Complications of third stage of Labour | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Complications of Third stage of Labor
- Post partum hemorrhage
- Retained placenta
- Adherent placenta
- Inversion of uterus
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Obstetric shock
Post partum hemorrhage
Definition and Timing
- PPH refers to bleeding after delivery categorized into Primary (within 24 hours) and Secondary (24 hours to 6 weeks).
- Thresholds: ≥500 ml after vaginal delivery, ≥1000 ml after cesarean, except in anemia or concealed hemorrhage (hematocrit drop >10%).
Preventive Measures
- Active management during the third stage of delivery.
- Immediate oxytocin injection post-delivery.
- Employing the Brant-Andrews technique (control cord traction) and uterine massage.
- Addressing nutrition and anemia correction.
- Consideration of tertiary healthcare admission for anticipated PPH.
Treatment
- Immediate replacement of lost blood, initiating a 16G IV cannula, and cross-matching blood.
- Fluid resuscitation and monitoring urine output and body fluid status.
- Oxygen supplementation as needed.
- If placenta isn't delivered, use controlled cord traction and uterotonics. Verify uterine contraction post-placental delivery.
- Atonic PPH is ruled out if proper uterine contraction is observed; explore traumatic or secondary PPH.
- Traumatic PPH: Inspect the genital tract with a speculum, suture lacerations, or perform intrauterine packing if necessary.
- Secondary PPH due to retained placenta fragments: Rule out via ultrasound, potential infection, high vaginal swab for culture, start high-spectrum antibiotics, and evacuate uterus if no sepsis signs or continue antibiotics before evacuation if sepsis is suspected.
- Atonic PPH management: Employ uterotonic agents like oxytocin, ergometrine, carborprost, or misoprostol. If bleeding persists, consider various compression techniques, intrauterine packing, or surgical interventions like hysterectomy or arterial ligation.

Ruptured Uterus Management
- Severity and Impact: Ruptured uterus in labor poses serious risks to maternal health, leading to significant morbidity and mortality.
- Immediate Steps:
- Prompt resuscitation measures.
- Intravenous administration of colloids/crystalloids.
- Blood transfusion to address hemorrhage.
- Surgical Intervention:
- Laparotomy to address the rupture.
- Figure-of-eight suturing of the placental bed.
- Ligating the ovarian and uterine arteries.
- Extraction of fetus and placenta during laparotomy.
- Infection Control:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics to combat peritonitis.
- Future of the Uterus:
- Hysterectomy:
- When the patient opts against retaining the uterus.
- When the uterus is beyond repair.
- Conservative Surgery:
- Uterine repair for patients wishing to preserve the uterus for future pregnancies.
- Note: Higher risk of rupture in subsequent pregnancies.
- Hysterectomy:
Retained Placenta: Causes and Management
- Definition: Retained placenta is characterized by the failure of placental expulsion within 30 minutes after the baby's birth when the third stage of labor is actively managed.
Causes of Retained Placenta
- Impaired Uterine Contractions: Inadequate uterine contractions contribute to retention.
- Formation of Constriction Rings: Constriction rings may hinder the natural expulsion process.
- Adherent Placenta/Placenta Accreta: Conditions like placenta accreta can lead to retained placenta.
Management
- Immediate Post-Delivery (15-20 minutes):
- Assess stability and absence of bleeding.
- If conditions permit, wait up to 60 minutes.
- Maintain preparedness for intervention with compatible blood.
- Continue Oxytocin drip to facilitate placental delivery.
- After 60 Minutes or Bleeding Manifestations (20-60 minutes):
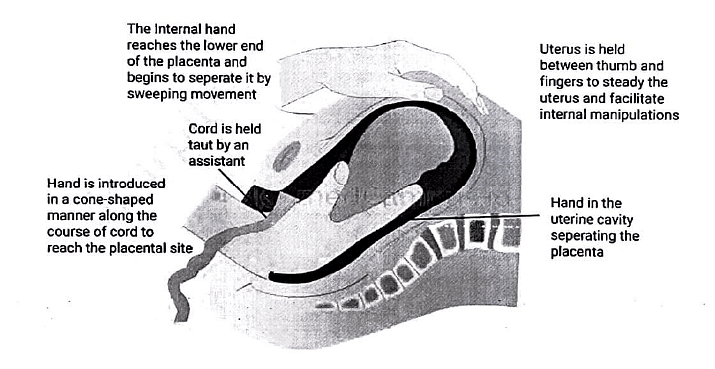
- If signs of bleeding or elapsed time demand, manually remove the placenta.
- Adherent Placenta (Placenta Accreta):
- In cases of placenta accreta, consider surgical removal of the uterus (hysterectomy).
- Hysterectomy prevents potential life-threatening blood loss associated with attempts to separate the adherent placenta.
Acute Uterine Inversion: Causes, Clinical Presentation, and Management
Types of Uterine Inversion
- Acute Inversion (Within 24 hours): Most common type.
- Subacute Inversion (24 hours to 4 weeks): Presents within 4 weeks of delivery.
- Chronic Inversion (After 4 weeks): Presents 4 weeks after delivery.
Definition: Acute uterine inversion is an obstetric emergency where the uterine fundus collapses into the endometrial cavity, turning the uterus partially or completely inside out following vaginal birth.
Risk Factors
- Nulliparity.
- Cord traction (Brandt-Andrews maneuver) and excessive fundal pressure (Crede's maneuver) during the third stage of labor.
- Difficult placental removal.
- Use of uterine muscle relaxants (e.g., magnesium sulfate).
- Fetal macrosomia.
- Uterine anomalies or tumors.
- Placenta accreta.
- Previous uterine inversion.
- Excessively short umbilical cord (<35 cm).
Progressive Degrees of Uterine Inversion
- Fundus beginning to invert.
- Fundus continues to invert but not visible outside.
- Inverted uterus visible at the introitus.
- Complete uterine inversion.
Clinical Findings
- Brisk postpartum hemorrhage.
- Round mass (inverted uterus) protruding from the cervix or vagina.
- Absent fundus during transabdominal palpation.
Diagnosis
- Clinical findings.
- Ultrasound confirmation (hyperechoic mass with central hypoechoic cavity).
Treatment
- Discontinue oxytocin.
- Administer crystalloids and blood products as needed.
- Manually reposition the uterus; if impossible:
- Administer uterine relaxants (e.g., nitroglycerine, terbutaline, or magnesium sulfate).
- If ineffective, use Halogenic anesthesia.
- Following successful repositioning, administer oxytocin to induce placental extraction and prevent reinversion.
- If manual repositioning fails:
Vaginal Method
- Acute cases: O'Sullivan's hydrostatic method.
- Chronic cases: Spinelles technique.
Abdominal Method
- Huntington procedure: Application of atraumatic clamps to round ligaments with upward traction.
- Haultain's technique: If constriction ring persists, make a longitudinal surgical cut (Haultain incision) to expose the fundus and permit reinversion.
Reinversion After Repositioning: Uterine Compression Sutures.
Complications:
- Hemorrhagic shock.
- Maternal death.
Complications of Third stage of Labour-Repeats
Q1: Enumerate the complications of 3rd stage of labour. Write in detail the management of PPH (post-partum hemorrhage) (2001).
Q2: Enumerate the causes of Postpartum Hemorrhage. How will you prevent it? Give management of a case of Postpartum Hemorrhage (2005).
Q3: Diagnosis and management of Traumatic Post-Partum Hemorrhage (PPH) (1999)
Q4: Describe the prevention and management of post-partum hemorrhage. (2010)
Q5: Define Postpartum Haemorrhage (PPH). What are the causes of PPH? How would you manage the case of PPH just after delivery? Discuss the preventive measures for control of PPH. (2017)
Q6: Describe the etiology, clinical features and management of ruptured uterus (1999)
Q7: Write short notes on how would you manage a case of retained placenta (2002)?
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Complications of third stage of Labour - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the common complications of the third stage of labor? |  |
| 2. What is postpartum hemorrhage and how is it managed? |  |
| 3. What can cause a ruptured uterus during the third stage of labor and how is it managed? |  |
| 4. What are the causes of retained placenta during the third stage of labor and how is it managed? |  |
| 5. What are the causes, clinical presentation, and management of acute uterine inversion during the third stage of labor? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















