Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Nutrition in Animals
Q1. Write about pseudopodia.
Ans: Pseudopodia are fascinating features found in certain single-celled organisms, such as Amoeba. The term 'pseudopodia' directly translates to 'false feet', and they certainly live up to their name.
- These structures are not permanent, but rather, they are temporary projections that an amoeba can create for itself out of its own body whenever they are required.
- The primary functions of these pseudopodia are to aid in the amoeba's movement and to assist in the capture and ingestion of its food.
- These 'false feet' reach out and envelop the food particles, pulling them into the amoeba's body for digestion, which is an amazing adaptation for survival in its microscopic world.
Q2. Name some of the components of food.
Ans: Food, which is essential for our survival and well-being, is made up of various important components.
- These include carbohydrates, which are the main source of energy for our bodies. Proteins are another vital component, which are essential for growth and repair of body tissues.
- Minerals and vitamins are needed in smaller amounts but are crucial for various bodily functions. Fats, although often seen negatively, are also necessary as they provide energy and help absorb certain vitamins.
- Water is another key component, making up about 60% of our body and playing a central role in many bodily functions. Lastly, roughage or dietary fibre is necessary for maintaining a healthy digestive system.
Q3. Write the names of various digestive organs of the body.
Ans: The process of digestioninvolves several organs, each with a specific role in breaking down food into nutrients. The main digestive organs include:
- Buccal cavity (mouth): Food is mechanically broken down by teeth and chemically by saliva.
- Oesophagus: Transports food to the stomach through a process called peristalsis.
- Stomach: Further breaks down food using stomach acid and digestive juices.
- Small intestine: Completes digestion and absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream.
- Large intestine: Absorbs water from indigestible food and forms waste.
- Rectum: Stores faeces until they are expelled.
- Anus: The final part of the digestive tract where waste is excreted.
These organs work together to ensure that food is properly digested and nutrients are absorbed, while waste is efficiently expelled from the body.
Q4. Explain the mode of feeding of starfish.
Ans:
The starfish has a unique method of feeding, which is both fascinating and effective. Here’s how it works:
- Starfish primarily prey on animals with hard shells, such as clams and oysters.
- Using its strong and flexible arms, the starfish pries open the shell of its prey.
- Once the shell is open, the starfish extends its stomach out of its body and into the shell.
- The stomach envelops the soft-bodied animal inside and begins the process of digestion.
- After digestion, the stomach retracts back into the starfish's body, leaving only the empty shell behind.
This feeding method showcases the remarkable adaptability of life in the sea.
Q5. Write the functions of different types of teeth in human beings.
Ans:
- Incisors: These teeth are designed for cutting and biting food.
- Canines: They are used for piercing and tearing food.
- Premolars: These teeth assist in chewing and grinding food.
- Molars: Similar to premolars, they also help in chewing and grinding food.
Q6. Explain rumination.
Ans: The process of rumination occurs in certain animals, known as ruminants, such as cows and deer. Here’s how it works:
- These animals quickly swallow grass and store it in a part of their stomach called the rumen.
- In the rumen, the food is partially digested and forms a substance known as cud.
- Later, the cud is regurgitated back into the mouth in small lumps.
- The animal then chews the cud thoroughly before swallowing it again.
This unique digestive process allows ruminants to efficiently break down tough plant materials, such as cellulose, which many other animals, including humans, cannot digest.
Q7. Define tongue. What are its functions?
Ans: The fleshy muscular organ attached at back to the floor of the buccal cavity is called tongue. It is free at front and can move in all directions.
The functions of tongue are:
- It mixes saliva with food.
- It helps in swallowing the food.
- It helps in identifying the various tastes of different food materials, as it has various taste buds which help in detecting them.
Q8. Write about Amoeba.
Ans: Amoeba is a fascinating creature. It can be described as a small, microscopic, single-celled organism that is typically found in the water of ponds.
- This intriguing organism is characterized by a cell membrane, a dense and round nucleus, and numerous small, bubble-like vacuoles which are located within its cytoplasm.
- One of the most fascinating characteristics of an Amoeba is its ability to constantly change both its shape and position. This trait makes it an organism of great interest in the field of biology.
Q9. Explain digestion of food in mouth.
Ans: The digestion of food begins in the mouth, specifically in the buccal cavity.
- The food enters this cavity through the mouth, where it is subsequently chewed by the teeth and mixed with saliva with the assistance of the tongue.
- This saliva contains an enzyme known as ptyalin, which is also referred to as salivary amylase. This enzyme is responsible for converting complex carbohydrates such as starch into sugars.
- The saliva also serves to moisten the food and shapes it into a round, swallowable mass known as a bolus.
Q10. Why the large intestine is shorter and wider than small intestine?
Ans:
- The large intestine is shorter and wider than the small intestine because it has a specific role in the digestive system.
- Its main function is to absorb water from undigested food, which requires a design that is shorter and wider.
- In contrast, the small intestine is longer and narrower, as it is where most digestion and nutrient absorption occur.
- This structure allows for a greater surface area to effectively absorb nutrients.
Q11. Define dental plaque. What harm can it cause? How can the formation of plaque be prevented?
Ans: If teeth are not cleaned regularly and properly they get covered with a sticky, yellowish layer of food particles and bacteria. This is called ‘dental plaque’.
Because plaque entirely covers the teeth by its layer, the alkaline saliva cannot reach their surface to neutralise the acid formed by bacteria. Hence, tooth decay is caused. Tooth decay can be prevented by brushing and cleaning the teeth as well as mouth properly and regularly.
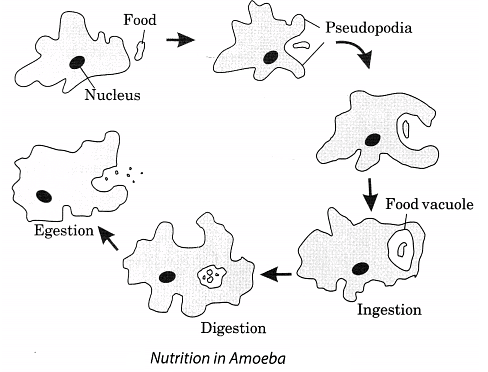
Q12. Explain feeding and digestion in Amoeba with a labelled diagram.
Ans: Amoeba is a microscopic, single-celled organism that feeds on tiny organisms. Its feeding and digestion process involves the following steps:
- Detection of Food: When Amoeba senses food, it extends finger-like projections called pseudopodia around the food particle.
- Ingestion: The pseudopodia engulf the food, trapping it in a food vacuole.
- Digestion: Digestive juices are secreted into the food vacuole, breaking down the food into simpler substances.
- Absorption: The digested nutrients are absorbed into the cell for growth and energy.
- Egestion: Any undigested food is expelled from the cell through the vacuole.
The following diagram illustrates the process:
Q13. What is diarrhoea? How is it caused? How can it be prevented?
Ans: Diarrhoea is a condition characterised by frequent and watery bowel movements. It can be caused by:
- Infections
- Food poisoning
- Indigestion
This condition can lead to severe dehydration due to the excessive loss of water and salts from the body, which can be fatal if not treated. To prevent diarrhoea, it is important to:
- Drink plenty of boiled and cooled water
- Add a pinch of salt and sugar to the water to create an Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS)
Q14. Explain the process of nutrition in human beings from ingestion to egestion.
Ans:
(i) Ingestion: It is the process of taking food into the mouth; i.e., starting point of the alimentary canal.
(ii) Digestion: Digestion is the process of breaking of ingested food into simpler substances. Digestion occurs through two processes, i.e., mechanical (chewing, grinding, mixing, churning) and chemical (enzymes, bile, acid). Mechanical processes helps in breaking the large food particles into smaller ones and mixing them well with the chemicals secreted by alimentary canal.
Digestion of starch starts at mouth with the action of salivary amylase. Digestion of protein starts in stomach with the help of enzyme pepsin and digestion of all the three components of food, viz., carbohydrate, protein and fat is completed in the small intestine.
(iii) Absorption: Digested food is absorbed into the blood through finger-like structures, called villi, present in the small intestine.
(iv) Assimilation: It is the process where absorbed substances are transported to different organs of the body via blood vessels to build complex substances like protein, enzyme, etc.
(v) Egestion: The process of elimination of undigested food through anus is called egestion.
Q15. Explain human digestive system with a labelled diagram.
Ans: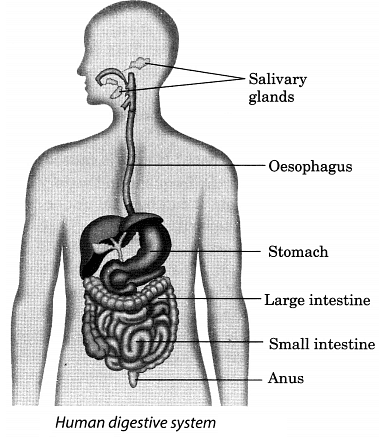 The digestive system in humans consists of an alimentary canal and digestive glands which help in digestion. Different parts of alimentary canal are:
The digestive system in humans consists of an alimentary canal and digestive glands which help in digestion. Different parts of alimentary canal are:
- Mouth: Digestion starts here. Teeth break food into small pieces, while saliva begins starch digestion and softens food into a pulp. The tongue mixes food with saliva, forming a bolus.
- Oesophagus: This muscular tube transports food from the mouth to the stomach through coordinated contractions.
- Stomach: A muscular bag that secretes digestive juices. Hydrochloric acid kills bacteria, and the enzyme pepsin breaks down proteins into amino acids. Food turns into a semi-fluid mixture called chyme.
- Small intestine: Here, bile from the liver and pancreatic juices aid in digestion. Bile emulsifies fats, while pancreatic juice digests starch and proteins. Intestinal juices complete digestion, and tiny finger-like structures called villi absorb nutrients into the bloodstream.
- Large intestine: This section absorbs water and some nutrients from undigested food. The remaining waste is expelled as faeces through the anus.
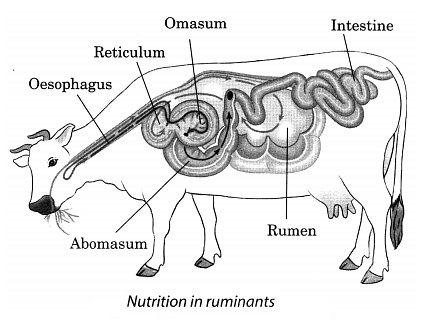
Q16. Write a short note on nutrition in ruminants.
Ans: Nutrition in Ruminantsis a specialised process that allows these animals to efficiently digest fibrous plant material. Here are the key points:
- Ruminants include animals like cows, sheep, and deer, which have a unique digestive system.
- They possess a specialised stomach with four compartments: the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum.
- Food is initially swallowed and stored in the rumen, where it is mixed with bacteria that help break down cellulose.
- After initial digestion, the food, known as cud, is regurgitated and chewed again to aid further digestion.
- This process, called rumination, allows ruminants to extract maximum nutrients from their plant-based diet.
- Ruminants can digest cellulose, a carbohydrate that many animals, including humans, cannot.
- They also have a large caecum that aids in the fermentation of undigested food.
This unique digestive process enables ruminants to thrive on a diet primarily composed of grass and other fibrous plants.
Q17. With the help of labelled diagram show the gradual decay of tooth.
Ans: Sweets and Tooth Decay The tooth is covered by white, hard outer covering of tooth called Enamel enamel below which dentine is present. It is similar to bone which Pulp cavity (with nerves and blood vessels) protects the pulp cavity having nerves and blood vessels. Bacteria are Gum present in our mouth but they are not harmful to us. However, if we do not clean our teeth and mouth after eating, many harmful bacteria also begin to live and grow in it. These bacteria breakdown the sugars present from the leftover food and release acids. The acids gradually damage the tooth. This is called tooth decay.
Therefore, tooth decay is defined as the process of rotting of tooth and formation of cavity or holes in it which leads to the toothache.
When the holes or cavity reaches to the pulp cavity, it causes pain. If these cavities are not treated on time it causes severe toothache and may result in tooth loss.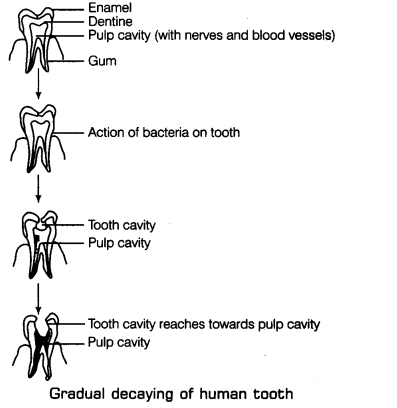
Tooth decay can be prevented by adapting following measures.
(i) One should rinse and clean its teeth thoroughly after every Pulp cavity meal.
(ii) We should clean our teeth with the help of datun or brush Gradual decaying of human tooth and toothpaste, twice a day.
(iii) We should use dental floss which is a special strong thread. It is moved between two teeth to take out trapped food particles.
(iv) Dirty fingers or unwashed objects must be avoided to put in the mouth.
(v) We should avoid the use of sweets, chocolates, toffees, ice-cream, etc. Much use of cold drink should also be avoided.”
Q18. Name the various components of food and their simpler forms.
Ans: The various components of food and their simpler forms are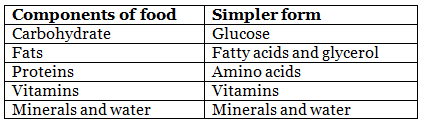
Q19. Discuss the various associated glands of digestive system and their role in digestion.
Ans: The digestive system includes several important glands that aid in digestion:
- Salivary Glands: These glands begin the digestion of starch in the mouth by producing saliva.
- Liver: The liver secretes bile, which is essential for the digestion of fats.
- Pancreas: This gland produces pancreatic juices that break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into simpler compounds.
Additionally, the stomach and small intestine also secrete digestive juices that further assist in the breakdown of food.
Q20. List the preventive measures that one should adopt for avoiding tooth decay.
Ans: Sweets and Tooth Decay The tooth is covered by white, hard outer covering of tooth called Enamel enamel below which dentine is present. It is similar to bone which Pulp cavity (with nerves and blood vessels) protects the pulp cavity having nerves and blood vessels. Bacteria are Gum present in our mouth but they are not harmful to us. However, if we do not clean our teeth and mouth after eating, many harmful bacteria also begin to live and grow in it. These bacteria breakdown the sugars present from the leftover food and release acids. The acids gradually damage the tooth. This is called tooth decay.
Therefore, tooth decay is defined as the process of rotting of tooth and formation of cavity or holes in it which leads to the toothache.
When the holes or cavity reaches to the pulp cavity, it causes pain. If these cavities are not treated on time it causes severe toothache and may result in tooth loss.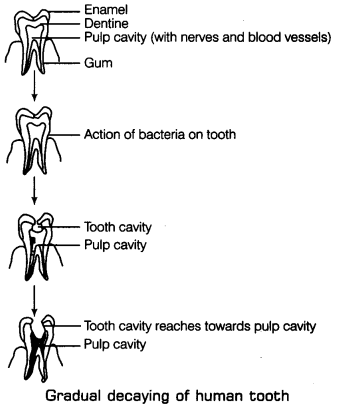
Tooth decay can be prevented by adapting following measures.
(i) One should rinse and clean its teeth thoroughly after every Pulp cavity meal.
(ii) We should clean our teeth with the help of datun or brush Gradual decaying of human tooth and toothpaste, twice a day.
(iii) We should use dental floss which is a special strong thread. It is moved between two teeth to take out trapped food particles.
(iv) Dirty fingers or unwashed objects must be avoided to put in the mouth.
(v) We should avoid the use of sweets, chocolates, toffees, ice-cream, etc. Much use of cold drink should also be avoided.”
Q21. Write the difference between milk teeth and permanent teeth.
Ans: The difference between milk teeth and permanent teeth are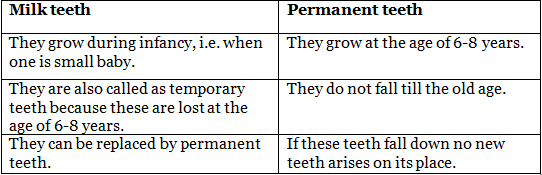
Q22. Label the given figure as directed below in A to D and give the name of each type of teeth.
(a) The cutting and biting teeth as A
(b) The piercing and tearing teeth as B
(c) The grinding and chewing teeth as C
(d) The grinding teeth present only in adult as D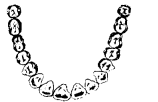
Ans: 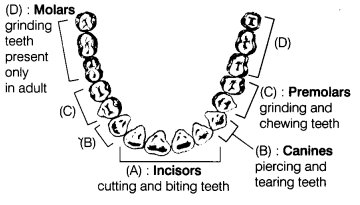
Q23. Define oral rehydration solution and when it is given to the patient? How can you prepare ORS at home?
Ans: Oral rehydration solution is the solution of sugar and salt in a particular ratio in the clean water.
- When a person passes out watery stools frequently, the disease is called diarrhoea. In this condition there is a loss of water and salt from the body of a person.
- This is called dehydration which may be fatal if not cured at proper time. In order to prevent dehydration, the person or patient should be given ORS. ORS makes up the loss of water and salts in the body and sugar provides energy which helps in the recovery of disease. It should be given to a patient suffering from diarrhoea at a regular interval.
- At home the ORS can be prepared by dissolving a teaspoonful of sugar and pinch of salt in a glass of clean water. The water used for preparing ORS should be first boiled and then cooled so that all the microorganisms or harmful bacteria may be killed.
Q24. Explain how the digestion of cellulose occurs in grass eating animals.
Ans: Digestion in Grass-Eating Animals
- Grass-eating animals, like cows and buffaloes, consume grass quickly.
- The grass is stored in a stomach compartment called the rumen, where it is not fully chewed.
- The rumen contains bacteria that help break down cellulose through fermentation.
- This partially digested grass is known as cud.
- The cud is brought back to the mouth in small lumps for further chewing, a process called rumination.
- After thorough chewing, the cud is swallowed again.
- This time, it moves to other stomach compartments and then into the small intestine for complete digestion and absorption.
- Humans and other carnivores lack the necessary bacteria to digest cellulose, making it indigestible for them.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Nutrition in Animals
| 1. What are the main types of nutrition found in animals? |  |
| 2. How do herbivores and carnivores differ in their digestive systems? |  |
| 3. What role do enzymes play in animal nutrition? |  |
| 4. Why is water important in animal nutrition? |  |
| 5. How do animals adapt their feeding habits to their environments? |  |
















