Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Question Answers - Structure of the Atom
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Draw the atomic structure of the hydrogen atom.Ans:
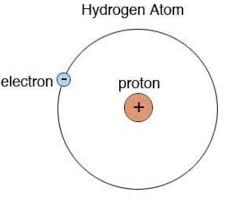
1 proton, 1 electron, 0 neutron in protium 1H1.
Q2: Why are some elements chemically inert?
Ans: Because their outermost shell is completely filled.
Q3: Why is an atom electrically neutral?
Ans: An atom is considered electrically neutral because it contains an equal number of protons and electrons.
Q4: What is the charge and mass of alpha particles?
Ans: Charge is + 2 and Mass is 4 a.m.u.
Q5: What are valence electrons?
Ans: Electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons.
Q6: An atom has atomic number 12, what is its valency and name the element?
Ans: Atomic number = 12
∴ Protons = Electrons = 12 Electrons Configuration = K, L, M -2,8,2.
∴ Valency = 2
The element is magnesium.
Q7: Find the number of neutrons in 27X13.
Ans: Mass number = 27
∴ p + n = 27 p = 13, (Atomic No. = Number of protons)
∴ 13 + n = 27
∴ n = 14
∴ Neutron =14
Q8: Where is the mass of an atom concentrated?
Ans: The Mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
Q9: Name two elements with the same number of protons and neutrons?
Ans: Carbon and Oxygen are two elements that have the same number of protons and neutrons:
- Carbon (Protons = Neutrons = 6)
- Oxygen (Protons = Neutrons = 8)
Q10: Draw the atomic structure of a sodium atom.
Ans:
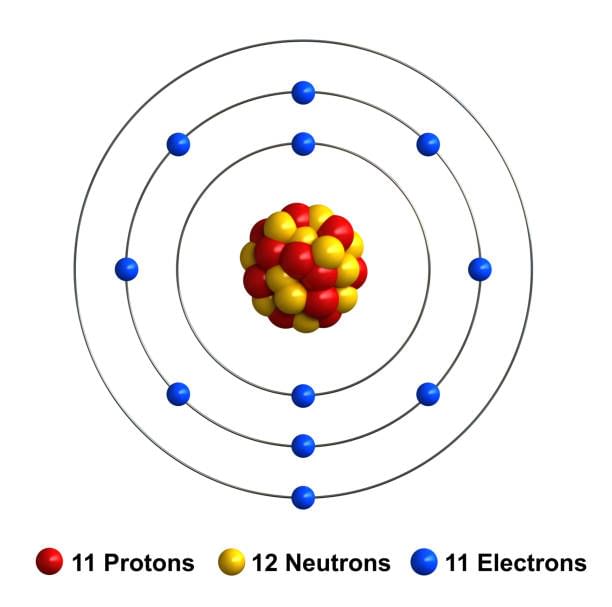
Q11: Name the isotope used for the treatment of cancer.
Ans: Isotope of cobalt.
Q12: AXZ What does this symbol represent?
Ans: X —> Symbol of element
A —> Mass number
Z —> Atomic number
Q13: Can the value of ‘Z’ be the same for two different atoms?
Ans: No, the atomic number (Z) is unique to each element. Two different atoms cannot have the same atomic number.
Q14: Can the value of A’ be the same for two different atoms?
Ans: Yes, it can be, e.g. Ca and Ar have A-40 (i.e., mass number).
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Name the scientist who discovered protons and neutrons in an atom.Ans: Protons were discovered by E. Goldstein in 1886, and neutrons were discovered by J, Chadwick in 1932.
Q2: What is the contribution of Bohr and Bury together to the structure of the atom?
Ans: Bohr and Bury gave the distribution of electrons into different atoms by giving the formula 2n2, where n = shell number.
This formula indicates:
- First shell (K-shell, n=1): 2 electrons
- Second shell (L-shell, n=2): 8 electrons
- Third shell (M-shell, n=3): 18 electrons
- Fourth shell (N-shell, n=4): 32 electrons
- Electrons fill the shells in a specific order, starting from the innermost shell.
Q3: Draw the atomic structure of (i) an atom with the same number of sub-atomic particles, (ii) an atom with the same number of electrons in L and M shells.
Ans: (i) An atom with the same number of sub-atomic particles is Helium
No. of protons = 2
No. of electrons = 2
No. of Neutrons = 2
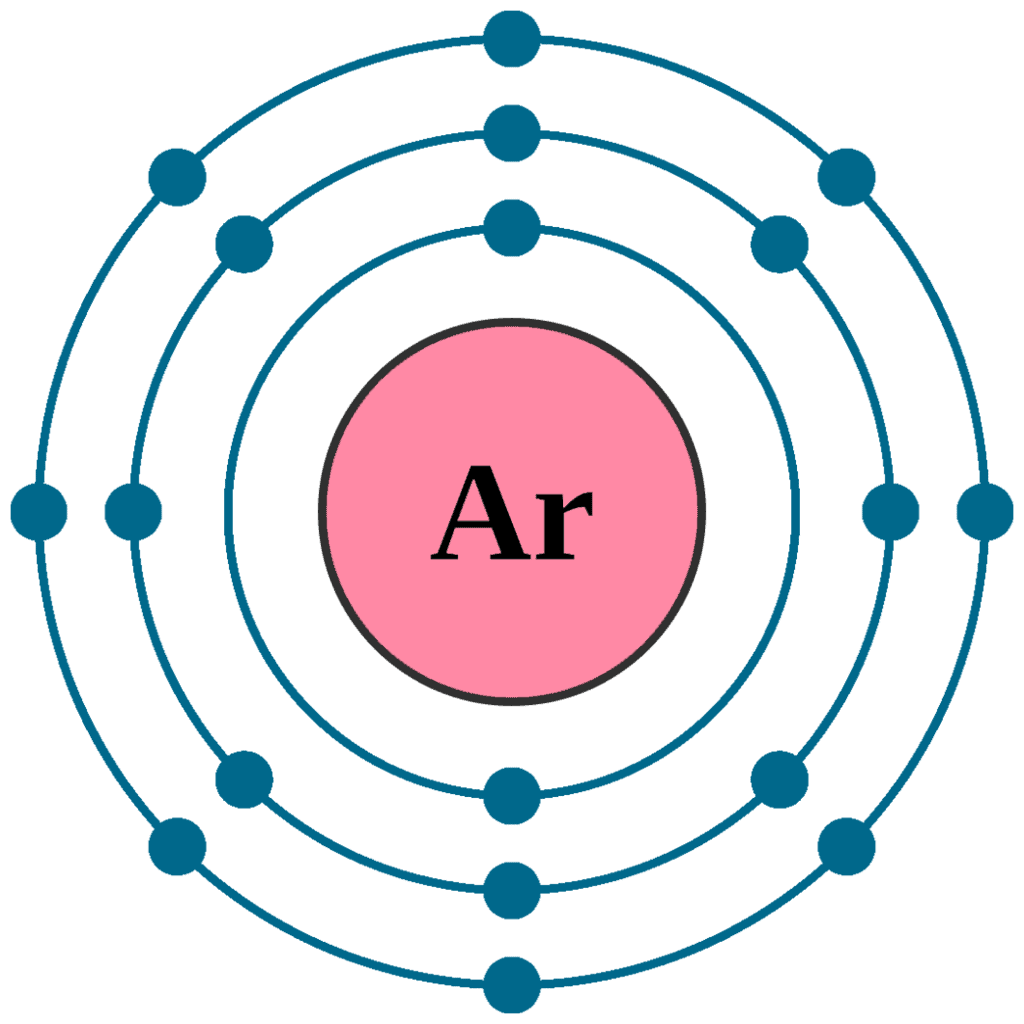
(ii) Argon is an atom with L and M shells filled —->K, L, M- 2, 8, 8
Q4: What is an octet? Why would atoms want to complete their octet?
Ans: When the outermost shell of an atom, i.e., L, M or N, is completely filled with 8 electrons in the shell, it is said to be an octet. Atoms would want to complete their octet because they want to become stable.
Q5: Find the valency of 14N 7 and 35Cl17
Ans: The atomic number of nitrogen = 7, No. of protons = 7, No. of electrons = 7
Electronic configuration = K, L =2 ,5
Valency = 3
Because it will either gain three electrons or share 3 electrons to complete its octet.
The atomic number of chlorine = 17, p = 17, e=17
Electronic configuration = K, L ,M= 2 ,8 ,7
Valency = 1
Because it will gain 1 electron to complete its octet.
Q6: Pick up the isotopes among the following and state the reason.
Ans: The isotopes are 35X 17 and 37X 17, as both the atoms show the same atomic number but a different mass number.
Q7: Pick up atoms that have the same number of neutrons from the following:
Ans:
Q8: What are nucleons? What is the name given to those atoms which have the same number of nucleons?
Ans: Protons and neutrons present in the nucleus are called nucleons. Isobaric elements have the same number of nuclei. In other words, we can say that the same mass number.(Mass number = Protons + Neutrons)
Element | Protons | Neutrons | (Protons + Neutrons) |
Argon | 18 | 22 | 40 |
Calcium | 20 | 20 | 40 |
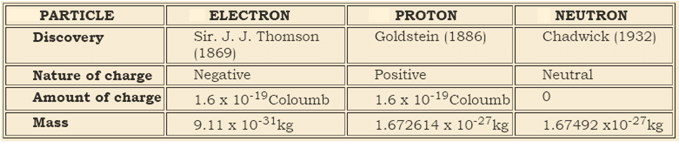
Q9: Give the difference between the three sub-atomic particles.
Ans: Three sub-atomic particles are the electron, proton and neutron
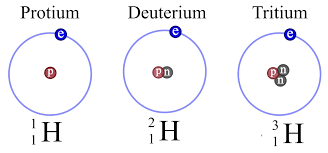
Q10. Give the names of three atomic species of hydrogen.
Ans: Three atomic species of hydrogen are: Protium, Deuterium, Tritium.
Q11: Atomic Mass exists as a whole number. Why do we write the atomic mass of chlorine as 35.5 u?
Ans: Chlorine has two isotopes, and the mass of an atom is taken as the average mass of all the naturally occurring atoms of that element.
This is obtained by knowing the percentage of each isotopic form, and then the average mass is calculated Cl = 35, its isotopic form percentage 75% and Cl = 37, its isotopic form percentage 25%.
∴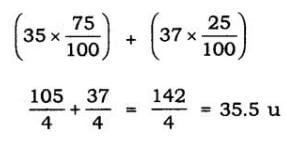
Q12: Give the difference between isotopes and isobars.
Ans:
Isotopes | Isobars |
Are atoms of the same element. | Are atoms of different elements |
Have the same atomic number | Have different atomic numbers |
Have different mass numbers | Have the same mass number |
The number of protons and electrons are same in these atoms. | The number of protons and electrons is not the same in these atoms. |
Q13: The Number of protons and electrons are same in an atom. Then why is it wrong to say that the atomic number of an atom is equal to its number of electrons?
Ans: Atomic number ≠ Number of electrons, although number of protons = number of electrons because the electron’s number can change in an atom by loss, or gain of it. But the proton’s number remains constant (as it does not take part in loss or gain).
Q14: An atom is electrically neutral, on loss or gain of electrons why does it become charged?
Ans: An atom is electrically neutral because it has an equal number of protons and electrons. However, when it loses or gains electrons, it becomes charged:
- If an atom loses electrons, it has more protons than electrons, resulting in a positive charge.
- If an atom gains electrons, it has more electrons than protons, leading to a negative charge.
Q15: In the structure of an atom, why are protons present in the centre and are not pulled outside by the electrons, as both are oppositely charged with the same unit of charge?
Ans: Protons are located at the centre of an atom, forming the nucleus, due to their significant mass. Here are the key reasons:
- Protons have a mass of approximately 1 unit, making them much heavier than electrons.
- Electrons have a negligible mass, roughly 1/1800 that of protons.
- Despite being oppositely charged, the mass of electrons is insufficient to pull protons away from the nucleus.
This structure ensures stability within the atom.
Q16: According to you, among the structures of an atom studied, which model is correct and why?
Ans: Bohr’s model of the atom is the most accurate because it effectively explains the arrangement of nucleons (protons and neutrons) at the centre, with electrons orbiting around them in specific, discrete paths.
- Electrons in these orbits do not lose energy.
- This stability allows them to remain in their respective shells.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are isotopes? State its characteristics, and give the uses of isotopes?
Answer: Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers are isotopes.
Characteristics:
(1) Physical properties of the isotopes are different, e.g. mass, density.
(2) Chemical properties of the isotopes are the same due to the same number of electrons.
Uses:
(1) Uranium isotope is used as a fuel in a nuclear reactor.
(2) Cobalt isotope is used for the treatment of cancer.
(3) Iodine isotope is used in the treatment of goitre.
Q2: Explain Rutherford’s α-particle scattering experiment and give its observation and the conclusion drawn.
Ans: Rutherford’s α-particle scattering experiment:
Fast-moving α-particles were made to fall on a thin gold foil. Particles have + 2 charge and 4u mass, and a considerable amount of energy.
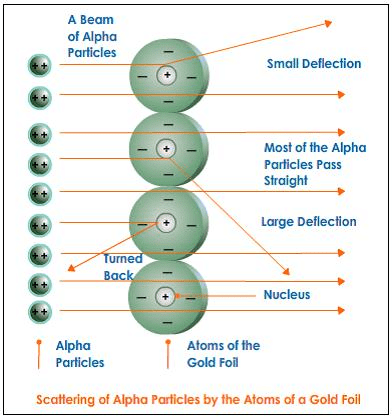
Observations:
(1) Most of the α-particles passed straight through the foil.
(2) Some of the α-particles were deflected by small angles by the foil.
(3) One out of every 12000 particles rebounded.
The conclusion from observation:
(1) Most of the space inside the foil is empty.
(2) The positive charge of the atom occupies very little space.
(3) The mass of the atom is concentrated in the centre, with all positive charge concentrated in a small volume within the atom.
Q3: Establish the relationship between atomic number, mass number, isotopes, isobars and valency of an atom.
Ans: Atomic number — Gives the number of protons (Z)
Mass number — Gives the number of protons and neutrons (A)
Isotopes — When atoms of the same element have the same number of protons (Z) but a different number of neutrons (s) such atoms are called isotopes.
Isobars — When atoms of different elements have the same mass number (A) but different atomic number (Z) such atoms are called isobars.
Valency — It is the combining capacity of an atom.
Q4: Why do Helium, Neon and Argon have zero valency?
Ans: Helium, Neon, and Argon have a zero valency because their outermost electron shells are full, making them stable and unreactive. They don't need to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
- In Helium, the outermost orbit contains two electrons, forming a stable duplet configuration and remains inert in most reactions.
- Both Neon and Argon have eight electrons in their outermost shell, resulting in a stable octet configuration, which makes them unreactive under normal conditions.
Q5: What were the drawbacks of Rutherford’s model of an atom?
Ans: The drawbacks of Rutherford's model of an atom are significant in understanding the limitations of his atomic theory. Rutherford conducted an experiment where he directed alpha particles at a thin gold foil and observed their deflection patterns. However, his model faced several challenges:
1. Stability of Electrons: Rutherford's model couldn't explain how electrons, which are charged particles, could continuously move in orbits around the nucleus without losing energy
2. Radiation Concerns: According to classical physics, any accelerating charged particle emits electromagnetic radiation. If this were the case, the electron would lose energy, spiral inward, and collapse into the nucleus, contradicting the stability of the atom.
Q6. Compare the properties of electrons, protons and neutrons.
Ans:

|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Question Answers - Structure of the Atom
| 1. What are the main components of an atom? |  |
| 2. How are the atomic number and mass number defined? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of electrons in an atom? |  |
| 4. How do isotopes differ from each other? |  |
| 5. What is the structure of the atom according to the Bohr model? |  |






















