Resistors in Series & Parallel Combinations | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Combination of Resistance
A number of resistance can be connected in a circuit and any complicated combination can be, in general, reduced essentially to two different types, namely series and parallel combinations.
Resistance in Series
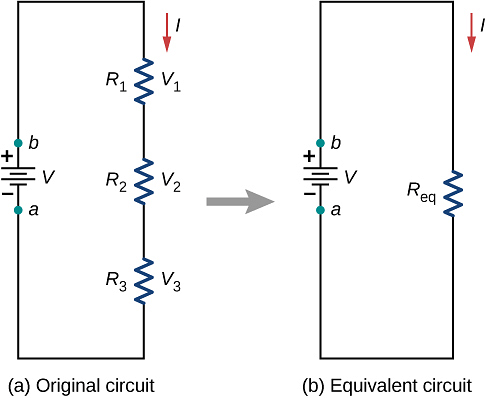
- In this combination the resistance are joined end to end. The second end of each resistance is joined to first end of the next resistance and so on. A cell is connected between the first end of first resistance and second end of last resistance. Figure shows three resistances R1, R2 and R3 connected in this way. Let V1, V2 and V3 are the potential differences across these resistances.
- In this combination current flowing through each resistance will be same and will be equal to current supplied by the battery.
- As resistances are different and current flowing through them is same, hence potential differences across them will be different. Applied potential difference will be distributed among three resistances directly in their ratio.
- As i is constant, hence V is directly proportional to R
i.e., V1 = iR1, V2 = iR2, v3 = iR3 - If the potential difference between the points A and D is V, then
V = V1 + V2 + V3 = I(R1 + R2 + R3) - If the combination of resistances between two points is replaced by a single resistance R such that there is no change in the current of the circuit in the potential difference between those two points, then the single resistance R will be equivalent to combination and V = i R i.e.,
IR = I(R1 + R2 + R3)
R = R1 + R2 + R3 - Thus in series combination of resistances, important conclusion are:
(i) Equivalent Resistance > highest individual resistance
(ii) Current supplied by source = Current in each resistance
or =
=  =
=  =
= 
(iii) The total potential difference V between points A and B is shared among the three resistances directly in their ratio
V1 : V2 : V3 = R1 : R2 : R3
Resistance in Parallel
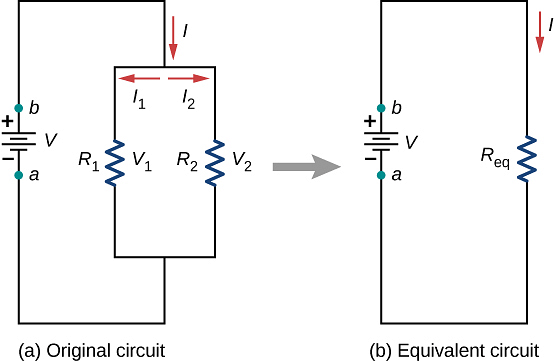
- When two or more resistance are combined in such a way that their first ends are connected to one terminal of the battery while other ends are connected to other terminal, then they are said to be connected in parallel. Figure shows three resistances R1, R2 and R3 joined in parallel between two points A and B. Suppose the current flowing from the battery is i. This current gets divided into three parts at the junction A. Let the currents in three resistance R1 , R2 and R3, are i1, i2, i3 respectively.
- Suppose potential difference between points A and B is V. Because each resistance is connected between same two points A and B, hence potential difference across each resistance will be same and will be equal to applied potential difference V.
- Since potential difference across each resistance is same, hence current approaching the junction A is divided among three resistances reciprocally in their ratio.
As V is constant, hence i µ (1/R) i.e.,

- Because i the main current which is divided into three parts i1, i2 and i3 at the junction A.
hence,
- If the equivalent resistance between the points A and B is R, then i =

Thus, or
or 
- Thus in parallel combination of resistance important conclusion are :
(i) Equivalent resistance < lowest individual resistance
(ii) Applied potential difference = Potential difference across each resistance.
or iR = i1R1 = i2R2 = i3R3
(iii) Current approaching the junction A = Current leaving the junction B and current is shared among the three resistances in the inverse ratio of resistances
i1 : i2 : i3 =
Note: (i) If two or more resistance are joined in parallel then i1R = i1R2 = i3R3............
i.e., iR = constant i.e., a low resistance joined in parallel always draws a higher current.
(ii) When two resistance R1 and R2 are joined in parallel, then
or
or
or
i.e., heat produced will be maximum in the lowest resistance.
Example1. Find current which is passing through battery.

Sol. Here potential difference across each resistor is not 30 V
Q battery has internal resistance here the concept of combination of resistors is useful.
Req = 1 1 = 2?

Example 2. Find equivalent Resistance

Sol. 
Here all the Resistance are connected between the terminals A and B. So, Modified circuit is
So Req= 

Example 3. Find the current in Resistance P if voltage supply between A and B is V volts

Sol. Req = 

I =  Modified circuit
Modified circuit 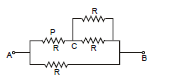
Current in  =
= 

Example 4. Find the current in 2 W resistance.
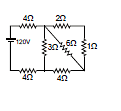
Sol. 2Ω, 1Ω in series = 3Ω
3Ω, 6Ω in parallel = 
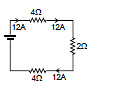
2Ω, 4Ω in series = 6Ω
6Ω, 3Ω is parallel = 2Ω
Req = 4 + 4 + 2 = 10 Ω

So current in 2 ? Resistance = 

Special Problems

We wish to determine equivalent resistance between A and B. In figure shown points (1,2) (3, 4, 5) and (6, 7) are at same potential Equivalent circuit can be redrawn as in figure shown.
The equivalent resistance of this series combination is



In the figure shown, the resistances specified are in ohms. We wish to determine the equivalent resistance between point A and D. Point B and C, E and F are the the same potential so the circuit can be redrawn as in figure shown.
Thus the equivalent resistance is 1 ?.


 In the network shown in figure shown all the resistances are equal, we wish to determine equivalent resistance between A and E. Point B and D have same potential, similarly F and H have same potential. The equivalent circuit is shown in figure shown. The equivalent resistance of network is 7R/2.
In the network shown in figure shown all the resistances are equal, we wish to determine equivalent resistance between A and E. Point B and D have same potential, similarly F and H have same potential. The equivalent circuit is shown in figure shown. The equivalent resistance of network is 7R/2.


|
97 videos|370 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Resistors in Series & Parallel Combinations - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the formula to calculate the total resistance of resistors in series? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the total resistance of resistors in parallel? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between series and parallel circuits? |  |
| 4. Can resistors be connected in both series and parallel in the same circuit? |  |
| 5. How do you calculate the total resistance of a combination circuit? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















