NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Additional Study Material for NEET > Classification of Bryophyta: Liverworts, Hornworts & Mosses
Classification of Bryophyta: Liverworts, Hornworts & Mosses | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Hepaticopsida (Liver Worts) |

|
| Anthocerotopsida (Hornworts) |

|
| Bryopsida or Musci (Mosses) |

|
| Habitat of Some Important Bryophytes |

|
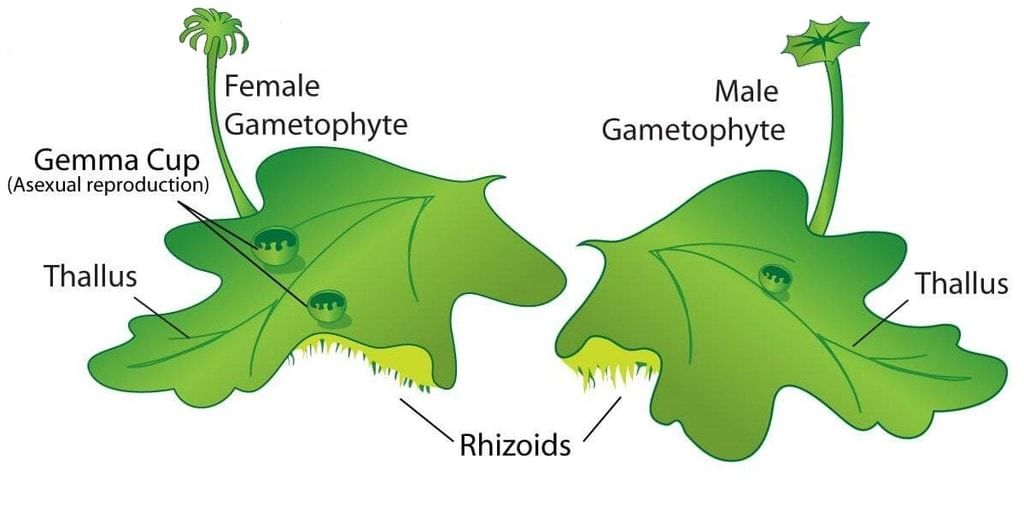
Hepaticopsida (Liver Worts)
 Hepaticopsida
Hepaticopsida
- All the bryophytes included in this class have shape like liver, so they are known as liverworts.
- Plant body of this group is like thallus. Rhizoids and scales are present on thallus. Rhizoids are unicellular and unbranched. Scales are multicellular.
- The sporophyte of Liverworts is completely dependent on gametophyte i.e. it is dependent on gametophyte for food, water and habitat.
- The sporophyte of Liverworts is made up of foot, seta and capsule. (Except Riccia sporophyte is made up of only capsule).
- In this class formation of spores and nurse cells takes place by the cells of endothecium. Cells of amphithecium form only wall of sporophyte.
Amphithecium = Wall of sporophyte
Endothecium = sporogenous cells = spore mother cells + nurse cells - Elaters are present in sporophyte of some members of liverworts. (eg. Marchantia - In Marchantia nurse cells are modified into elaters). Elaters are hygroscopic and they help in dispersal of spores.
Example: Riccia, Marchantia, Cryptothallus, Riella, Pellia, Porella.
Note : In Bryophytes, sporophyte of Riccia is the simplest.
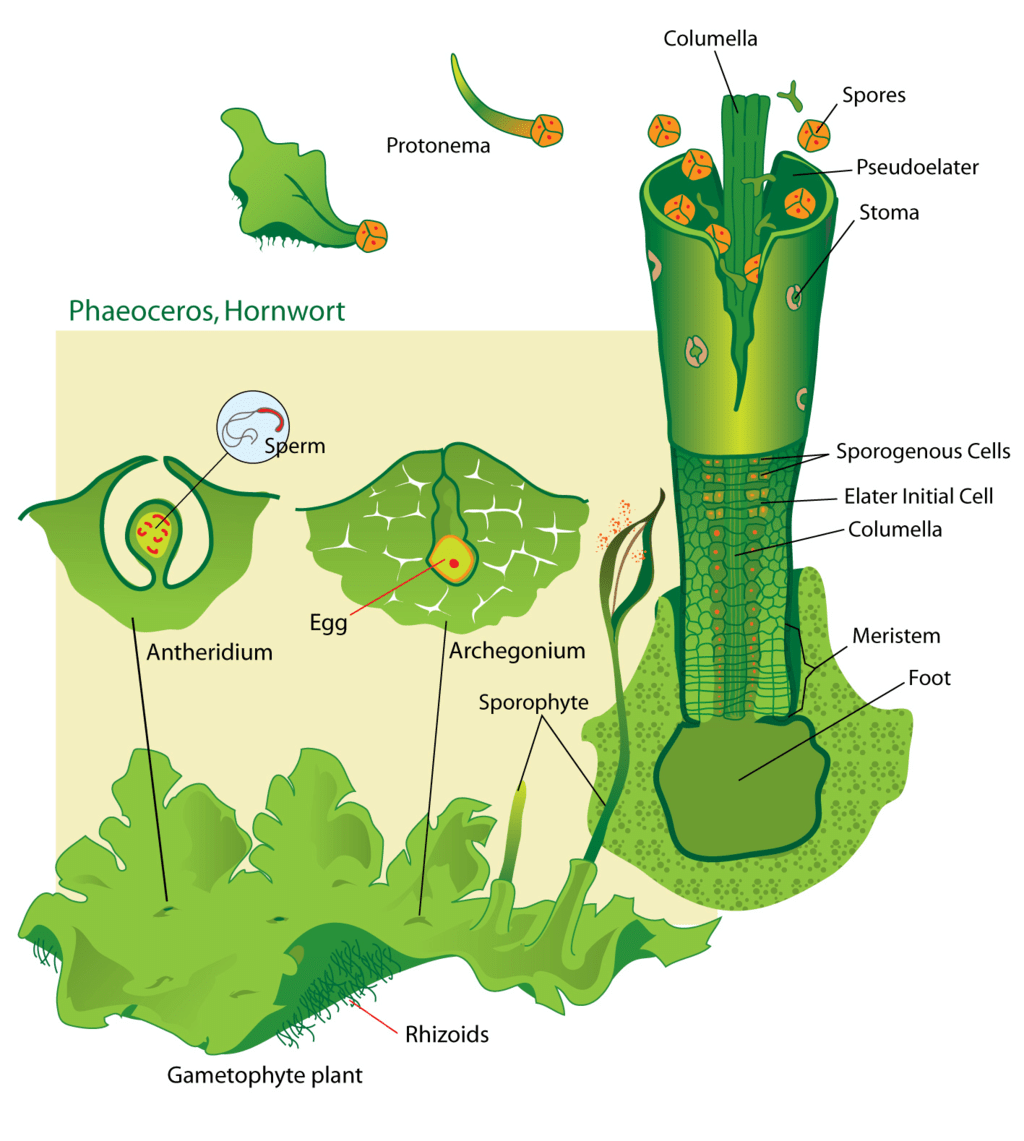
Anthocerotopsida (Hornworts)
 Anthocerotopsida
Anthocerotopsida
- The plant body of this group is also thallus like. Scales are absent but rhizoids are present on thallus. Rhizoids are unicellular and unbranched.
- The sporophyte of Hornworts is divided into foot and capsule.
- The sporophyte of Hornworts is not completely dependent on its gametophyte i.e. it is semi-parasite because its sporophyte is photosynthetic therefore it can manufacture its own food. So it does not depend on gametophyte for food, it depends only for water and habitat.
- In Hornworts, wall of sporophyte and spores are formed by cells of amphithecium. Cells of endothecium formed only elaters.
Amphithecium = Wall of sporophyte and Spores
Endothecium = Elaters - In hornworts spore forming cells and elaters forming cells are separate, so elaters are known as pseudoelaters.
Pseudoelaters are structurally and functionally similar to true elaters. - In Hornworts on the basal part of sporophyte, a special, type of meristem is present. Due to the activeness of this meristem, the sporophyte grows rapidly. It grows like the horn of animals.
Example: Notothylus, Anthoceros
Anthoceros have some Algae like characters such as:
- Archegonia is jacketless.
- In each cell of Anthoceros, only one chloroplast is present which is a character of green algae. In the cells of higher plants, many chloroplast are present.
- Pyrenoides (starch storing granules) are present in the chloroplast of Anthoceros, which is an algal character.
- Anthoceros shows ancestral characters which prove that bryophytes have originated from green algae.
Note: Due to these reasons, Anthoceros are also termed as synthetic-archegoniatae.
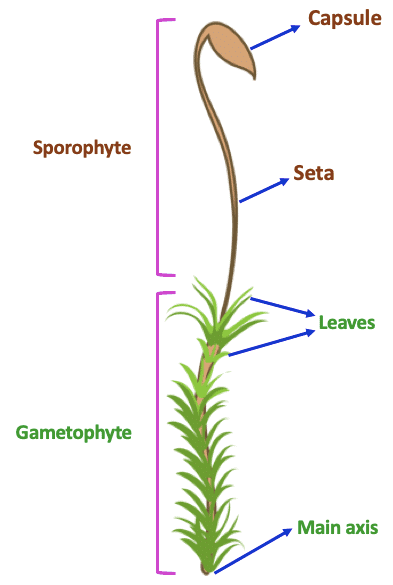
Bryopsida or Musci (Mosses)
 Bryopsida
Bryopsida
- All the Mosses are included in this class. The plant body of mosses is made up of stem, leaves and rhizoids.
- The Rhizoids present in the plants of this class are multi-cellular and branched. These rhizoids have oblique septa.
Note: The presence of leaves in gametophyte is one of the unique character of Moss. In plant kingdom not a single gametophyte has leaves.
- The sporophyte of moss in bryophyta is highly developed while the sporophyte of liverwort is the simplest. The sporophyte of moss is divided into foot, seta, capsule.
- The sporophyte of mosses is also semi-parasite like, that of Hornworts. i.e. it is photosynthetic. The sporophyte absorbs the water from gametophyte with the help of foot.
- Capsule is the fertile part of the sporophyte i.e. formation of spores takes place in it. Foot and seta are the sterile part of the sporophyte.
- Seta helps the capsule to remain in the air, due to which the dispersal of spores can take place conveniently.
- In bryopsida, cells of amphithecium form wall of sporophyte. Cells of endothecium form spores. Elaters and nurse cells are absent in bryopsida.
Amphithecium = Wall of sporophyte
Endothecium = Spores
Note :
- In Riccia, the sporophyte is made up of only capsule i.e. the whole sporophyte is fertile in it.
- During evolution there occur gradual sterilization of sporophyte i.e. gradual reduction of fertile part and gradual development of sterile part.
- Asexual reproduction in Marchantia takes place by fragmentation of thalli, or by the formation of specialised structures called gemmae (sing. gemma). Gemmae are green, multicellular, asexual buds, which develop in small receptacles called gemma cups located on the thalli. The gemmae become detached from the parental body and germinate to form new individuals.
Examples of Mosses:
- Funaria: Rope moss or Cord moss
- Andria: Granite moss
- Polytrichum: Hair cap moss
- Fontinalis: Brook moss
- Dawsonia: Australian moss - The highest bryophyte - 45 cm.
- Buxbaumia: Saprophytic moss - Photosynthesis absent.
- Sphagnum
Habitat of Some Important Bryophytes
- Some bryophytes are found in water.
Example: Riccia fluitans, Riccia abuensis, Ricciocarpus natans, Riella, Fontinalis - Some bryophytes are found in epiphytic form i.e. they grow on other plants.
Example: Dendroceros - Some bryophytes are saprophytes (Non photosynthetic)
Example: Buxbaumia and Cryptothallus.
Difference Between Bryophytes

The document Classification of Bryophyta: Liverworts, Hornworts & Mosses | Additional Study Material for NEET is a part of the NEET Course Additional Study Material for NEET.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Classification of Bryophyta: Liverworts, Hornworts & Mosses - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What are the characteristics of liverworts, hornworts, and mosses? |  |
Ans. Liverworts, hornworts, and mosses are all bryophytes, which are non-vascular plants. They share some common characteristics such as small size, lack of true roots, stems, and leaves, and dependence on water for reproduction. Liverworts have leafy or thalloid structures, hornworts have horn-shaped sporophytes, and mosses have leafy stems and capsules.
| 2. What are the major differences between liverworts, hornworts, and mosses? |  |
Ans. The major differences between liverworts, hornworts, and mosses lie in their reproductive structures. Liverworts have structures called archegonia and antheridia, which produce eggs and sperm, respectively. Hornworts have a unique elongated sporophyte structure resembling a horn, which contains sporangia. Mosses have leafy stems with capsules that contain sporangia. Additionally, liverworts and hornworts have a primitive photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll b, while mosses have chlorophyll a and b.
| 3. Where do liverworts, hornworts, and mosses commonly grow? |  |
Ans. Liverworts, hornworts, and mosses can be found in various habitats, including moist and shaded areas. They are commonly found in forests, woodlands, wetlands, and even on rocks and trees. These bryophytes are often found in areas with high humidity and abundant moisture, as they require water for reproduction and survival.
| 4. What is the ecological importance of liverworts, hornworts, and mosses? |  |
Ans. Liverworts, hornworts, and mosses play crucial roles in ecosystems. They help in soil formation and erosion control by stabilizing the soil with their roots and trapping sediments. They also provide habitats and food for various microorganisms and invertebrates. Additionally, they contribute to the water cycle by absorbing and retaining water, and they can act as indicators of air pollution levels due to their sensitivity to environmental changes.
| 5. How are liverworts, hornworts, and mosses related to the NEET exam? |  |
Ans. In the NEET exam, which is the national level medical entrance examination in India, questions related to plant diversity and classification are commonly asked. Liverworts, hornworts, and mosses are important groups of plants that are included in the syllabus for NEET. Understanding their characteristics, differences, and ecological importance is crucial for scoring well in the biology section of the NEET exam.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















