Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 8 > Short & Long Answer Question - Human Resources
Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Resources and Development
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. In what respects do different human beings differ?
Ans. Human beings vary in age, gender, education, ethnicity, culture, physical abilities, and mental strengths. These differences contribute to unique perspectives, skills, and experiences that shape individual identities and interactions within society.
Ans. Human beings vary in age, gender, education, ethnicity, culture, physical abilities, and mental strengths. These differences contribute to unique perspectives, skills, and experiences that shape individual identities and interactions within society.
Q2. With the help of figures, describe how the population varies across continents.
Ans. The global population distribution across continents is as follows: Asia holds about 61%, Europe 12%, Africa 13%, Central/South America 8%, North America 5%, and Oceania 1% of the total population. These figures illustrate the varying concentration of people across different continents.
Q3. If 600 people live in your colony, and the area of your colony is 2 sq km, what is the population density of your colony?
Ans. In a 2 sq km area with 600 people, the population density is calculated by dividing the population by the area. Thus, the density is 300 people per sq km, as there are around 300 individuals residing within every 1 sq km of the colony.
Q4. Compare the population density of the world with that of India.
Ans. Globally, the population density is approximately 45 people per sq km. In contrast, India's population density is considerably higher, exceeding 320 people per sq km. This highlights the significantly greater concentration of people in India compared to the average density across the world.

Q5. How does climate affect the population distribution of an area?
Answer. Climate strongly influences population distribution. Moderate climates are more appealing for habitation, leading to higher population densities. Harsh climates, whether extremely cold or hot, tend to discourage settlement. Consequently, areas with milder weather patterns attract more inhabitants, resulting in greater population concentration.
Q6. What is life expectancy?
Ans. Life expectancy denotes the projected average lifespan of an individual, grounded in statistical data. It represents the anticipated number of years a person is likely to live, serving as a valuable indicator of the overall health and well-being of a population.
Q7. What is the general trend of migrations from one country to another? Why is it so?
Ans. Migration often involves movement from less developed nations to more developed ones. This pattern is driven by the pursuit of improved employment prospects, higher standards of living, and enhanced amenities in the destination country. Individuals seek better opportunities and enhanced quality of life, prompting them to migrate from areas with limited resources and opportunities to regions offering greater socio-economic advantages.
Q8. What is an age-sex pyramid?
Ans. An age-sex pyramid is a graphical representation illustrating the distribution of a population based on both age and gender. It presents the number or percentage of males and females within specific age brackets, providing insights into demographic trends such as birth rates, death rates, and overall population structure.
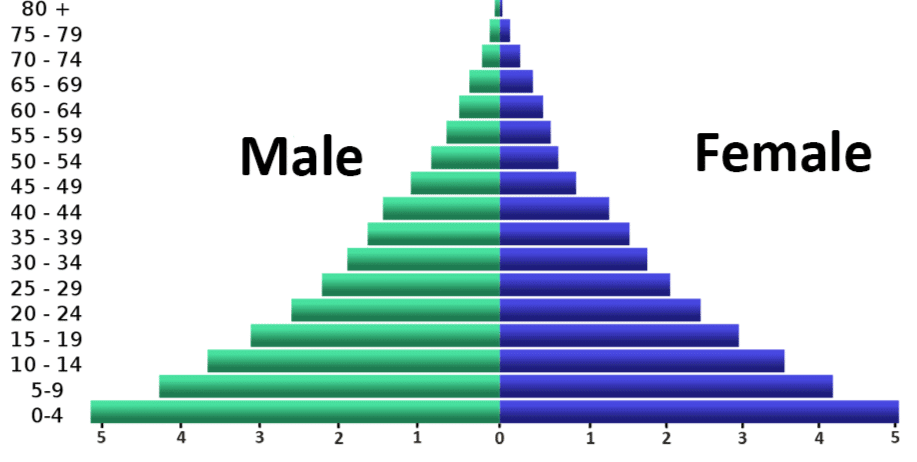
Q9. Which of these countries is more densely populated: one with a small population in a large area or one with a large population in a small area?
Ans. Among the two options, a country characterized by a large population residing in a small area is more densely populated. This scenario results in a higher concentration of individuals within a limited geographical space, leading to greater population density compared to a country with a smaller population dispersed across a larger expanse.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. Describe how various factors affect population distribution.
Ans. Various factors affecting population are:
Geographical Factors:
Ans. Various factors affecting population are:
Geographical Factors:
- Topography: Plains attract more settlement than mountains or plateaus.
- Climate: Moderate climates are preferred over extremely hot or cold regions.
- Soil: Fertile lands are chosen for agriculture, impacting population distribution.
- Water: Proximity to freshwater sources influences habitation patterns.
- Minerals: Areas with mineral resources tend to have higher population densities.
Social Factors: Quality of housing, education, and healthcare facilities contribute to population concentration.
- Culture and History: Places with cultural or historical significance often have larger populations.
- Employment: Regions with job opportunities attract more people.
Q2. Describe how the population of the world has grown in history. What has caused the population explosion?
Ans. The world population grew steadily initially. It reached a billion in the year 1820. But the next two billion were added in just a hundred and fifty years. By 1970 the population was 3 billion. In the next 29 years, i.e. by the year 1999, the population had
doubled to 6 billion. The population explosion has been mainly caused by the growth in medical facilities, which has decreased the death rate by a large extent.

Q3. What are the factors affecting the population change in a region? [Imp.]
Ans. Factors affecting the population change in a region are birth rate, death rate and migrations. Birth rate is a statistic that measures the number of live births per 1000 people. Death rate is a statistic that measures the number of deaths per 1000 people. Along with birth and death rate, another factor affecting population change is migration. Migration refers to the movement of people from one area to another. People leaving a country are called emigrants and the phenomenon is called emigration. People arriving in a country are called immigrants and the phenomenon is called immigration.
The document Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Resources and Development is a part of the Class 8 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Resources and Development
| 1. What is the role of human resources in an organization? |  |
Ans. Human resources play a crucial role in an organization as they are responsible for managing and developing the organization's workforce. They are involved in activities such as recruitment, hiring, training, and performance management. Additionally, HR professionals also handle employee relations, benefits administration, and ensure compliance with employment laws.
| 2. How can human resources contribute to employee engagement? |  |
Ans. Human resources can contribute to employee engagement by implementing various strategies. They can create a positive work environment, promote open communication, and provide opportunities for employee development and growth. HR can also organize team-building activities, recognition programs, and wellness initiatives to enhance employee engagement and satisfaction.
| 3. What are the key challenges faced by human resources professionals today? |  |
Ans. Human resources professionals face several challenges in today's dynamic work environment. Some of the key challenges include managing diversity and inclusion, adapting to technological advancements, ensuring compliance with changing employment laws, and addressing the needs and expectations of a multigenerational workforce. They also face challenges in talent acquisition and retention in a competitive job market.
| 4. How can human resources contribute to organizational culture? |  |
Ans. Human resources can contribute to organizational culture by promoting values, beliefs, and behaviors that align with the organization's mission and vision. They can develop and implement policies and procedures that reflect the desired culture. HR can also foster a culture of open communication, recognition, and collaboration, which helps in creating a positive work environment and enhancing employee engagement.
| 5. What are the benefits of investing in employee training and development? |  |
Ans. Investing in employee training and development brings numerous benefits to both the employees and the organization. It helps in enhancing employee skills, knowledge, and expertise, which leads to improved job performance and productivity. Training and development also contribute to employee satisfaction, engagement, and retention. From an organizational perspective, it leads to a skilled and competent workforce, increased innovation, and a competitive advantage in the market.
Related Searches

















