Concept of Core Competence | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Academics define core competency as the specific proficiency of an individual or a set of actions that a company excels in compared to other functions, whether in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, or superior quality. The key characteristic of core competencies lies in their potential to evolve into competitive advantages for small businesses and their owners. Informed entrepreneurs adeptly identify and manage their core competencies to foster the development of streamlined, high-performance organizations. Core competence represents a blend of skills that distinguishes a company, serves as a catalyst for new business endeavors, and forms the foundational element of a company's competitive edge. It emerges from the harmonious integration of diverse skills and various technologies (Drejer, 2002).
Origin of Core Competency:
- Coined by Dr. C.K. Prahalad and Prof. Gary Hamel in 1989.
- Core competencies lead to the creation of essential products used to develop a variety of customer products.
Concept Evolution:
- Evolved from the idea that a company's competitive advantage relies on possessing unique, hard-to-copy skills, knowledge, and resources.
- Linked to the resource-based view of the firm.
Management Perspective:
- Seen as capabilities within a firm, contributing significantly to corporate competitiveness.
- Applied through operational processes to create products and services.
Elements of Core Competence:
- Involves skills, resources, and processes.
- Requires communication, involvement, and a deep commitment across organizational boundaries.
Success Factors:
- Knowledge resources, creativity, and expertise contribute to a firm's core competencies.
- Described as problem-solving insights fostering strategic growth alternatives.
Organizational Learning and Culture:
- Vital for organizational learning and culture development.
- Core competence develops from collective learning within the organization.
Aggregates of Capabilities:
- Viewed as an aggregate of capabilities creating synergy for value delivery.
- Comprises at least two complementary critical capabilities.
Objective:
- Aims to achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
- Studies show that core competencies impact organizational performance positively.
Competitive Advantage:
- Significant when related to attributes valued by the market.
- Customers must perceive consistent differences in key attributes between a company's products and those of its competitors.
Practical Application:
- Practical way to consider core competencies is as a combination of capabilities.
- Critical capabilities within core competencies distinguish a company from others.
Chart: Process of core competency from initial assessment to new job description
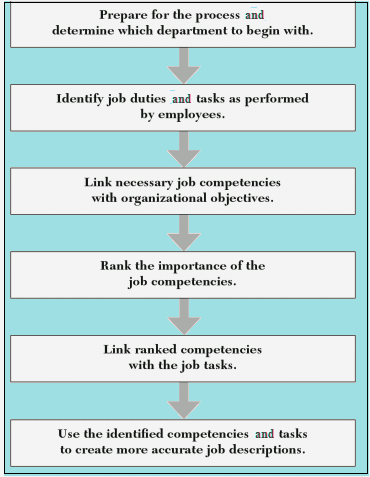
Managing Core Competencies
Basis of Core Competencies:
- Core competencies are rooted in activities, skills, and disciplines, known as primary capabilities.
- Employees' abilities, skills, and motivation are crucial for developing core competencies because they carry knowledge to achieve the company's goals.
Sustainability of Core Competencies:
- Core competencies must be capabilities that the organization can maintain over time.
- Management of technological competencies is vital for generating economic benefits, especially when focusing on knowledge assets and processes that are rare and valuable.
Development Factors:
- Core competence development involves capabilities, resources, organizational learning, research, technology, and teamwork.
- The shape and content of core competencies are influenced by the organization's goals, structure, and culture.
Building Competence:
- Building competence requires extensive employee participation and rigorous analytical activity.
- Organizational learning is also essential for competence development.
Strategic Alignment:
- Core competencies should be aligned with strategic business factors to address key performance gaps within the business.
Critical Competence:
- Critical competence identifies a firm's unique competencies through generic techniques.
- While core competencies vary between firms, critical competence is universal.
- Hamel (1994) distinguishes between meta-competencies, core competencies, and constituent skills.
Managing core competency of organization
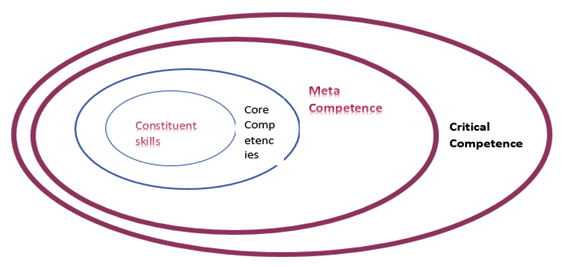
Importance of Core Competencies
Enhanced Value Creation:
- Core competencies are crucial for companies operating in competitive markets.
- They represent the collective knowledge and expertise within the organization, encompassing the ability to coordinate diverse production skills and integrate various technologies.
Increased Productivity:
- Companies that recognize and leverage their core competencies can generate more value and enhance their overall productivity.
- Core competencies serve as a foundation for creating products and services that outperform competitors.
People-Centric Focus:
- Core competencies are not just about technologies or processes; they must revolve around the individuals working within the organization.
- Employees play a vital role in identifying, building, and supporting these competencies.
Dynamic Nature of Competences:
- Unlike physical assets, which may depreciate over time, competences improve with application and sharing across the organization.
- This dynamic nature allows competences to adapt to changing market conditions and technological advancements.
Business Cohesion and Development:
- Core competencies serve as a unifying force, bringing different aspects of the business together.
- They not only enhance current operations but also pave the way for new business development and growth opportunities.
Guiding Principles for Expansion:
- Core competencies act as guiding principles for businesses seeking to enter new markets and explore diversification.
- They provide a strategic roadmap for expansion and help in navigating challenges in unfamiliar territories.
Organizational Core Competencies
Function-Specific Competencies:
- In smaller companies, core competencies are often linked to specific business functions, such as marketing, manufacturing, or customer service.
- The development of these competencies is influenced by the owner's personal experience, the team they assemble, and the organization's responses to market changes.
Specialized Skills for Success:
- A business might excel in certain areas, such as manufacturing high-quality products, but may lack expertise in others, like tax accounting.
- Core competencies should be tailored to provide a competitive edge, offering access to a broad market and contributing significantly to the benefits of the end product or service.
Imitation Challenge:
- Core competencies must be challenging for competitors to imitate.
- They should represent a unique combination of skills, knowledge, and processes that set the business apart in the market.
Competencies
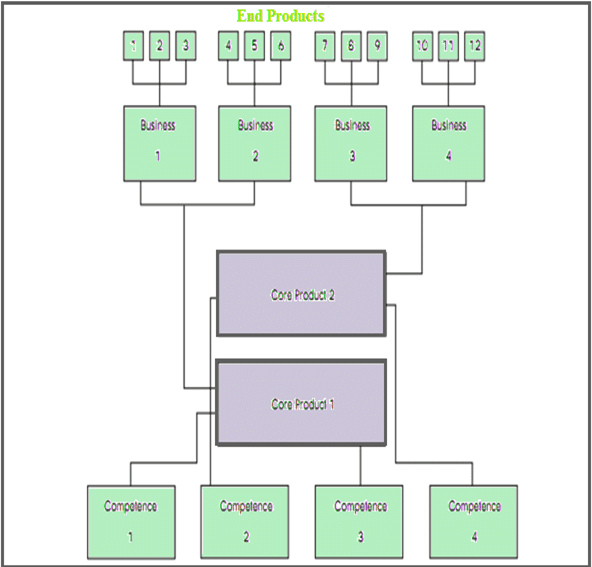
Identification of core competencies plays a crucial role in the leveraging process. This recognition can be achieved through applying three straightforward tests:
- Does the trait provide a significant competitive differentiation?
- Does it offer a unique value proposition to the organization?
- Does the trait have a broad impact across the entire business or is it specific to a particular business unit?
Additionally, considerations include whether the trait is beneficial for the current business only or extends to new ventures, and if it poses a challenge for competitors to imitate. Core competencies encompass the entire organization and are integral to strategic learning.
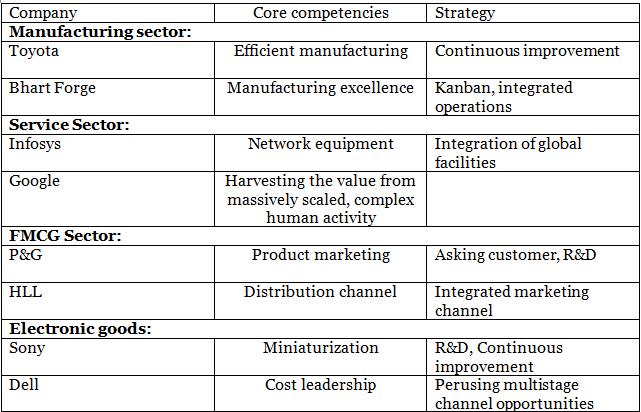
Development Process:
- Developing new core competencies involves a blend of knowledge, practice, coordination, and refinement.
- Knowledge assets need to be built, improved, combined, and synchronized in an environment conducive to experimentation and development.
- It's a complex endeavor as sustained competitive advantage comes from assets that are difficult to copy.
Knowledge Management Perspective:
- Core competency development entails accumulating specific tacit knowledge and expertise across various departments or functions.
Benefits of Core Competencies
Long-term Competitive Advantage:
- Core competencies provide a lasting competitive advantage by bridging the gap between performance and opportunities.
- They position a company as a potential leader in the industry by linking traditional business practices to future products and services.
- They also guide the company's diversification efforts.
Resource Utilization:
- Core competencies indicate efficient utilization of resources in the right places and in the right amounts.
- Outsourcing non-core activities streamlines operations, fostering a learning environment aligned with competencies.
Product Development:
- Core competencies facilitate the development of core products by providing access to essential components necessary for long-term success in the industry.
- These products can form a pipeline for future offerings.
Market Perception:
- Core competencies are valuable if they align with attributes valued by the market.
- Customers should perceive consistent differences between a company's offerings and those of its competitors.
Strategic Management Application:
- Core competencies encompass a combination of knowledge, skills, technologies, and processes that deliver products or services valued by customers.
- Researchers in strategic management use core competencies to gain competitive advantage.
- Examples of core competencies include technical superiority, efficient customer relationship management, and highly effective processes.
FAQs on Concept of Core Competence - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the concept of core competence? |  |
| 2. How can core competencies be managed effectively? |  |
| 3. Why are core competencies important for organizations? |  |
| 4. How can organizations develop core competencies? |  |
| 5. Can core competencies change over time? |  |
















