Class 10 Social Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term II (2021-22) - 5 | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-X |

|
| Time: 120 |

|
| Minutes |

|
| M.M: 40 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
| Section - E |

|
Class-X
Time: 120
Minutes
M.M: 40
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
- This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A: Question no. 1 to 5 are very Short Answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are Short Answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
- Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are long Answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
- Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section - A
Q.1. Describe any two main features of the ‘Salt March’.
(i) On 11th March, 1930, Mahatma Gandhi started his famous 'Salt March' accompanied by 78 of his trusted volunteers.
(ii) He ceremonially violated the salt law by manufacturing salt by boiling sea water. This marked the beginning of Civil Disobedience Movement.
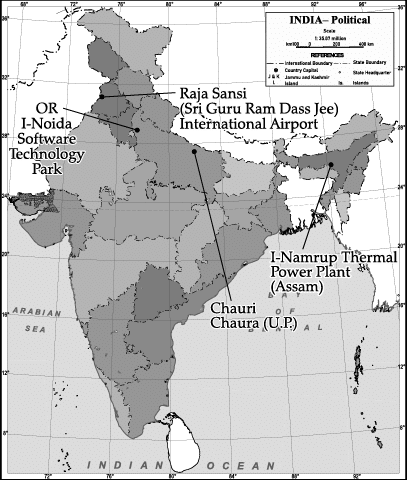
Q.2. What are Software Technology Parks? State any two points of significance of Information Technology industry in India?
Software Technology Park: Software Technology parks provide single window service and high data communication facility to software experts.
Significance of IT industry:
(i) A major impact of this industry has been an employment generation. Up to 31st March, 2005, the IT industry employed over one million persons.
(ii) It is encouraging to know that 30 per cent of the people employed in this sector are Women.
Q.3. Suggest any two effective measures to reform Political Parties.
Effective measures to reform Political Parties are:
(i) A law should be made to regulate the internal affairs of Political Parties.
(ii) It should be made compulsory for political parties to maintain a register of its members.
(iii) It should be made mandatory for political parties to give a minimum number of tickets, about 1/3rd to its women candidates.
(iv) There should be a quota for women in the decision making bodies of the Party.
Q.4. Why do banks or lenders demand collateral against loans?
Collateral is demanded by the banks or lenders before granting a loan as it is an asset that is owned by the borrower and it can be used as a guarantee to the banks until the loan is repaid. The banks can sell the collateral in case the borrower is unable to pay off his loan.
Q.5. Read the data in the chart given below and answer the questions that follow:
(5.1) Challenges faced by the jute industry are:
(i) Stiff competition in the international market from synthetic substitutes.
(ii) To stimulate demand the products need to be diversified.
(iii) The cost of production is very high.
(5.2) Objective of National Jute Policy:
(i) Increasing productivity.
(ii) Improving quality.
(iii) Ensuring good prices to the jute farmers.
(iv) Enhancing the yield per hectare.
Section - B
Q.6. Assess any three advantages of Globalization.
The advantages of Globalization are as follows:
(i) Under the Globalization process, goods and services along with capital, resources, and technology can move freely from one nation to another.
(ii) It has increased the movement of people between countries. People usually move from one country to another in search of better income, better jobs , or better education. Earlier the movement of people between countries was less due to various restrictions.
(iii) Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the Globalization process. For instance, advancement in transportation technology has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs. Container services have led to a huge reduction in port handling costs. The cost of air transport has fallen which has enabled much greater volumes of goods being transported by airlines.
Q.7. “Some people think that democracy produces a less effective government." Analyse the statement.
OR
Explain any three functions of opposition Political Parties.
It is true some people think that democracy produces a less effective government because:
(i) Non-Democratic rulers do not have to bother about deliberation in assemblies or worry about majorities and public opinion.
(ii) They can be very quick and efficient in decision- making and implementation.
(iii) But democracy is based on the idea of deliberation and negotiation. So, some delay is bound to take place.
(iv) Most democracies fall short of elections that provide a fair chance to everyone.
(v) Democratic governments do not have a very good record when it comes to sharing information with citizens.
(vi) Democracy often frustrate the needs of the people and often ignore the demands of a majority of their population.
OR
Functions of opposition Political Parties are:
(i) Those parties that lose in the elections play the role of opposition to the parties in power.
(ii) Criticizing the government for its failures or wrong policies.
(iii) Opposition parties mobilize opposition to the government.
(iv) Shape public opinion.
Q.8. Why did merchants moved to the countryside Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries? Explain.
Merchants moved to the countryside Europe because:
(i) Expansion of world trade and the acquisition of colonies.
(ii) Powerful urban craft and trade guilds did not allow expansion of production in towns.
(iii) Producers regulated production, competition, prices.
(iv) Rulers also granted different guilds the monopoly right to produce and trade in specific products.
Section - C
Q.9. Why can’t Modern Democracies exist without Political Parties? Explain any five reasons.
Modern Democracies cannot exist without Political Parties because:
(i) Without political parties, democracies cannot exist.
(ii) If we do not have political parties, in such a situation every candidate in elections will be independent.
(iii) No one will be able to make any promises to the people about any major policy changes.
(iv) The government may be formed but its utility will remain uncertain.
(v) Elected representatives will be accountable to their constituency for what they do in their locality. But no one will be responsible for how the country will run.
(vi) The role of an opposition party in a democracy necessitates the existence of political parties.
(vii) As societies become large and complex, they also need some agencies to gather different views on various issues and to present these to the government.
Q.10. Explain any two features each of formal sector loans and informal sector loans.
OR
Technology has stimulated the Globalisation process.” Support the statement with examples.
Formal Sector Loans include loans from banks and cooperatives.
Features of formal sector loans are:
(i) Formal sectors provide cheap and affordable loans and their rate of interest is monitored by Reserve Bank of India.
(ii) Formal sector strictly follows the terms of credit, which include interest rate, collateral, documentation and the mode of repayment.
Informal Sector Loan include loans from moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends, etc.
Features of informal sector loans are:
(i) Their credit activities are not governed by any organisation, therefore they charge a higher rate of interest.
(ii) Informal sector loan providers know the borrowers personally, and hence they provide loans on easy terms without collateral and documentation.
OR
Rapid improvement in technology has stimulated the globalisation process:
(i) Transportation technology has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
(ii) There are even more remarkable developments in information and communication technology.
(iii) Telecommunication facilities are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas.
(iv) Through the internet, one can obtain and share information on almost anything. It also allows sending e-mail and talking across the world at negligible costs.
(v) For example, a news magazine published for London readers is to be designed and printed in Delhi. The text of the magazine is sent through the internet to the Delhi office. The designers in the Delhi office get orders on how to design the magazine from the office in London using telecommunication facilities. The designing is done on a computer. After printing, the magazines are sent by air to London.
Even the payment of money for designing and printing from a bank in London to a bank in Delhi is done instantly through the internet.
Section - D
Q.11. Read the given text and answer the following questions:
A range of products could be produced only with hand labour. Machines were oriented to produce uniforms, standardised goods with intricate designs and specific shapes. In mid-nineteenth century Britain, for instance, 500 varieties of hammers were produced along with 45 kinds of axes. These required human skill and not Mechanical Technology.
In Victorian Britain, the upper classes – the Aristocrats and the Bourgeoisie – preferred things produced by hand. Handmade products came to symbolise refinement and class. They were better finished, individually produced and carefully designed. Machine made goods were for export to the Colonies.
In countries with labour shortage, industrialists were keen on using mechanical power so that the need for human labour can be minimized. This was the case in nineteenth-century America. Britain, however, had no problem hiring human hands.
(11.1) Which were standardised products produced for a mass market?
(11.2) Who were considered as the upper classes in Victorian Britain?
(11.3) Why were homemade products popular among upper classes?
(11.1) Uniforms.
(11.2) Aristocrats and bourgeoisie were considered as the upper classes.
(11.3) In Victorian Britain, the upper classes preferred things produced by hand because handmade products came to symbolise refinement and class. They were better finished, individually produced and carefully designed.
Q.12. Read the given text and answer the following questions:
Every litre of waste water discharged by our industry pollutes eight times the quantity of fresh water. How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced? Some suggestions are: Minimizing the use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages. Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements. Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds. Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases.
Primary treatment by mechanical means: It involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation. Secondary treatment by biological process. Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of waste water. Overdrawing of groundwater reserves by industry where there is a threat to groundwater resources also needs to be regulated legally. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise. Noise absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and earphones.
The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with environmental concerns.
(12.1) Treatment from industrial effluents can be done in how many stages?
(12.2) What could be done to reduce pollution of machinery and equipment?
(12.3) How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced?
(12.1) Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases- Primary, Secondary and Tertiary.
(12.2) In order to reduce pollution of machinery and equipment generators fitted with silencers can be used.
(12.3) (i) Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
(ii) Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds. Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases.
(iii) Primary treatment by mechanical means: It involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation.
(iv) Secondary treatment by biological process. Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of waste water.
Section - E
Q.13. (13.1) On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it.
(A) The place where Non-Cooperation Movement was called off due to violence.
(13.2) On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(I) Namrup Thermal Plant
OR
Noida Software Technology Park
(II) Raja Sansi (Sri Guru Ram Dass Jee) International Airport
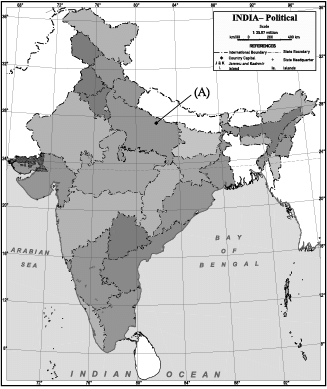
(13.1) (A) Chauri Chaura (UP)
(13.2)
|
88 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|