Nature of Matter & Its Properties | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Matter? |

|
| States of Matter |

|
| Classification of Matter |

|
| Properties of Matter |

|
| Units for Measurement |

|
What is Matter?
Anything that has mass and occupies space is called matter. The quantity of matter is its mass. Example: chalk, table, car, air, pen, YOU!.
States of Matter
Matter can exist in three physical states viz. solid, liquid, and gas.
The constituent particles of matter in these three states can be represented as shown in the figure:
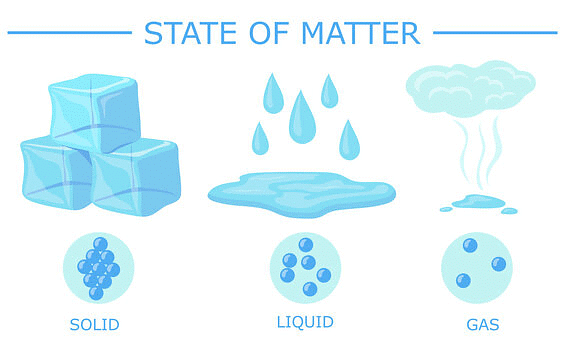 States of Matter
States of Matter
- In solids, these particles are held very close to each other and their movement is highly restricted. The particles can vibrate about their mean positions only.
- In liquids, the particles are close to each other but they can move around.
- In gases, the particles are far apart as compared to those in solid or liquid states and their movement is easy and fast.
Because of such an arrangement of particles, different states of matter exhibit the following characteristics:
- Solids have definite volume and definite shape. They are not fluid in nature.
- Liquids have a definite volume but not a definite shape. They take the shape of the container in which they are placed. Liquids can flow.
- Gasses have neither a definite volume nor a definite shape. They completely occupy the container in which they are placed. Gasses also exhibit the property of fluidity.
Note: These three states of matter are interconvertible by changing the conditions of temperature and pressure.
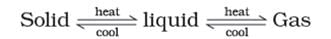
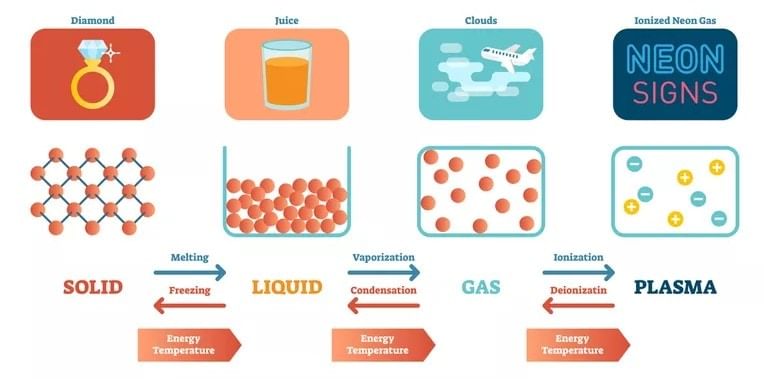 Interconversion of States of Matter
Interconversion of States of Matter
Classification of Matter
The classification of matter is based on the chemical composition of various substances. This matter can be further divided into two types: pure substances and mixtures.
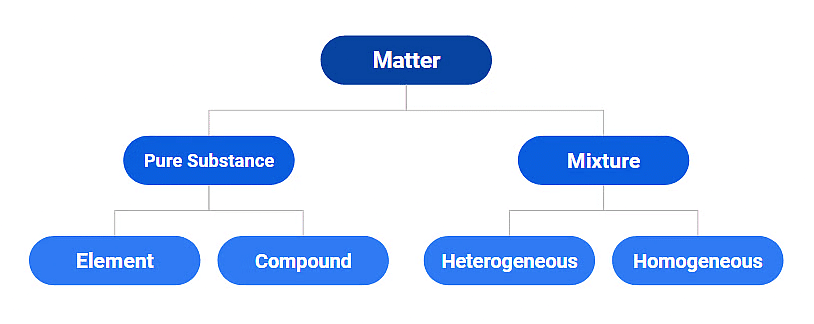 Classification of Matter
Classification of Matter
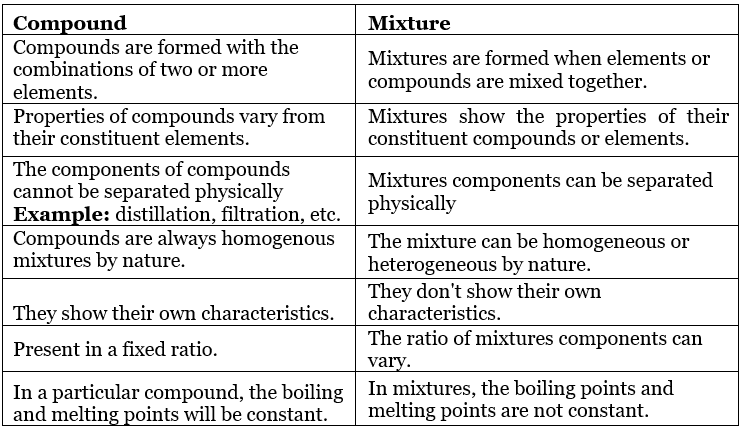
Pure Substances:
A pure substance is a form of matter that has a constant composition throughout. They are entirely made of a single type of atom or molecule. Depending on whether they are made up of a single type of atoms or molecules they are further classified into ELEMENTS and COMPOUNDS.
Elements
- Elements are pure forms of matter which are made up of a repeating, single type of atom(atoms having the same number of electrons, protons, and neutrons).
- Sodium, copper, silver, hydrogen, oxygen, etc. are some examples of elements. They all contain atoms of one type. However, the atoms of different elements are different in nature.
- A total of 118 elements are known till the date out of which 92 are naturally occurring elements and the rest are results of artificial transmutation. There are 88 metals, 18 nonmetals, and 6 metalloids.
 Different Elements
Different Elements
Compound
- Compounds are pure forms of matter that are made up of a repeating, single type of molecule( Molecules having the same type and number of combining atoms). Chemical bonds link together the atoms in a molecule.
Example: Water and methane are made up of molecules, H20 and CH4 respectively.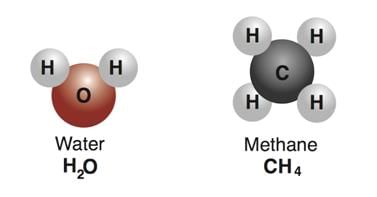 Water and Methane Molecules
Water and Methane Molecules
Mixture
Mixtures are the aggregate of more than one type of pure substance whose chemical identity remains maintained even in mixtures. Their constituent ratio may vary, unlike compounds.
Example: Sugar + Water = Sugar Syrup
Gunpowder: 75% KNO3 + 10% Sulphur + 15% carbon
There are two types of mixture:
(a) Homogeneous mixtures
(b) Heterogenous mixtures
- Homogeneous mixtures are those mixtures which have the same proportions of their components throughout.
- The mixed components are not physically separable from each other.
Example: Salt solution, sugar solution, Air.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are those mixtures that do not have the same proportions of their components throughout
- The mixed components are physically separable from each other.
Example: Soil, a mixture of sand and water.
Table: Comparison between Homogeneous and Heterogeneous mixtures
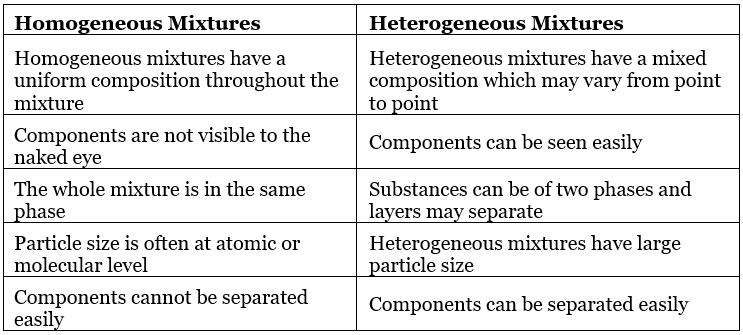
Table: Comparison between Compound and Mixtures
Properties of Matter
- Physical Property: The property that can be measured without changing the chemical composition of matter is known as physical property, in other words, matter doesn't lose its identity while measuring a physical property.
Examples: mass, volume, density, refractive index, boiling point, melting point, etc. - Chemical Property: The property that can be evaluated at the cost of matter itself is known as chemical property, in other words, matter loses its identity while measuring a chemical property.
Example: Combustibility is a chemical property and a substance has to burn in air to evaluate its combustibility.
Units for Measurement
All physical quantities have to be measured. The value of a physical quantity is expressed as the product of the numerical value and the unit in which it is expressed. For example, for the physical quantity length, say “7 meter”, “7” represents the numerical value, and “meter” represents the unit.
Fundamental Units
Fundamental units are those units that can neither be derived from one another nor can be further resolved into any other units.
- The Metric System was based on the decimal system.
- The International System of Units (SI)
The International System of Units (in French Le Systeme International d’Unites– abbreviated as SI) was established by the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM from Conference Generale des Poids at Measures). The SI system has seven base units.
Table: The Seven Fundamental Units of measurement in S.I. system.
Definitions of S.I. Base Units
- Unit of length, Metre: The meter is the length of the path travelled by light in a vacuum during a time interval of 1/299 792 458 of a second. Unit of mass kilogram
- The kilogram is the unit of mass; it is equal to the mass of the international prototype of the kilogram.
- Unit of time, Second: The second is the duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium-133 atom.
- Unit of electric current, Ampere: The ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed 1 meter apart in vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2 × 10–7 newton per meter of length.
- Unit of thermodynamic, Kelvin: is the fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water.
- Unit of the amount of substance, Mole: The mole is the amount of substance of a system that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram of carbon-12; its symbol is “mol.” 2. When the mole is used, the elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles.
- Unit of luminous intensity, Candela: The candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 hertz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian.
Derived Units
Some quantities are expressed as a function of more than one fundamental unit known as derived units.
Example: Velocity, acceleration, work, energy, area, density, etc.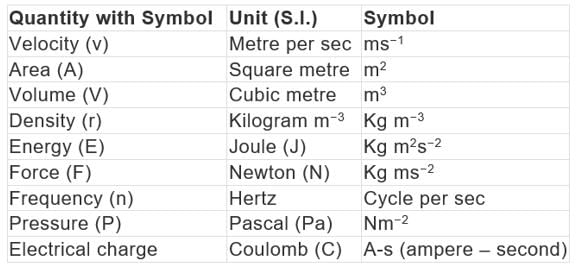 Example of Derived Units
Example of Derived Units
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Nature of Matter & Its Properties - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the three main states of matter? |  |
| 2. How is matter classified based on its composition? |  |
| 3. What are some properties of matter? |  |
| 4. What are the common units used for measuring matter? |  |
| 5. What do we mean by the nature of matter and its properties? |  |
















