they are produced, to other parts of the plant.
- Utilising the phloem, a type of vascular tissue, for this transport.
- Delivering essential nutrients, including amino acids, to storage organs such as roots, fruits, and seeds.
- Facilitating movement in both upward and downward directions through sieve tubes and companion cells.
Translocation is vital for distributing energy throughout the plant, ensuring that all parts receive the necessary nutrients for growth and development.
Q11: (a) Sometimes while running, the athletes suffer from muscle cramps. Why? How is the respiration in this case different from aerobic respiration?
OR
(b) Write the other name given to lymph. State its two functions. (3 Marks) (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
i. The formation of lactic acid in muscles leads to cramps.
ii. Aerobic respiration occurs with oxygen, while cramps result from anaerobic respiration, which happens without oxygen.
iii. End products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and energy, whereas anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid and energy.
OR
(b) Tissue fluid / Extracellular fluid Functions:
i. Carries digested and absorbed fats from the intestine.
ii. Drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood.
iii. Fight against infections.
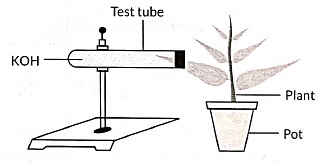
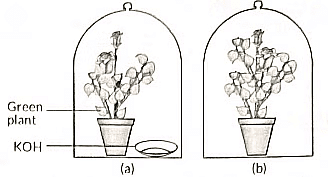
Q12: (a) Design an experiment to demonstrate that carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis. Write the observation and conclusion of the experiment. (3 Marks) (CBSE 2024)
OR
(b) (i)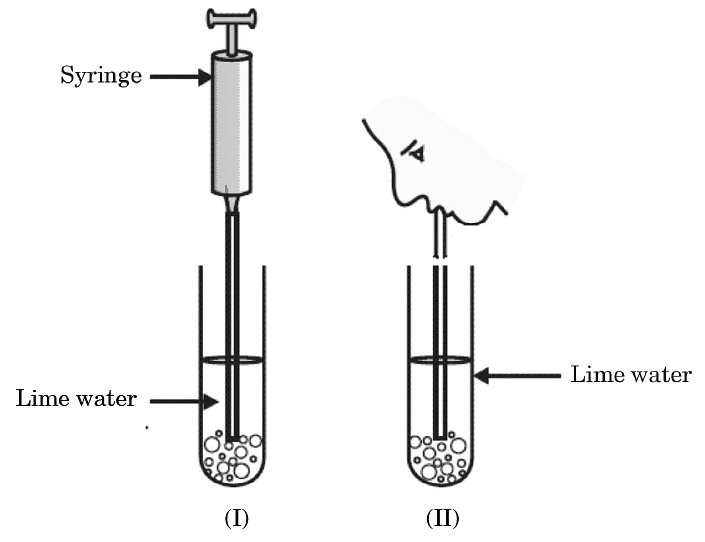 In the experimental set-up shown above in diagram (I) atmospheric air is being passed into lime water with a syringe while in diagram (II) air is being exhaled into lime water. The time taken for the lime water to turn milky in both the test tubes is different. Give reason.
In the experimental set-up shown above in diagram (I) atmospheric air is being passed into lime water with a syringe while in diagram (II) air is being exhaled into lime water. The time taken for the lime water to turn milky in both the test tubes is different. Give reason.
(ii) Draw the diagram of an open stomatal pore and label (I) Guard cells, and (II) Chloroplast on it. Mention two functions performed by stomata.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Take two healthy potted plants, A and B of nearly the same size.
- Keep them in darkness for three days. (Destarch the plant)
- Place a watch glass containing potassium hydroxide by the side of potted plant A but not in potted plant B.
- Cover both the plants with separate bell jars and seal the bottom of the jars with Vaseline.
- Keep both the plants in sunlight for two hours.
- Pluck one leaf each from both the plants and test for the presence of starch with iodine solution.
- Observation: The leaf of the potted plant A with KOH did not turn blue-black, indicating that starch was not present. The leaf of the potted plant B turns blue.
- Conclusion: KOH absorbs CO2 so photosynthesis did not occur in potted plant A.
OR
(b) (i) In set up (I) lime water turns milky in more time as compared to set up (II) because the air we exhaled contains high percentage of CO2 as compared to atmospheric air.
(ii)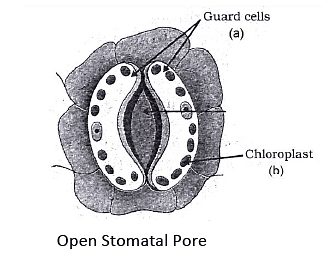
Two labellings: (I) Guard Cells
(II) Chloroplast Two functions performed by stomata:
Gaseous exchange
Transpiration
Q13: In human respiratory system, when a person breathes in, the position of ribs and diaphragm will be: (1 Mark) (CBSE 2024)
(a) lifted ribs and curve/dome shaped diaphragm.
(b) lifted ribs and flattened diaphragm.
(c) relaxed ribs and flattened diaphragm.
(d) relaxed ribs and curve/dome shaped diaphragm.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The correct answer is (b) lifted ribs and flattened diaphragm. When a person breathes in, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, while the ribs are lifted upward and outward. This movement creates more space in the chest cavity, allowing air to fill the lungs.
Q14: For Q. Nos., two statements are given - One labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below: (1 Mark) (CBSE 2024)
Assertion (A): The rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much faster than in terrestrial organisms.
Reason (R): The amount of oxygen dissolved in water is very high as compared to the amount of oxygen in air.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The correct answer is (c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. Aquatic organisms do breathe faster than terrestrial organisms because they need to extract enough oxygen from water, which has less oxygen available than air. Therefore, while the assertion is correct, the reason given is incorrect because it states that water has a high amount of dissolved oxygen, which is not true compared to air.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q1: Opening and closing of stomata is due to (1 Mark) (2023)
(a) High pressure of gases inside the cells
(b) Movement of water in and out of the guard cells
(c) Stimulus of light in the guard cells
(d) Diffusion of CO2 in and out of the guard cells.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The opening and closing of stomata are indeed regulated by the movement of water in and out of guard cells. Here’s a brief explanation of how it works:
Mechanism of Stomatal Movement:
Guard Cells and Stomata:
- Stomata are small openings on the surfaces of leaves and stems that allow for gas exchange (CO2, O2, and water vapor) between the plant and the atmosphere.
- Each stoma is flanked by a pair of guard cells, which control the opening and closing of the stoma.
Opening of Stomata:
- When guard cells take up water by osmosis, they become turgid (swollen).
- The turgidity of guard cells is primarily driven by the active transport of potassium ions (K⁺) into the guard cells. This lowers the water potential inside the guard cells, causing water to enter by osmosis.
- As the guard cells swell, they bow outward, causing the stomatal pore to open.
Closing of Stomata:
- When the guard cells lose water, they become flaccid (less swollen).
- The loss of turgor pressure in the guard cells is usually due to the active transport of potassium ions (K⁺) out of the guard cells. This raises the water potential inside the guard cells, causing water to exit by osmosis.
- As the guard cells lose turgor and shrink, the stomatal pore closes.
Q2: Assertion (A): The inner walls of the small intestine have finger like projections called villi which are rich in blood. (1 Mark) (2023)
Reason (R): These villi have a large surface area to help the small intestine in completing the digestion of food.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Assertion (A):
- This statement is true. The small intestine is lined with villi, which are small, finger-like projections rich in blood vessels. These vessels help absorb nutrients from digested food into the bloodstream.
Reason (R):
- This statement is false. While it is true that the villi increase the surface area of the small intestine, their primary role is to aid in the absorption of nutrients, not in the digestion of food. Digestion is primarily completed by enzymes within the small intestine.
Conclusion: (A) is true, but (R) is false.
Q3: Water in the root enters due to (1 Mark) (2023)
(a) The function of the root to absorb water
(b) Difference in the concentration of ions between the root and the soil
(c) Excess water present in the soil
(d) Diffusion of water in the roots
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Roots absorb water from the soil through a process called osmosis.
- This process occurs because of a difference in ion concentration between the roots and the soil.
- As a result, water moves into the roots to balance this concentration difference.
Q4: As compared to terrestrial organisms, the rate of breathing in aquatic organism is (1 Mark) (2023)
(a) Faster because they need more oxygen for their survival
(b) Faster because the amount of dissolved oxygen in water is fairly low
(c) Slower because the amount of dissolved oxygen in water is fairly low
(d) Slower because the capacity of water of dissolving atmospheric air is limited
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
In aquatic organisms, the rate of breathing is higher.
These organisms utilize oxygen dissolved in water.
The amount of dissolved oxygen in water is relatively low compared to the oxygen available in the air.
Therefore, aquatic organisms need to breathe faster to obtain sufficient oxygen for their survival.
Q5: Observe the following diagram and identify the process and its significance from the following options: (1 Mark) (2023)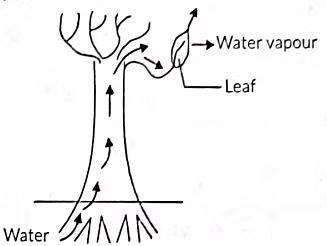 (a) Evaporation : maintains water contents in leaf cells.
(a) Evaporation : maintains water contents in leaf cells.
(b) Transpiration : creates a suction force which pulls water inside the plant.
(c) Excretion : helps in excreting out waste water from the plant.
(d) Translocation : helps in transporting materials from one cell to another.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Transpiration is a vital process in plants that involves the loss of water vapour from the aerial parts, primarily leaves. This process plays a crucial role in several ways:
- Water Movement: It creates a suction force that pulls water from the roots through the xylem.
- Nutrient Transport: Transpiration aids in the upward movement of water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves.
- Temperature Regulation: It helps maintain optimal temperatures within the plant.
During the day, when the stomata are open, transpiration becomes the main driving force for water movement. At night, root pressure assists in this transport. Overall, transpiration is essential for maintaining the plant's hydration and nutrient supply.
Q6: The process in which loss of water in the form of vapours from the aerial parts of plants takes place is X, which helps in Y. Here, X and Y respectively are (1 Mark) (2023)
(a) Transpiration and photosynthesis
(b) Transpiration and temperature regulation
(c) Translocation and movement of soluble products of photosynthesis in phloem
(d) Translocation and absorption of water and minerals from soil by roots.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Process (X): Transpiration
Transpiration is the process where water is lost in the form of vapours from the aerial parts of plants, primarily through the stomata in the leaves. - Significance (Y): Temperature Regulation
Transpiration helps in temperature regulation by cooling the plant. As water evaporates from the leaf surfaces, it dissipates heat, thus maintaining optimal temperature conditions for various physiological processes, including photosynthesis.
Q7: Assertion (A) : The walls of atria are thicker than those of the ventricles. (1 Mark) (2023)
Reason (R) : Ventricles have to pump blood into various organs at high pressure.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Assertion (A): The walls of atria are thicker than those of the ventricles.
- This statement is false. In reality, the walls of the ventricles are thicker than those of the atria.
- Ventricles have thicker muscular walls because they pump blood out of the heart to the lungs and the rest of the body, which requires more force (pressure).
Reason (R): Ventricles have to pump blood into various organs at high pressure.
- This statement is true. Ventricles indeed pump blood into the arteries and throughout the body at high pressure to ensure blood reaches all organs and tissues.
Therefore, while Reason (R) correctly explains the physiological need for thicker ventricular walls due to high-pressure pumping, Assertion (A) is incorrect because the ventricular walls are thicker than atrial walls, not the other way around.
Q8: Two green plants are kept separately in oxygen-free containers, one in the dark and the other in sunlight. It was observed that plants kept in the dark could not survive longer. Give a reason for this observation. (2 Marks) (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The plant kept in the dark could not survive longer because:
- It cannot perform photosynthesis, which is essential for producing food.
- Photosynthesis requires light to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- Without light, the plant lacks the energy needed for this process, leading to its inability to produce the oxygen necessary for respiration.
As a result, the plant in the dark cannot sustain itself and eventually dies.
Q9: List the events that take place during the process of photosynthesis in the proper sequence. (2 Marks) (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The three events that occur during the process of photosynthesis are;
(i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy (in the form of ATP and NADPH) and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
(iii) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates (carbon assimilation).
Q10: (i) How does Paramecium obtain its food? (3 Marks) (2023)
(ii) List the role of each of the following in our digestive system:
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Trypsin
(c) Muscular walls of the stomach
(d) Salivary amylase
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) In Paramecium, a unicellular protozoan, the hair-like outgrowth cilia are present on the entire surface and help collect the food. They sweep the food inside the body through the oral groove.
(ii) (a) Role of hydrochloric acid: It helps to maintain the acidic pH in the stomach required for activation of the enzyme pepsin that digests proteins in the stomach.
(b) Role of trypsin in our digestion system: Trypsin breaks down protein into smaller peptides in the duodenum of the small intestine. It helps in digesting dietary protein by breaking the chain of amino acids. It also activates some proenzymes present in pancreatic juice.
(c) Role of muscular walls in the stomach in our digestive system: The muscular walls in the stomach contract periodically and thereby help in the churning and mixing of the food with the digestive enzymes and HCI. It helps in chemical digestion.
(d) Role of salivary amylase in our digestive system: Salivary amylase found in saliva breaks down the starch and converts it into the simplest sugar.
Q11: (a) With the help of an activity, explain the action of saliva on the food we eat. (3 Marks) (2023)
(b) Why is bile juice important in the process of digestion?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The action of saliva on food can be demonstrated through a simple activity:
- Take two test tubes, A and B.
- In test tube A, add one teaspoon of boiled rice.
- In test tube B, add one teaspoon of boiled rice that has been chewed for 3 to 5 minutes.
- Add 3.4 mL of water to both test tubes.
- Add a few drops of iodine solution to each test tube.
Results:
- In test tube A, the rice changes colour due to the absence of enzymes.
- In test tube B, there is no colour change because the amylase enzyme in saliva breaks down the starch into simple sugars.
(b) Bile juice plays a crucial role in digestion:
- It breaks down fats into fatty acids, making them easier to absorb.
- Bile also provides an alkaline fluid that neutralises the acidic food from the stomach.
Q12: What is the other name of 'tissue fluid'? Write its two functions. (2 Marks) (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Tissue fluid is also called lymph. The functions of tissue fluid are:
(i) It carries digested and absorbed fat from the intestine.
(ii) It drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood.
Q13: What will happen if: (2 Marks) (2023)
(a) Xylem tissue in a plant is removed.
(b) We are injured and start bleeding?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) If the xylem is removed, transport of water and minerals from the soil would not occur, which leads to the wilting of leaves and, ultimately, the death of the plant.
(b) In case of any injury, when bleeding occurs, platelets circulate around the body and form a mesh-like network or clot at the site of injury.
Q14: (i) What is double circulation? (3 Marks) (2023)
(ii) Why is the separation of the right side and the left side of the heart useful? How does it help birds and mammals?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Double circulation is a system where blood passes through the heart twice during one complete cycle. It consists of two main pathways:
- Systemic circulation: Carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body.
- Pulmonary circulation: Transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
 (ii) The separation of the heart into right and left sides is beneficial because:
(ii) The separation of the heart into right and left sides is beneficial because:
- It prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- This separation allows for a more efficient supply of oxygen to the body.
- Birds and mammals, being warm-blooded, have high energy needs and require a constant oxygen supply.
- Mixing blood could lead to inefficient oxygen delivery, which is critical for their complex metabolism.
In summary, the distinct sides of the heart ensure that oxygen-rich blood is effectively circulated to all body parts, supporting the energy demands of these animals.
Q15: Write one specific function of each of the following organs in relation to excretion in human beings: (2 Marks) (2023)
(i) Renal Artery
(ii) Urethra
(ii) Glomerulus
(iv) Tubular part of nephron
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Renal artery: Carries blood from the aorta to the kidneys for filtration.
(ii) Urethra: Transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
(iii) Glomerulus: Filters blood to initiate the formation of urine.
(iv) Tubular part of nephron: Enables selective reabsorption of essential substances like glucose, amino acids, salts, and water into the blood.
Q16: Explain in brief two ways by which leaves of a plant help in excretion. (2 Marks) (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Leaves of a plant assist in excretion in the following ways:
- Stomata: Most carbon dioxide is released through tiny openings called stomata in the leaves.
- Transpiration: Plants lose excess water through a process known as transpiration, which is the evaporation of water from the leaf surface.
- Waste Storage: Many waste products are stored in leaves, which are eventually shed, allowing the plant to excrete these materials.
Q17: An organism which breaks down the food material outside the body and then absorbs it is:
(a) a plant parasite, Cuscuta
(b) an animal parasite, Tapeworm
(c) a bacteria, Rhizobium
(d) a fungi, Rhizopus (1 Mark) (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
(i) Rhizopus is a fungus that performs extracellular digestion. It secretes digestive enzymes outside its body to break down food material into simpler substances, which are then absorbed.
(ii) Cuscuta is a plant parasite that absorbs nutrients directly from the host plant.
(iii) Tapeworm is an animal parasite that lives inside the host's body and absorbs pre-digested nutrients.
(iv) Rhizobium is a nitrogen-fixing bacterium associated with legume roots; it does not break down food outside the body for absorption.
Therefore, (d) a fungi, Rhizopus is correct, as it digests food material outside its body and then absorbs it.
Q18: Consider the following statements about small intestine and select the one which is NOT correct:
(a) The length of the small intestine in animals differ as it depends on the type of food they eat.
(b) The small intestine is the site of complete digestion of food.
(c) The small intestine receive secretions from liver and pancreas.
(d) The villi of the small intestine absorb water from the unabsorbed food before it gets removed from the body via the anus. (1 Mark) (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
(a) This statement is correct. The length of the small intestine varies among animals depending on their diet. Herbivores generally have longer small intestines than carnivores to allow more time for digesting plant material.
(b) This statement is correct. The small intestine is the primary site for the complete digestion of food, where nutrients are broken down and absorbed.
(c) This statement is correct. The small intestine receives secretions from the liver (bile) and the pancreas (pancreatic enzymes) that aid in digestion.
(d) This statement is incorrect. The main function of the villi in the small intestine is to absorb nutrients, not water. Water absorption primarily occurs in the large intestine, not the small intestine.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d), as it is the statement that is NOT correct.
Q19: Name the type of blood (oxygenated/ deoxygenated) transported by each of the following mentioning the path i.e., from one organ (which place) to another (which place).
(A) Vena cava
(B) Pulmonary artery (3 Marks) (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Vena cava: The vena cava consists of two main veins:
- Superior vena cava: Carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body and arms to the right atrium.
- Inferior vena cava: Transports deoxygenated blood from the legs and abdominal area to the right atrium.
(B) Pulmonary artery:
- It carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- In the lungs, the blood becomes oxygenated.
Q20: (A) State the role of ATP in cellular respiration.
(B) What ensures sufficient exchange of gases in plants?
(C) State the conditions on which the direction of diffusion of gases in plant depend upon. (3 Marks) (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) ATP in Cellular Respiration:
- ATP is the energy currency of cells.
- Most ATP is produced in the mitochondrial matrix during cellular respiration.
- Each glucose molecule can generate around 32 ATP molecules.
(B) Gas Exchange in Plants:
- Plants exchange gases through stomata.
- Large intercellular spaces ensure all cells contact air.
- Carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged by diffusion.
(C) Conditions Affecting Gas Diffusion:
- The direction of diffusion depends on environmental conditions.
- It also relies on the needs of the plant.
- At night, carbon dioxide is mainly released; during the day, oxygen is produced.
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q1: In human alimentary canal, the specific enzyme/ juice secreted in locations (i), (ii) and (iii) are (2022)
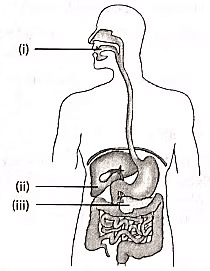 (a) (i) Amylase (ii) Pepsin (iii) Bile
(a) (i) Amylase (ii) Pepsin (iii) Bile
(b) (i) Amylase (ii) Bile (iii) Trypsin
(c) (i) Lipase (ii) Amylase (iii) Pepsin
(d) (i) Trypsin (ii) Bile (iii) Amylase
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Saliva is secreted in the mouth (i) and contains the enzyme salivary amylase, which helps digest carbohydrates. The liver (ii) secretes bile to emulsify fats, breaking them into smaller globules for easier digestion. The pancreas (iii) produces pancreatic juice, which contains enzymes like trypsin for protein digestion.
Q2: Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to (iv). (2022)
Take a healthy potted plant with elongated leaves. Select a leaf and insert about one half of this leaf in a test tube containing KOH and make it air tight. Place the set-up in sun for two hours. Take out the leaf from the test tube and dip it in boiling water for a few minutes. Put this leaf in a beaker with alcohol and boil it in a water bath. Wash the leaf with water and then dip the leaf in iodine solution for a few minutes. The portion of the leaf dipped in KOH solution will not show any change when dipped in iodine solution.
(i) The function of KOH taken in the test tube is to absorb
(a) Released water vapours
(b) Released CO2
(c) Released O2
(d) Chlorophyll.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
In the given experiment, KOH (Potassium hydroxide) in the test tube absorbs carbon dioxide; thus, due to the absence of CO2, the leaf fails to produce starch which proves that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis.
(ii) On the basis of this activity, we may conclude that the factor for photosynthesis is
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Oxygen
(c) Chlorophyll
(d) Water vapour.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The given experiment demonstrates the requirement of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. When KOH absorbs the available CO2 from the portion of leaf dipped in it, formation of sugar and starch is inhibited and the portion of leaf dipped in KOH did not show any change when dipped in iodine solution. Thus, it is proved that CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis.
(iii) The event that does not occur in photosynthesis is
(a) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
(b) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
(c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
(d) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Following are the three events that occur during the process of photosynthesis
(i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
(iii) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
(iv) Iodine solution gives blue-black colour with
(a) Starch
(b) Proteins
(c) Glucose
(d) Fats.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The brown coloured iodine will turn blue-black when it reacts with starch.
Q3: The correct statements with reference to single celled organisms are (2022)
(i) complex substances are not broken down into simpler substances
(ii) simple diffusion is sufficient to meet the requirement of exchange of gases
(iii) specialised tissues perform different functions in the organism
(iv) entire surface of the organism is in contact with the environment for taking in food.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv).
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Unicellular organisms are one-celled and perform all the life processes that are essential for maintaining the life of cell or organisms like nutrition, respiration, reproduction, excretion, etc. In single-celled organisms such as Amoeba, complex substances are broken into simpler substances.
Q4: Which one of the following conditions is true for the state of stomata of a green leaf shown in the given diagram?
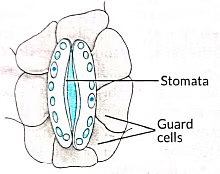
(a) Large amount of water flows into the guard cells.
(b) Gaseous exchange is occurring in large amount.
(c) Large amount of water flows out from the guard cells.
(d) Large amount of sugar collects in the guard cells.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The opening and closing of the stomatal pore depend on the turgidity of the guard cells. When guard cells lose water, they become flaccid, leading to a closed stomatal pore. Conversely, when they swell with water, the pore opens.
Q5: Assertion (A): Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and is taken up by plants in the form of inorganic nitrates or nitrites. (2022)
Reason (R) : The soil is the nearest and richest source of raw materials like nitrogen, phosphorus and other minerals for the plants.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The correct answer is (b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). Nitrogen is indeed essential for plant growth, and plants absorb it mainly as inorganic nitrates or nitrites. However, while the soil is a rich source of nutrients for plants, the reason provided does not directly explain why nitrogen is taken up in that specific form, so it’s not a correct explanation of the assertion.
Q6: A student was asked to write a stepwise procedure to demonstrate that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis. He wrote the following steps. The wrongly worded step is (2022)
(a) Both potted plants are kept in dark room for at least three days
(b) Bottom of the bell jars is sealed to make them air tight
(c) Both potted plants are kept in sunlight after the starch test
(d) A leaf from both the plants is taken to test the presence of starch.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Both potted plants should be kept in sunlight for about two hours before the starch test.
Q7: The length of small intestine in a deer is more as compared to the length of small intestine of a tiger. The reason for this is (2022)
(a) Mode of intake of food
(b) Type of food consumed
(c) Presence or absence of villi in intestines
(d) Presence or absence of digestive enzymes.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The length of the small intestine in a deer is greater than that of a tiger due to their differing diets.
- Herbivores, like deer, consume grass, which is high in cellulose. This requires a longer small intestine for effective digestion.
- Carnivores, such as tigers, eat meat, which is easier to digest, allowing for a shorter small intestine.
The structure of the small intestine is adapted to the dietary needs of each animal, reflecting their evolutionary differences.
Q8: The sequence of anaerobic respiration in our muscle cells during heavy exercise is (2022)
(a) 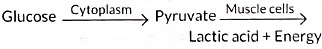
(b) 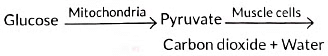
(c) 
(d) 
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
During heavy exercise, when oxygen is scarce in our muscle cells, the process of anaerobic respiration occurs. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Glucose (a six-carbon molecule) is broken down into pyruvate (a three-carbon molecule).
- This conversion leads to a build-up of lactic acid in muscles, which can cause cramps.
- In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid and energy.
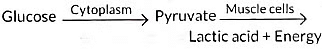
Q9: The energy released during cellular respiration is used to synthesise (2022)
(a) Ribosomes
(b) RBC
(c) ATP
(d) mitochondria.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The energy released during cellular respiration is immediately used to synthesise a molecule called ATP which is energy currency of the cell and is used as fuel for cellular activities.
Q10: Which of the following statements are correct in reference to the role of A (shown in the given diagram) during a breathing cycle in human beings? (2022)
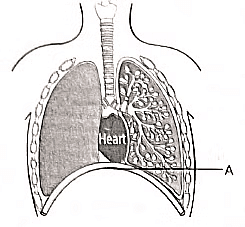
(i) It helps to decrease the residual volume of air in lungs.
(ii) If flattens as we inhale.
(iii) It gets raised as we inhale.
(iv) It helps the chest cavity to become larger.
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
During inhalation, we lift our ribs and flatten our diaphragm (A), which enlarges the chest cavity. This creates a vacuum that pulls air into the lungs, filling the expanded alveoli.When we exhale, our ribs and diaphragm return to their normal positions, causing the chest cavity to shrink. This pushes air out of the lungs.
- The lungs always retain a residual volume of air, ensuring there is enough time for oxygen absorption and carbon dioxide release.
- This residual volume remains constant under normal conditions.
Q11: Assertion (A): The rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much slower than that seen in terrestrial organisms. (2022)
Reason (R): The amount of oxygen dissolved in water is very low as compared to the amount of oxygen in air.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much slower than that seen in terrestrial organisms.The rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is actually much faster than in terrestrial organisms due to the following reasons:
- The amount of dissolved oxygen in water is relatively low compared to the oxygen available in the air.
- Aquatic animals must breathe rapidly to obtain enough oxygen from the water.
- Fish, for example, take in water through their mouths and push it past their gills, where oxygen is absorbed into their blood.
Q12: The function of the lining of mucus in the nasal passage of human beings is to (2022)
(a) Increase the temperature of inhaled air
(b) Move the air in and out
(c) Filter the air that we breathe in
(d) Absorb oxygen from the air.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The mucus lining in the nasal passage serves several important functions:
- It helps to moisten the air we breathe.
- It warm the inhaled air.
- It traps dust particles and other impurities, acting as a filter.
Q13: In living organisms during respiration which of the following products are not formed if oxygen is not available? (2022)
(a) Carbon dioxide + Water
(b) Carbon dioxide + Alcohol
(c) Lactic acid + Alcohol
(d) Carbon dioxide + Lactic Acid
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
In aerobic respiration, glucose is completely broken down to CO2 and H2O with the production of a large amount of energy (ATP).
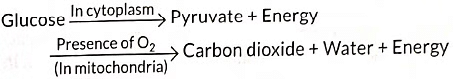
Thus, CO2 and water are formed as a result of aerobic ; respiration and will not formed in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic respiration).
Q14: Respiratory structures of two different animals-a fish and a human being are shown. (2022)
Observe (A) and (B) and select one characteristic that hold true for both of them.
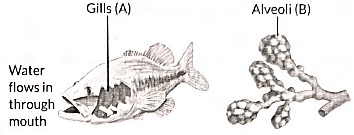
(a) Both are placed internally in the body of animal.
(b) Both have thin and moist surface for gaseous exchange.
(c) Both are poorly supplied with blood vessels to conserve energy.
(d) In both the blood returns to the heart after being oxygenated.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Both fish and humans have respiratory structures that facilitate gas exchange.
- Both possess thin and moist surfaces for efficient gas exchange.
- In fish, this occurs in the gills, while in humans, it takes place in the alveoli.
- This structure allows for the diffusion of oxygen into the blood and the removal of carbon dioxide.
Q15: Observe the diagram of an activity given below. What does it help to conclude, when the person exhales into the test-tube? (2022)
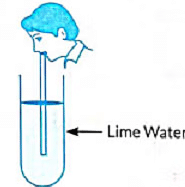
(a) Percentage of carbon dioxide is more in inhaled air.
(b) Fermentation occurs in the presence of oxygen.
(c) Percentage of carbon dioxide is more in the exhaled air.
(d) Fermentation occurs in the presence of carbon dioxide.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- When a person exhales into a test tube containing lime water, the following occurs:
- The lime water turns milky due to the formation of a white precipitate.
- This change indicates that the air we exhale contains a higher level of carbon dioxide.
- The reaction occurs because exhaled air has more carbon dioxide compared to inhaled air.
Q16: The separation of the right side and the left side of heart is useful to (2022)
(a) Keep oxygenated blood from mixing with deoxygenated blood
(b) Allow a slow supply of oxygen in the body
(c) Supply energy to animals with low energy needs
(d) Often change their body temperature.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The right side handles deoxygenated blood, sending it to the lungs for oxygen.
- The left side manages oxygenated blood, distributing it to the body.
- This separation prevents mixing of the two blood types, ensuring a more efficient supply of oxygen.
- It is particularly beneficial for animals with high energy needs, such as birds and mammals, which require constant energy to maintain their body temperature.
Q17: In spring, sugar stored in root or stem tissue of plants is transported to the buds for (2022)
(a) The energy needs of the buds to grow
(b) Temperature regulation
(c) Balancing the storage in different organs
(d) Diffusion process.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
In spring, new buds are formed. These buds need more energy to grow than other parts of the plant. This energy comes from the sugar stored in root or stem tissue and is transported to the buds by phloem.
Q18: Upward movement of water in tall trees is due to (2022)
(a) Translocation
(b) Excretion
(c) Photosynthesis
(d) Transpiration.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The upward movement of water in tall trees is primarily driven by transpiration. This process involves:
- Water evaporating from the stomata in the leaves.
- This evaporation creates a negative pressure in the leaves and xylem tissues.
- As a result, water is pulled up from the roots through the xylem.
In summary, transpiration not only aids in the movement of water but also helps regulate the plant's temperature.
Q19: Thin walled blood vessels are called (2022)
(a) Aorta
(b) Capillaries
(c) Arteries
(d) Vena cava
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Capillaries are tiny blood vessels with very thin walls, just one cell thick. They play a crucial role in the body by:
- Allowing the exchange of materials between blood and surrounding cells.
- Facilitating the transfer of oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
- Collecting waste products from cells for removal.
After the exchange, capillaries merge to form veins, which carry blood away from the tissues.
Q20: Consider the following statements in connection with the functions of the blood vessels marked A and B in the diagram of a human heart as shown. (2022)
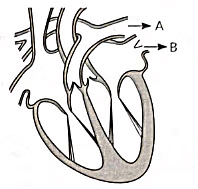
(i) Blood vessel A - It carries carbon dioxide rich blood to the lungs.
(ii) Blood vessel B - It carries oxygen rich blood from the lungs.
(iii) Blood vessel B - Left atrium relaxes as it receives blood from this blood vessel.
(iv) Blood vessel A - Right atrium has thick muscular wall as it has to pump blood to this blood vessel.
The correct statements are
(a) (i) and (ii) only
(b) (ii) and (iii) only
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii).
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Blood vessel A represents the pulmonary artery, while blood vessel B signifies the pulmonary vein.
The key functions of these blood vessels are:
- Pulmonary artery: Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
- Pulmonary vein: Transports oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Thus, oxygen-rich blood from the lungs enters the heart via the pulmonary vein, ensuring efficient oxygen supply to the body.
Q21: Identify the two components of phloem tissue that help in transportation of food in plants. (2022)
(a) Phloem parenchyma and sieve tubes
(b) Sieve tubes and companion cells
(c) Phloem parenchyma and companion cells
(d) Phloem fibres and sieve tubes
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The two components of phloem tissue that assist in the transportation of food in plants are:
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
Q22: Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to (iv). (2022)
The figure shown below represents a common type of dialysis called as haemodialysis- It removes waste products from the blood, such as excess salts, and urea which are insufficiently removed by the kidney in patients with kidney failure. During the procedure, the patient's blood is cleaned by filtration through a series of semi-permeable membranes before being returned to the blood of the patient. On the basis of this answer the following questions.
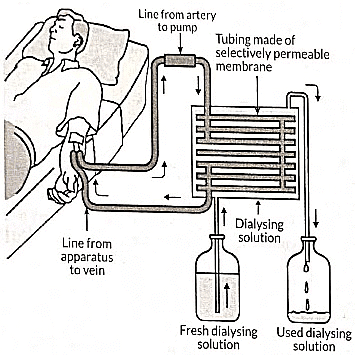
(i) The haemodialyser has semi-permeable lining c tubes which help
(a) To maintain osmotic pressure of blood
(b) To filter nitrogenous wastes from the dialysin solution
(c) In passing the waste products in the dialysing solution
(d) To pump purified blood back into the body of the patient.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The haemodialyser contains tubes with a semi-permeable lining that serve several important functions:
- They help to filter waste products like urea and creatinine from the blood.
- They allow the passage of these waste products into the dialysing fluid.
- This process mimics the kidney's function, although it does not involve re-absorption of substances.
- Finally, the purified blood is pumped back into the patient's body.
(ii) Which one of the following is not a function of artificial kidney?
(a) To remove nitrogenous wastes from the blood
(b) To remove excess fluids from the blood.
(c) To reabsorb essential nutrients from the blood.
(d) To filter and purify the blood.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- An artificial kidney does not reabsorb essential nutrients from the blood.
- Its primary functions include:
- Removing nitrogenous wastes from the blood.
- Eliminating excess fluids from the blood.
- Filtering and purifying the blood.
(iii) The 'used dialysing' solution is rich in
(a) Urea and excess salts
(b) Blood cells
(c) Lymph
(d) Proteins.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The used dialysing solution is rich in waste products.
- It contains high levels of urea and excess salts.
- During dialysis, the patient's blood flows through tubes with a semi-permeable lining.
- As blood passes through, waste products diffuse into the dialysing fluid.
- This process helps to purify the blood before it is returned to the patient.
(iv) Which part of the nephron in human kidney, serves the function of reabsorption of certain substances
(a) Glomerulus
(b) Bowman's Capsule
(c) Tubules
(d) Collecting Duct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The tubules of the nephron are responsible for the selective reabsorption of essential substances.
- These substances include: Glucose, Amino acids, Salts, Water
- This process allows these useful substances to return to the blood capillaries.
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q1: (i) Plants absorb water from the soil. Explain how it is taken up and transported from the soil. (2021)
(ii) "When we are injured and start bleeding, it requires the loss of blood from the system to be minimized." What will happen if the blood loss is not stopped? Is there anything the system could do on its own to prevent the loss?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i)
- Minerals and water needed by the plants are absorbed by roots.
- The root hairs absorb water from the soil by the process of osmosis and take in minerals by the process of diffusion.
- Thus, a difference in concentration of ions is created between the roots and the soil, which enables the water to enter into the roots to compensate for the difference in concentration.
- This water, along with dissolved minerals from the root hairs, passes into xylem vessels through cells of the cortex, endodermis, and pericycle, and then ascent of sap takes place from the xylem of roots into the xylem of stem and finally leaf veins through vessels and tracheids.
(ii) Bleeding leads to a loss of pressure, which reduces the efficiency of the pumping system. When an injury is caused, the blood platelets release certain chemicals which are called the platelet factors (e.g., thromboplastin). These platelet factors help in the clotting of blood.
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q1: In the human body, the site of absorption of digested food is the small intestine. How is the process of absorption carried out, and why is the absorption of digested food necessary? (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The small intestine is the main region for the absorption of digested food.
- It consists of the following parts:
- The inner surface of the small intestine has millions of tiny finger-like projections called villi.
- These villi increase the surface area for efficient food absorption.
- Within these villi, many blood vessels are present that absorb the digested food and carry it to the bloodstream.
- The small intestine in human beings is the site of the complete digestion of food like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- The absorption of digested food is necessary because an organism takes the complex organic materials by the process of absorption and then utilizes absorbed nutrients for various metabolic processes.
- With the help of these metabolic processes, the body uses these food nutrients for energy, growth, and cell repair.
Q2: Complete the following flow chart as per the given instructions. (2020)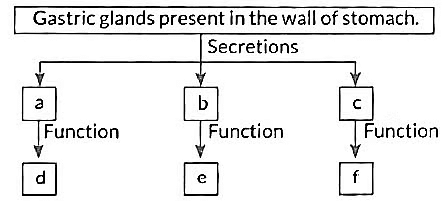
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: a - Hydrochloric acid (HCI)
b - Pepsin
c - Mucus
d - HCI makes medium acidic for the activation of an enzyme pepsin.
e - Pepsin acts in an acidic medium, which breaks down proteins into peptones.
f - The mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the corroding action of HCI.
Q3: (a) State the role played by the following in the process of digestion: (2020)
(i) Enzyme trypsin
(ii) Enzyme lipase
(b) List two functions of finger-like projections present in the small intestine.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i) Enzyme trypsin: This enzyme is produced by the pancreas in an inactive form called trypsinogen.
Trypsin converts the remaining proteins into peptones, and the peptones into peptides and amino acids.
(ii) Enzyme lipase: It is secreted by the pancreas and small intestine. Lipase converts fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
(b) Internally, the wall of the small intestine is provided with long finger-like projections called villi. Two functions of villi are:
(i) The villi greatly increase the absorptive surface area of the inner lining of the small intestine.
(ii) Villi are richly supplied with blood vessels that carry absorbed food to all cells of the body, where it is utilized for obtaining energy.
Q4: (a) In the process of respiration, state the function of alveoli. (2020)
(b) The rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much faster than that in terrestrial organisms. Give reasons.
(c) Complete the following pathway showing the breakdown of glucose.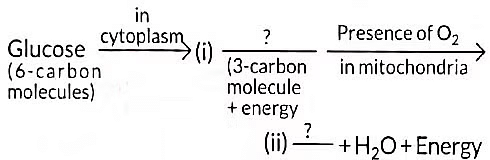
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Functions of alveoli are:
(i) They increase the surface area for the exchange of gases.
(ii) The thin walls of alveoli facilitate the rapid exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between alveolar air and blood.
(b) Aquatic animals like fishes obtain dissolved oxygen from water present through their gills. The amount of dissolved oxygen is quite small compared to the amount of oxygen in the air. Therefore, to obtain the required amount of oxygen from water, aquatic animals have to breathe much faster than terrestrial organisms.
(c)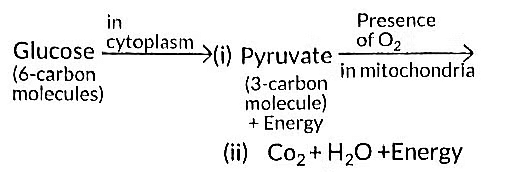
Q5: Give reasons: (2020)
(a) Ventricles have thicker muscular walls than atria.
(b) The transport system in plants is slow.
(c) Circulation of blood in aquatic vertebrates differs from that in terrestrial vertebrates.
(d) During the daytime, water and minerals travel faster through the xylem as compared to the night.
(e) Veins have valves, whereas arteries do not.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Since ventricles have to pump blood into various organs with high pressure, they have thicker walls than atria.
(b) The transport system in plants is slow due to:
- A less elaborate system compared to animals.
- Plants are generally less active, so their cells do not require rapid material supply.
(c)
- Circulation of blood in aquatic vertebrates differs from terrestrial vertebrates because:
- Aquatic vertebrates, like fish, have gills for oxygenation and exhibit single circulation, where blood passes through the heart once per cycle.
- Terrestrial vertebrates, like birds and humans, have lungs and use double circulation, with blood passing through the heart twice per cycle.
(d) During the daytime, water and minerals travel faster through the xylem because the rate of transpiration is higher during the daytime.
(e) The lumen of veins has valves, which allow the blood to flow in only one direction. Thus preventing the backflow of blood.
Q6: (a) "Blood circulation in fishes is different from the blood circulation in human beings”. Justify the statement.
(b) Describe "blood circulation” in human beings. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Fishes have only two chambers in their heart. The blood is pumped to the gills for oxygenation, and from there, it passes directly to the rest of the body. Thus, the blood goes only once through the heart during one cycle of passage through the body. This type of circulation is termed as single circulation.
- In human beings, during circulation, blood travels twice through the heart in one complete cycle of the body, which is called double circulation.
- The pathway of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart is called pulmonary circulation, and the pathway of blood from the heart to the rest of the body and back to the heart is called systemic circulation.
- In human beings, deoxygenated blood from the body tissues is poured into the right atrium.
- Contraction of the heart forces it into the right ventricle.
- From the right ventricle, deoxygenated blood flows to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
- Oxygenated blood from the lungs is returned to the left atrium and then into the left ventricle.
- The left ventricle forces the oxygenated blood to the whole body.
- Thus, to make one complete round or circulation circuit around all body parts, the blood passes through the heart twice.
- This is known as the double circulation of blood.
Q7: (a) Describe the structure and function of the basic filtering unit of the kidney. (2020)
(b) List two factors on which the reabsorption of water from urine depends.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Its main role is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium and other salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing the excess water that is needed, and excreting the rest as urine.
(b) Two factors on which the reabsorption of water from urine depends are:
- The amount of excess water which is present in the body.
- The amount of dissolved waste that needs to be excreted out of the body.
Q8: (a) Name the organs that form the excretory system in human beings. (2020)
(b) Describe in brief how urine is produced in the human body.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The Excretory system (urinary system) in human beings consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra.
(b)
- In the kidney, the wastes are converted to urine by three processes:
- (i) Ultrafiltration: A large amount of water, along with certain harmful substances like urea, uric acid, K, ammonium salts, creatinine, etc., and certain useful substances like glucose, amino acids, Na, etc., pass through glomerular capillaries and glomerular membrane into the cavity of Bowman’s capsule of nephrons under pressure. The filtrate so formed is called nephric filtrate, which is moved towards the ureter.
- (ii) Selective reabsorption: A large amount of water and sodium, a whole of glucose and amino acids, and a small amount of urea are passed back from the nephric filtrate into the blood capillaries. It occurs either by back diffusion (i.e., water and urea) or active transport (i.e., Na, glucose, and amino acids). It generally occurs in the PCT (Proximal convoluted tubule) of nephrons.
- (iii) Tubular secretion: Certain harmful chemicals like uric acid, creatinine, K, etc., are passed from blood capillaries surrounding the nephron into nephric filtrate by active transport. It generally occurs in the DCT (Distal convoluted tubule) of nephrons. Now, the fluid is termed as urine and is excreted out of the excretory organs.
Q9: (a) Why is nutrition necessary for the human body? (CBSE 2020)
(b) What causes the movement of food inside the alimentary canal?
(c) Why is the small intestine in herbivores longer than in carnivores?
(d) What will happen if mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Nutrition is necessary for the human body because the human body continuously requires energy for life activities like respiration, circulation, excretion, etc.
- Energy is required even when we are sleeping because a number of biological processes keep on occurring.
- All these processes require energy, and this energy is obtained from nutrition.
- It is also needed for the growth and repair of the human body.
- The wall of the alimentary tract contains muscles that can contract and expand alternately.
- The contraction and expansion movement of the wall of the food pipe is called peristaltic movement.
- The peristaltic movement moves the partially digested food in all the digestive organs throughout the alimentary canal.
- The small intestine in herbivores is longer than in carnivores because:
- Herbivores consume plants rich in cellulose, which takes longer to digest.
- They rely on enzymes from symbiotic bacteria to break down cellulose.
- Carnivores eat flesh, which is easier to digest, resulting in a shorter small intestine.
(d) If mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands:
- The inner lining of the stomach would be exposed to hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes.
- This could lead to erosion of the stomach lining, causing acidity and potentially ulcers.
Q10: (a) Why is there a difference in the rate of breathing between aquatic organisms and terrestrial organisms? Explain. (2020)
(b) Draw a diagram of the human respiratory system and label it - the pharynx, trachea, lungs, diaphragm and alveolar sac on it.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The difference in the rate of breathing between aquatic and terrestrial organisms is primarily due to their oxygen sources:
- Terrestrial organisms breathe in oxygen from the atmosphere, which contains about 21% oxygen.
- Aquatic organisms rely on oxygen that is dissolved in water, which is less than 1%.
- Oxygen diffuses through water much slower than in air.
- As a result, terrestrial organisms can obtain oxygen more easily and quickly.
- Aquatic organisms must work harder to extract the same amount of oxygen, leading to a faster breathing rate.
(b) The labelled diagram of the human respiratory system is as follows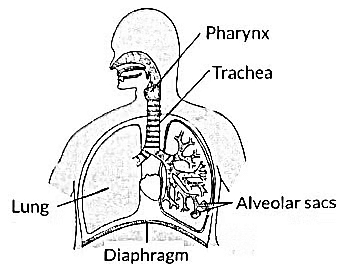
Q11: (A) Write the correct sequence of steps followed during journey of oxygen rich blood from lungs to various organs of human body. (B) What happens when the system of blood vessels develop a leak? (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Journey of oxygen rich blood from lungs to various parts of the body is as follows:
(i) The pulmonary vein brings the oxygenated blood from the lungs in the left atrium of the heart.
(ii) The left atrium contracts and pumps blood into left ventricle through the valve.
(iii) When the left ventricle contracts, the oxygenated blood enters the largest artery known as aorta.
(iv) The blood travels from the aorta to larger and smaller arteries into the capillaries.
(v) The aorta transports the blood to all the organs of the body except the lungs.
(vi) The oxygenated blood releases oxygen, nutrients and other substances and takes away carbon dioxide and waste substances.
(vii) The deoxygenated blood enters the vena cava, which carries it to the right atrium of the heart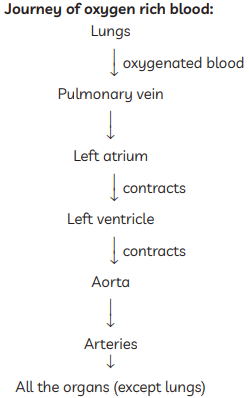
(B) When the system of blood vessels develop a leak, the platelets will increase, which will minimise the leakage. Whenever there is a leak in the blood vessels, the blood flows, through them. If not checked, that may cause an excessive loss of blood.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q1: Name an enzyme present in pancreatic juice. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Pancreatic juice contains the digestive enzyme trypsin.
Q2: What causes the movement of food inside the alimentary canal in human beings? (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The movement of food in the alimentary canal is primarily due to peristalsis. This is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the canal, which helps to push food downwards.
- Peristalsis occurs throughout the digestive tract.
- Food travels from the mouth to the stomach via the oesophagus.
- The stomach's muscular walls mix food with digestive juices.
Q3: (a) Write the function of the following in the human alimentary canal: (CBSE 2019)
(i) Saliva
(ii) HCI in the stomach
(iii) Bile juice
(iv) Villi
(b) Write one function for each of the following enzymes:
(i) Pepsin
(ii) Lipase
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i) Saliva contains salivary amylase and is released in our mouth. It breaks down starch into sugar (complex carbohydrates into simpler ones).
(ii) Acid (HCI) plays an important role in the process of digestion. These are:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) creates an acidic medium in the stomach, which is essential for the activation and functioning of the gastric enzyme pepsin.
- HCI kills the harmful bacteria present in the food.
- Bile brings about the emulsification of fat (i.e., breaks fat molecules into small globules).
- Internally, the wall of the small intestine is provided with long finger-like projections called villi. Two functions of villi are:
- The villi greatly increase the absorptive surface area of the inner lining of the small intestine.
- Villi are richly supplied with blood vessels that carry absorbed food to all cells of the body, where it is utilized for obtaining energy.
(b) (i) Pepsin is a protein-digesting enzyme present in gastric juice. Pepsin gets activated in an acidic medium and splits proteins into peptones and peptides.
(ii) Lipase is secreted by the pancreas and small intestine. Lipase converts fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Q4: Write two different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in the human body. Write the products formed in each case. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The two different ways by which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in the human body are:
(i) Aerobic respiration (In the presence of oxygen): The end products in aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and energy.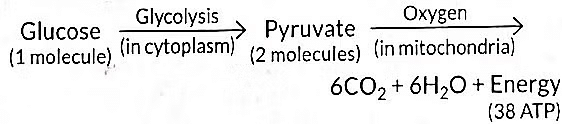
(ii) Anaerobic respiration (In the lack of oxygen): The end products are lactic acid and energy.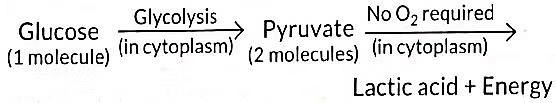
Q5: Explain the ways in which glucose is broken down in the absence or shortage of oxygen. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In the absence or shortage of oxygen, glucose is oxidized in the following ways:
(i) In cytoplasm, glucose is oxidized to pyruvate and release energy.
(ii) In the muscles of humans, i.e., under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate breaks down to lactic acid and releases energy.
(iii) In yeast, i.e., during the fermentation process, pyruvate converts to ethanol while carbon dioxide releases a certain amount of energy.
Q6: (a) List in tabular form two differentiating features between xylem and phloem. (2019)
(b) Write two advantages of transpiration in plants.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Differences between transport in the xylem and transport in the phloem are as follows: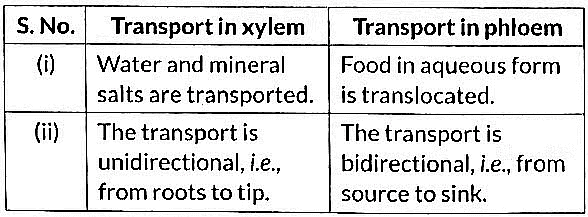
(b) Significance of transpiration in plants:
(i) The absorbed water is transported from roots to leaves through xylem vessels, which is greatly influenced by transpiration pull.
(ii) The water stream moving upwards carries dissolved minerals with it. Transpiration also helps in distributing these minerals throughout the plant.
(iii) The evaporation of water during transpiration provides a cooling effect to the leaves.
Q7: Write three types of blood vessels. Give one important feature of each. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The three types of blood vessels in the human body are:
(i) Arteries are the blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to various parts of the body. They are thick-walled, elastic, and muscular, which enables them to dilate but do not rupture when the heart contracts and forces blood into them.
(ii) Veins are thin-walled blood vessels that bring blood from the body back to the heart. They are larger and hold more blood than the arteries. The lumen of veins has valves which prevent the backflow of blood.
(iii) Capillaries are thin-walled and extremely narrow blood vessels that occur at the terminals of arteries and veins. The walls of capillaries are permeable to water and dissolved substances so that the exchange of materials between the blood and body cells can take place.
Q8: (a) Write two water-conducting tissues present in plants. How does water enter continuously into the root xylem? (2019)
(b) Explain why plants have low energy needs as compared to animals.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Xylem tracheids and vessels are two water-conducting tissues present in plants that help in the rapid movement of water.
- In xylem tissue, vessels and tracheids of the roots, stems, and leaves are interconnected to form a continuous system of water-conducting channels reaching all parts of the plant.
- Minerals and water needed by the plants are absorbed by root hairs from the soil by the process of osmosis and take in minerals by the process of diffusion.
- Thus, a difference in concentration of ions is created between the roots and the soil, which enables the water to enter into the roots to compensate for the difference in concentration.
- The water, along with dissolved minerals from root hairs, passes into xylem vessels through cells of the cortex, endodermis, and pericycle and then ascent of sap (i.e., upward movement of water and mineral salts from roots to the aerial parts of the plant against the gravitational force) takes place from xylem of the roots to the xylem of stem and leaves through vessels and tracheids.
- Evaporation of water molecules from the cells of leaves creates a suction pressure that pulls the water from the xylem cells.
Q9: List four functions of the human heart. Why is double circulation necessary in the human body? (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The functions of the human heart include:
- Maintaining blood pressure: The heart ensures that blood is pumped throughout the body effectively.
- Pumping vital substances: It delivers essential nutrients and substances to various body parts.
- Circulating oxygen-rich blood: The heart sends oxygenated blood from the lungs to the entire body and carries carbon dioxide-rich blood back to the lungs for purification.
- Removing metabolic waste: It helps eliminate waste products, such as carbon dioxide, from body tissues.
The human heart consists of two sides: the right side and the left side. The right side receives deoxygenated blood and sends it to the lungs for purification. The left side receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body. This process is known as double circulation.
Double circulation is necessary because:
- It separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, which is crucial for meeting the high energy demands of the body.
- This separation allows for efficient oxygen delivery to tissues, supporting the body's metabolic needs.
Q10: (a) Define the term excretion. Why should animals excrete waste matter? (2019)
(b) Name the main excretory organ of human beings and state the form in which the excretory matter is thrown out of the body.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Excretion is a biological process that removes harmful metabolic wastes from the body. Key points include:
- It eliminates substances like nitrogenous waste, which includes urea, salts, and water.
- Accumulation of these wastes can be harmful to the body.
- The main excretory organs in humans are the kidneys.
- Kidneys filter blood to produce urine, which carries away waste.
Overall, excretion is essential for maintaining the body's health by preventing the buildup of toxic substances.
(b) A pair of kidneys are the main excretory organs in a human being. It helps excrete nitrogenous waste in the form of urea, toxins, excess salts, water-soluble vitamins, etc. and then eliminates it in the form of urine.
Q11: In the experimental set-up to show that "CO2 is given out during respiration'' name the substance taken in the small test tube kept in the conical flask. State its function and the consequence of its use. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In the experiment in which carbon dioxide is given out during respiration, KOH (potassium hydroxide) solution or pellets are taken in a tube and placed within the conical flask. KOH absorbs the carbon dioxide, and it prevents the carbon dioxide from being utilized by the plant for the process of photosynthesis. Function of KOH
KOH: KOH solution kept in the flask absorbs carbon dioxide and creates a partial vacuum in the flask. The air present in the bent tube moves into a conical flask, and this pulls the water level up in the tube. Consequences:
- The whole amount of CO2 liberated gets absorbed by KOH to prevent it from being utilized by the plant for the process of photosynthesis.
- This CO2 absorption leads to creating a vacuum in a flask that causes an observable rise in the water level of the connected U tube.
- Any gas produced can neither escape nor can get outside air in.
- Germinating seed produces CO2 via the following reactions: Aerobic respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38ATP
Q12: In the experimental setup shown:
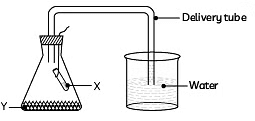 (A) Name the material X filled in the small test tube and the material Y placed at the bottom of the conical flask.
(A) Name the material X filled in the small test tube and the material Y placed at the bottom of the conical flask.
(B) Why is there a rise in water level in the delivery tube? (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) X - KOH pellets
Y - Wet germinating seeds
(B) Seeds use oxygen present in the flask and release carbon dioxide which is absorbed by potassium hydroxide. Thus, partial vacuum is created in the conical flask, as a result, water from the beaker rises in the delivery tube
Q13: Write the function of the following in the human alimentary canal: (CBSE 2019)
(i) Saliva
(ii) HCI in the stomach
(iii) Bile juice
(iv) Villi
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Saliva contains salivary amylase and is released in our mouth. It breaks down starch into sugar (complex carbohydrates into simpler ones).
(ii) Acid (HCI) plays an important role in the process of digestion. These are:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) creates an acidic medium in the stomach, which is essential for the activation and functioning of the gastric enzyme pepsin.
- HCI kills the harmful bacteria present in the food.
(iv) Internally, the wall of the small intestine is provided with long finger-like projections called villi. Two functions of villi are:
- The villi greatly increase the absorptive surface area of the inner lining of the small intestine.
- Villi are richly supplied with blood vessels that carry absorbed food to all cells of the body, where it is utilized for obtaining energy.
Q14: Give reasons for the following:
(A) There is a difference in the rate of breathing between aquatic organisms and terrestrial organisms.
(B) Plants have low energy needs as compared to animals. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) The rate of breathing differs between aquatic and terrestrial organisms due to their environments:
- Aquatic organisms breathe faster because they extract dissolved oxygen from water.
- Water contains less oxygen than air, necessitating a quicker breathing rate.
- Terrestrial organisms breathe more slowly as they obtain oxygen from the air, which is about 21% oxygen.
(B) Plants have lower energy needs compared to animals for several reasons:
- Plants are stationary and do not move, resulting in less energy expenditure.
- They are generally less active than animals.
- Many plant tissues contain a large amount of dead cells that provide structural support.
- As a result, plant cells do not require rapid supply of materials, leading to lower energy needs and a slower respiration rate.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q1: (a) Mention any two components of blood. (2018)
(b) Trace the movement of oxygenated blood in the body.
(c) Write the function of valves present in between atria and ventricles.
(d) Write one structural difference between the composition of arteries and veins.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Two components of blood are blood plasma and blood corpuscles.
(b) Oxygenated blood from lungs → Pulmonary veins → Left atrium of heart → Left ventricle → Aorta → Arteries → Body parts
(c) When blood is pumped, valves prevent the backflow of blood between ventricles and atria. They open and allow the right amount of blood to flow from one chamber to the other.
(d) Structural difference between veins and arteries is as follows:

Q2: (a) Name the process and explain the type of nutrition found in green plants. List the raw materials required for this process. Give a Chemical equation for the mentioned process. (2018)
(b) Write three events that occur during this process.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Photosynthesis is the process where green plants show autotrophic nutrition. The raw materials required for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide water, and energy in the form of sunlight.
The equation is as follows: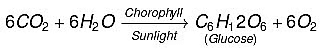
(b) The three events in photosynthesis are:
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
Q3: (a) Write the reaction that occurs when glucose breaks down anaerobically in yeast. (2018)
(b) Write the mechanism by which fishes breathe in water.
(c) Name the balloon-like structures present in the lungs. List its two functions.
(d) Name the respiratory pigment and write its role in human beings.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) 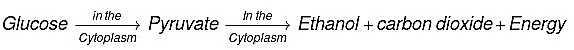
(b) Fishes breathe with the gills by diffusion.
(c) Alveoli are the balloon-like structures:
- They provide a surface for the exchange of gases.
- They contain a residual volume of air so that there is sufficient time for the exchange of gases.
(d) Haemoglobin is the respiratory pigment in humans. It transports a major part of oxygen and some amount of carbon dioxide through the blood.
Q4: (a) Mention any two components of blood. (2018)
(b) Trace the movement of oxygenated blood in the body.
(c) Write the function of valves present in between atria and ventricles.
(d) Write one structural difference between the composition of arteries and veins.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (а) Blood is composed of plasma and three types of cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
(b)
- Oxygenated blood from the lungs is brought to the left atrium by pulmonary veins.
- When the atrium contracts, blood is transferred to the left ventricle.
- When the ventricle contracts, blood is pushed into the aorta and through arteries to all parts of the body.
(c) The function of valves between the atria and ventricles is to:
- Prevent backflow of blood during pumping
- Ensure the correct amount of blood flows from one chamber to another
(d) 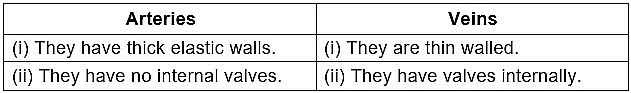
Q5: (а) Define excretion. (2018)
(b) Name the basic filtration unit present in the kidney.
(c) Draw the excretory system in human beings and label the following organs of the excretory system that perform the following functions:
(i) form urine.
(ii) is a long tube that collects urine from the kidney.
(iii) store urine until it is passed out.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) Excretion is the biological process of removal of harmful metabolic wastes from the body.
(b) Nephrons
(c) (i) Kidney, (ii) Ureter, (iii) Urinary bladder.
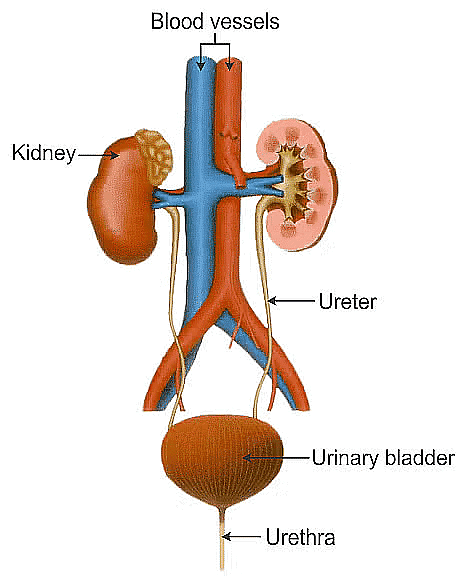 Excretory System of Human Beings
Excretory System of Human Beings
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q1: Diffusion is insufficient to meet the oxygen requirement of multicellular organisms like humans. State reason. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Due to the higher metabolic rate and the large volume of the body, oxygen cannot diffuse into all cells of the human body quickly as oxygen will have to travel large distances to reach each and every cell. So, diffusion is insufficient to meet the oxygen demand of multicellular organisms.
Q2: Name the vein that brings blood to the left atrium from the lungs. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Q3: Explain the significance of photosynthesis. Write the balanced chemical equation involved in the process. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Photosynthesis is important for a number of reasons:
(i) Food: By photosynthesis, green plants synthesize food from simple raw materials like CO2 and H2O. Thus, it sustains life on earth.
(ii) Oxygen: Oxygen released during the process of photosynthesis is needed by animals and humans for respiration. Oxygen also supports the combustion of fuels. The balanced chemical equation involved in the process of photosynthesis is given as: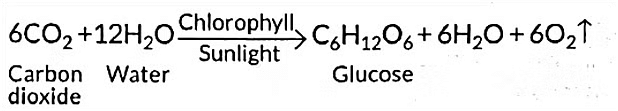
Q4: Differentiate between autotrophs and heterotrophs and give one example of each. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Differences between autotrophs and heterotrophs are as follows:
Q5: Explain how the translocation of materials in phloem tissue in plants is achieved by utilizing energy. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The phloem cells transport the soluble food materials to all parts of the plant.
- The transport of food from leaves to different parts of the plant is termed translocation.
- Components of phloem are sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem fibres.
- The food is manufactured in the mesophyll cells (or photosynthetic cells) of a leaf.
- The manufactured food enters into sieve tubes of the phloem and is transported as a dilute aqueous solution either in an upward or downward direction.
- Food is transported to all non-green parts of the plant for their growth and metabolic activities.
- Besides food molecules, the phloem also transports amino acids, hormones synthesized in the shoot tips and root tips, and other metabolites.
- In this process, glucose is transferred to phloem tissue using energy from ATP.
- This increases the osmotic pressure of the tissue, causing the water to move into it (endosmosis).
- Soluble material is then transferred from phloem tissue to other tissues which have less pressure than in the phloem.
- Thus, according to the plant’s requirement, the material is translocated from higher osmotic pressure areas to lower osmotic pressure areas.
Q6: Draw a diagram of the human excretory system and label kidney ureters on it. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The diagram of the human excretory system is as follows: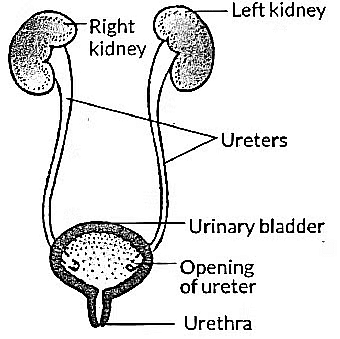
Q7: (a) Write the reaction that occurs when glucose breaks down anaerobically in yeast. (2017)
(b) Write the mechanism by which fishes breathe in water.
(c) Name the balloon-like structures present in the lungs. List its two functions.
(d) Name the respiratory pigment and write its role in human beings.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Glucose breaks down anaerobically i.e., in the absence of O2; in yeast in the following manner:
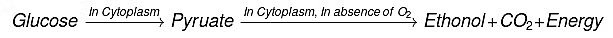
(b) Since fishes are aquatic, they take in O2 dissolved in water. They take water through their mouth, which goes to their gills, where the dissolved oxygen is taken up by the blood and transported. The CO2 is given out through the same passage.
(c) The balloon-like structures in our lungs are the alveoli.
Their functions are:
- They are very thin-walled and hence help in gaseous exchange.
- They contain an extensive network of blood vessels that help in the transport of respiratory gases.
- They increase the surface area for the absorption of gases.
(d) The respiratory pigment is Haemoglobin.
Its role is:
- It has an affinity for oxygen and hence helps in the transport of oxygen from alveoli to body tissues.
- It also has an affinity for CO2 and hence helps in the transport of CO2 from body tissues to alveoli.
Q8: (a) Name the process and explain the type of nutrition found in green plants. List the raw materials required for this process. Give the chemical equation for the mentioned process. (2017)
(b) Write three events that occur during this process.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The process of nutrition in green plants is Photosynthesis. The type of nutrition is autotrophic nutrition. Autotrophic nutrition requires sunlight, chlorophyll, water, and carbon dioxide.
Plants prepare their own food in the form of glucose, which gets converted to starch. This is done using CO2 and H2O, which are fixed using energy from sunlight from the chlorophyll molecules present in green plants.
Equation -

(b) The three events involved are:
- The absorption of sunlight occurs through chlorophyll.
- Conversion of this light energy into chemical energy and splitting of water into H+ and OH- using this energy.
- Reduction of CO2 to carbohydrate by using H+ produced due to splitting of water.
Q9: (a) Write the name of different components of the transport system in human beings and state their functions in brief. (2017)
(b) How does a blood clot form if a leak develops in the system of blood vessels?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Various components of the transport system and their functions:
(b) If there is a leak in the blood vessels due to injury, then the blood platelets help plug these leaks. The platelets make the clot by forming a mesh-like structure over the leak in which other blood cells get entangled, ultimately plugging the leak.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q1: Define translocation in reference to plants. (2016) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Translocation is the process by which plants transport the products of photosynthesis from the leaves to various parts of the plant, including:
- Roots
- Stems
- Branches
This transport occurs through the phloem, a type of vascular tissue, and involves:
- Movement of sucrose and other nutrients.
- Delivery to storage organs like roots, fruits, and seeds.
- Support for growing organs.
Translocation is an energy-dependent process, using ATP to increase osmotic pressure, which facilitates the movement of substances in the phloem.
This allows the plant to distribute nutrients according to its needs, such as transporting stored sugars to new buds in spring.
Q2: Mention the raw materials required for photosynthesis. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Raw materials required for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide (CO2), water, light, and chloroplast.
Q3: Write three points of difference between breathing and respiration. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Differences between breathing and respiration are as follows: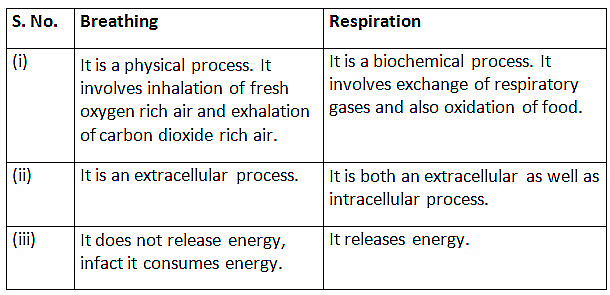
Q4: Draw a flow chart to show the breakdown of glucose by various pathways. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Glucose is first broken down in the cell cytoplasm into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. Pyruvate is further broken down in the following ways to provide energy.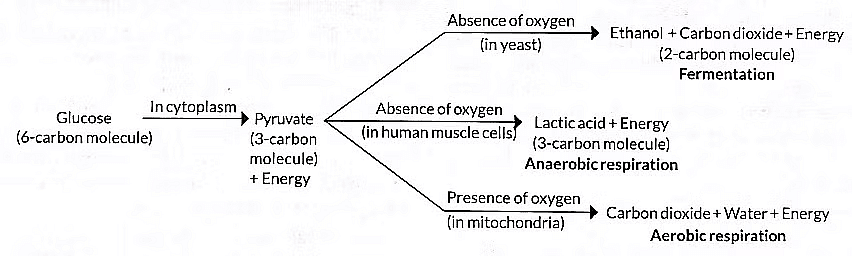
Q5: Draw a diagram of the human alimentary canal and label the following: (2016)
(i) Part in which starch digestion is initiated.
(ii) Organ in which bile is stored.
(iii) The gland that secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones.
(iv) Part of the alimentary canal where water is reabsorbed.
(v) Part of the gut where finger-like projections are present to facilitate absorption of digested food.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Mouth, (ii) Gall Bladder, (iii) Pancreas, (iv) Large Intestine, (v) Small intestine.
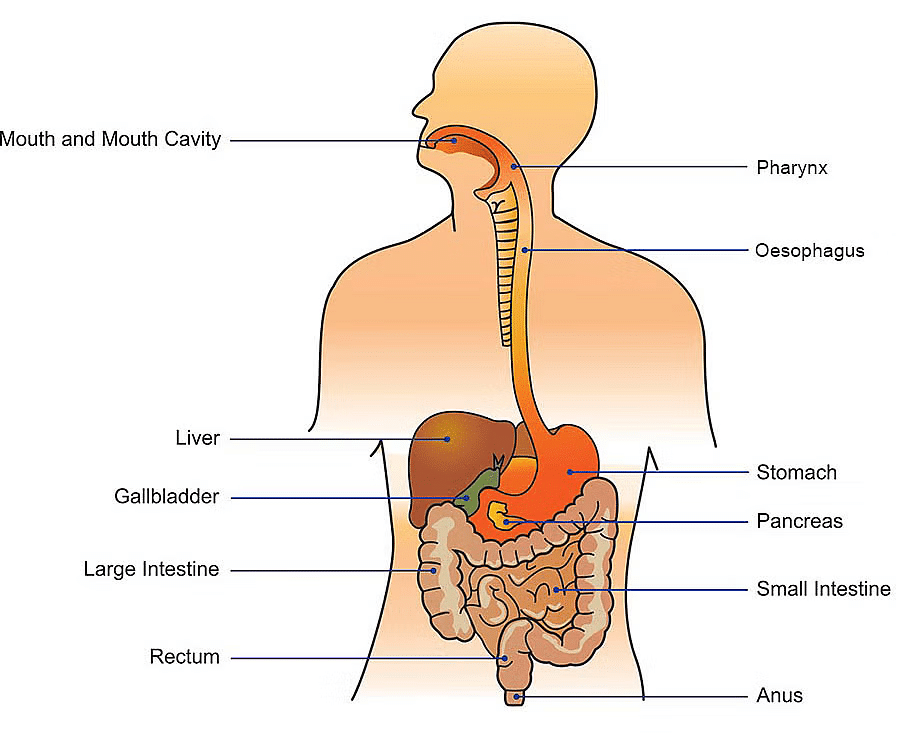
Q6: (a) State the form in which the following are stored : (2016)
(i) Unused carbohydrates in plants.
(ii) Energy derived from food in humans.
(b) Describe the process of nutrition in the amoeba with the help of a diagram.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a)
(i) As starch in fruits/storage roots tubers etc.
(ii) As glycogen.
(b) Amoeba is a unicellular eukaryotic organism that exhibits a holozoic mode of nutrition.
Five steps are involved in this mode of nutrition:
- Ingestion: Amoeba feeds on microscopic organisms. It takes in food using finger-like projections called pseudopodia. It encircles the food and engulfs or ingests it by a process called phagocytosis. The food comes to lie in a vesicle called a phagosome or food vacuole.
- Digestion: A lysosome fuses with a phagosome, and complex substances are broken down into simpler ones. Such a type of digestion that occurs within a cell is referred to as Intracellular digestion. The digested food then diffuses into the cytoplasm.
- Absorption and Assimilation: The digested food that has diffused into the cytoplasm is quickly absorbed by the organism and converted into various constituents of protoplasm.
- Egestion: The undigested food material reaches the rear end of the organism and is thrown out by the process of exocytosis. The membrane of the vesicle fuses with the surface membrane.
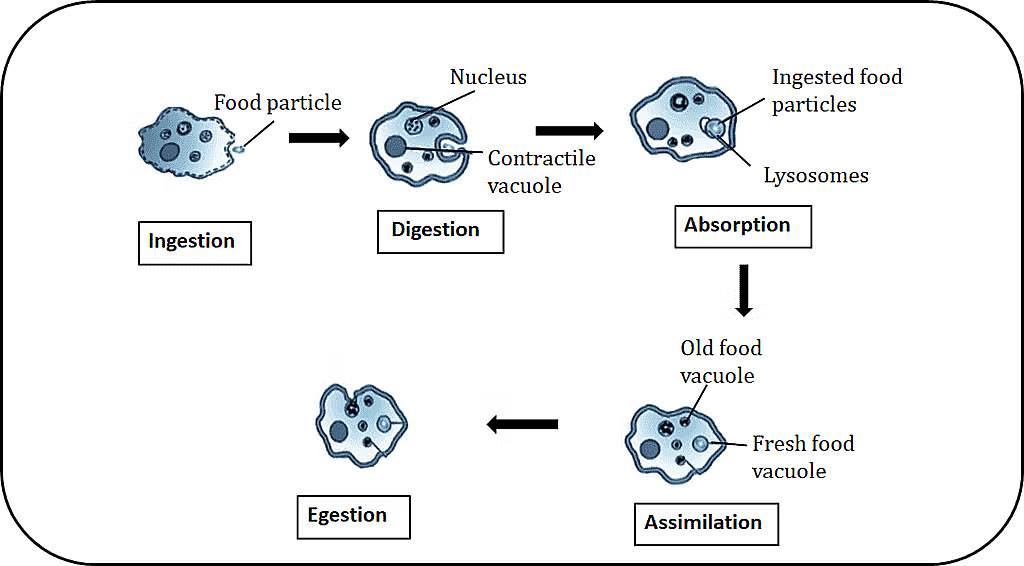
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q1: Give reason: (2015)
(l) Fine hair and mucus are present in the nasal passage.
(ii) Rings of cartilage are present in the throat.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Fine hair and mucus are present in the nasal passage so that any dust particles, pathogens, etc., can be trapped in here, and only clean air will enter the lungs. This is one of the defence mechanisms of our body.
(ii) Rings of cartilage are present in the throat so that the trachea does not collapse on respiration.
Q2: Define the term parasite. Name one plant parasite and one animal parasite. Some organisms break down the food material outside the body and then absorb it. Give two examples. (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Parasites are organisms that obtain nutrients from the bodies of other living organisms and harm them as a result.
(i) Plant parasite - cuscuta
(ii) Animal parasite - Tapeworm
Organisms that break down food outside the body and then absorb it are saprophytes.
Example: fungi, bacteria.
Q3: What do the following transport? (2015)
(i) Xylem
(ii) Phloem
(iii) Pulmonary vein
(iv) Vena cava
(v) Pulmonary artery
(vi) Aorta.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Material transported by:
(i) Xylem: Water and minerals.
(ii) Phloem: Organic molecules like sucrose.
(iii) Pulmonary vein: Oxygenated blood from lungs to heart.
(iv) Vena cava: Impure and deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart.
(v) Pulmonary artery: Deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
(vi) Aorta: Oxygenated blood from the heart to body parts.
Q4: In single-celled organisms, diffusion is sufficient to meet all their requirements for food, gas exchange, or removal of waste, but it is not in the case of multicellular organisms. Explain the reason for this difference. (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In the case of a single-celled organism, the entire surface of the organism is in contact with the environment, and hence, no specific organ for taking in food, exchanging gases, or removing waste may be needed. In multicellular organisms, only the cells of the skin are in direct contact with the environment. Diffusion is a very slow process, and it will take a very long time to reach all the cells of the body parts. Diffusion is insufficient to melt oxygen requirements.
Q5: State the role of the following in the human digestive system: (2015)
(a) Digestive enzymes
(b) Hydrochloric acid
(c) Villi
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Digestive enzymes digest the food we eat.
(b) Hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium to facilitate the action of the enzyme pepsin.
(c) Villi increases the surface area inside the small intestine to facilitate the absorption of food.
Previous Year Questions 2014
Q1: State the location and function of gastric glands. (2014) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Gastric glands are present in the wall of the stomach. They secrete gastric juices containing mucus, protein-digesting enzymes pepsin, rennin, and hydrochloric acid (HCI).
Q2: How does nutrition take place in Amoeba? How is it different in Paramoecium? (2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Nutrition in amoeba:
- Nutrition occurs through phagocytosis.
- Amoeba captures food using pseudopodia, which are temporary extensions of the cell.
- The ingested food is enclosed in a food vacuole.
- Inside the food vacuole, enzymes break down the food into simpler substances.
- Undigested food is expelled through the cell membrane.
Nutrition in Paramoecium:
- Paramoecium has a definite shape and takes in food at a specific location.
- Food is directed to this location by the movement of cilia that cover the cell's surface.
Q3: Why is it advisable to breathe through nose? (2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Breathing through the nose is advisable for several reasons:
- The inner lining of the nose contains fine hairs and mucus glands that filter incoming air, trapping germs and dust.
- This process helps to warm and humidify the air before it reaches the lungs.
- Breathing through the nose also promotes better oxygen absorption in the body.
Q4: Define transpiration. How does transpiration help in upward movement of water from roots to leaves? (2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Transpiration is the process through which water vapour is lost from the aerial parts of a plant, primarily via the stomata in the leaves.
This process plays a crucial role in the upward movement of water from the roots to the leaves:
- As water evaporates from the leaf cells, it creates a suction force.
- This suction pulls water from the xylem cells in the roots.
- Transpiration helps in the absorption of water and minerals, facilitating their movement to the leaves.
- It also aids in regulating the plant's temperature.
During the day, when the stomata are open, the transpiration pull is the main driving force for water movement in the xylem.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Previous Year Questions - Life Processes
| 1. What are the main life processes in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How do plants perform photosynthesis as part of their life processes? |  |
| 3. What is the role of respiration in living organisms? |  |
| 4. Why is excretion important for living organisms? |  |
| 5. How do reproductive processes differ between plants and animals? |  |

















