Cone: Area and Volume | The Complete SAT Course - Class 10 PDF Download
A cone is a three-dimensional shape in geometry that narrows smoothly from a flat base (usually circular base) to a point(which forms an axis to the centre of base) called the apex or vertex. We can also define the cone as a pyramid which has a circular cross-section, unlike pyramid which has a triangular cross-section. These cones are also stated as a circular cone.
Definition of Cone
A cone is a shape formed by using a set of line segments or the lines which connects a common point, called the apex or vertex, to all the points of a circular base(which does not contain the apex). The distance from the vertex of the cone to the base is the height of the cone. The circular base has measured value of radius. And the length of the cone from apex to any point on the circumference of the base is the slant height. Based on these quantities, there are formulas derived for surface area and volume of the cone. In the figure you will see, the cone which is defined by its height, the radius of its base and slant height.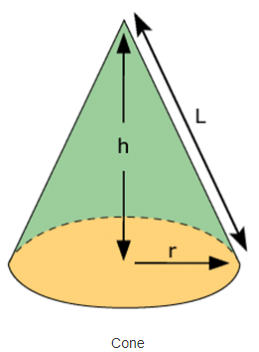
Cone Formula – Slant Height, Surface Area of Cone & Volume of Cone
The formula for the surface area and volume of the cone is derived here based on its height(h), radius(r) and slant height(l).
- Slant Height:
The slant height of the cone (specifically right circular) is the distance from the vertex or apex to the point on the outer line of the circular base of the cone. The formula for slant height can be derived by the Pythagoras Theorem.
Slant Height, l = √(r2+h2) - Volume of the Cone:
We can write, the volume of the cone(V) which has a radius of its circular base as “r”, height from the vertex to the base as “h”, and length of the edge of the cone is “l”.
Volume(V) = ⅓ πr2h cubic units - Surface Area of the Cone
The surface area of a right circular cone is equal to the sum of its lateral surface area(πrl) and surface area of the circular base(πr2). Therefore,
The total surface area of the cone = πrl + πr2
Or
Area = πr(l + r)
We can put the value of slant height and calculate the area of the cone.
Types of Cone
As we have already discussed a brief definition of the cone, let’s talk about its types now. Basically, there are two types of cones;
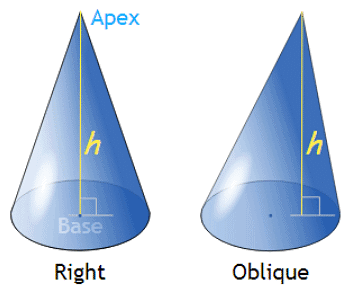
1. Right Circular Cone: A cone which has a circular base and the axis from the vertex of the cone towards the base passes through the center of the circular base. The vertex of the cone lies just above the center of the circular base. The word “right” is used here because the axis forms a right angle with the base of the cone or is perpendicular to the base. This is the most common types of cones which are used in geometry. See the figure below which is an example of a right circular cone.
2. Oblique Cone: A cone which has a circular base but the axis of the cone is not perpendicular with the base, is called an Oblique cone. The vertex of this cone is not located directly above the centre of the circular base. Therefore, this cone looks like a slanted cone or tilted cone.
Properties of Cone
- A cone has only one face, which is the circular base but no edges
- A cone has only one apex or vertex point.
- The volume of the cone is ⅓ πr2h.
- The total surface area of the cone is πr(l + r)
- The slant height of the cone is √(r2+h2)
Frustum of Right Circular Cone
Frustum of a cone is a piece of the given circular or right circular cone, which is cut in a manner that the base of the solid and the plane cutting the solid are parallel to each other. Based on this, we can calculate the surface area and volume also.
Example: Find the volume of the cone if radius, r = 4 cm and height, h = 7 cm.
By the formula of volume of the cone, we get,
V = ⅓ πr2h
V = (⅓) × (22/7) × 42 × 7
V = 117.33 Cubic Cm
Surface Area of a Cone
Surface area of a cone is the total area covered by its surface. The total surface area will cover the base area and lateral surface area of the cone. Cone is defined as a three-dimensional solid structure that has a circular base. A cone can be viewed as a set of non-congruent circular disks that are placed over one another such that the ratio of the radius of adjacent disks remains constant. In this article, let us discuss the formula for the surface area of a cone, its derivation with many solved examples.
What is Surface area of a Cone?
Surface area of a cone is the complete area covered by its two surfaces, i.e., circular base area and lateral (curved) surface area. The circular base area can be calculated using area of circle formula. The lateral surface area is the side-area of the cone. Let us see the formula to calculate the surface area of cone.
Surface Area of a cone Formula
The surface area of a cone is the total area occupied by its surface in a 3D plane. The total surface area will be equal to the sum of its curved surface area and circular base area.
Surface area of cone = πr(r+√(h2+r2))
where r is the radius of the circular base
h is the height of cone
Or
Surface area of cone = πr(r+L)
where L is the slant height of the cone
And
Curved Surface area of cone = πrl
Derivation of the Surface area of cone
Consider a cone as a triangle that is being rotated about one of its vertices. Now, think of a scenario where we need to paint the faces of a conical flask. Before painting, we need to know the quantity that is required to paint all the walls. We need to know the area of every face of the container to determine the quantity of paint required and this is known as the total surface area. The total surface area of a cone is the sum of areas of its faces.
Let’s derive a general Cone formula to calculate the surface area of a cone.
Take a paper cone and cut it along its slant height to observe the figure being formed by the surface of the cone. Mark the two endpoints as A and B and the point of the intersection of lines as O.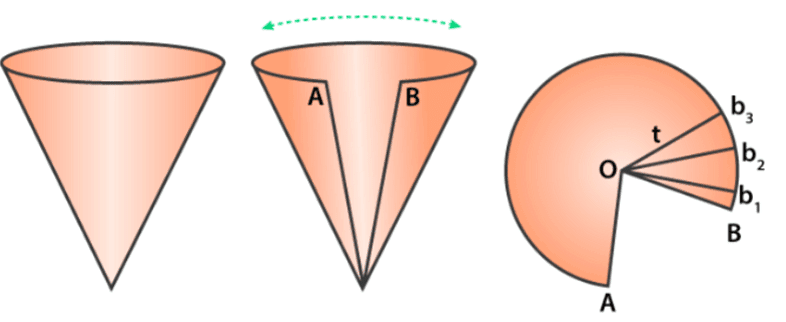
If you further cut this figure into multiple pieces’ viz. Ob1, Ob2, Ob3, …….., Obn each measuring the same length as the slant height of the original cone, you will observe n triangles are formed out of it.
Now, if you try calculating the total area of this figure, you just need to add an area of these individual triangles. Hence,
Area of figure = (1/2) × (b1 + b2 + b3 + ………….. + bn)
= (1/2)× (length of an entire curved boundary)
Length of entire curved boundary = circumference of base = 2π× r (where r is the radius of the base)
Thus,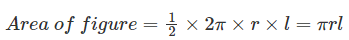
Hence,
The curved surface area of a cone = πrl
Total Surface Area of a Cone: The Total surface area of a cone includes the curved surface as well as area of its base, which is given as-
Base Area = πr2
Curved Surface Area = πrl
Thus the total surface area is given by-
πr2 + πrl = πr (r + l)
Surface area of Right Circular Cone
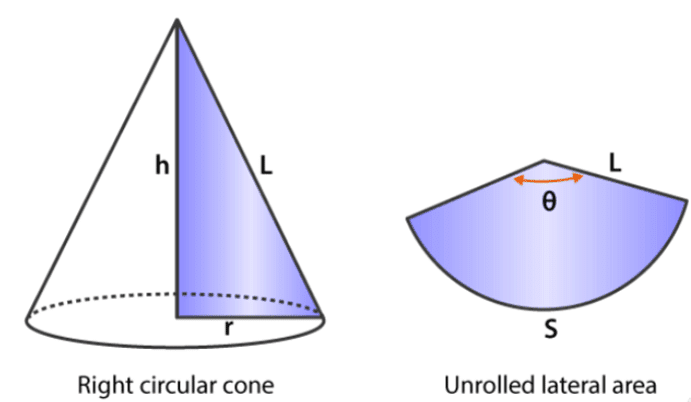
A circular cone is the one with the circular right section. A right circular cone is a circular cone whose axis is perpendicular to the base.
Surface area of cone = πr(r+√(h2+r2))
where r is the radius of the circular base
h is the height of the cone
Slant height of the cone, L = √(h2+r2)
Therefore,
Surface area = πr (r + L)
Curved Surface Area of a Cone
The curved surface of a cone is the area of the cone excluding the base. In other words, it is the area of the cone when it is unfolded as shown in the above figure as an unrolled lateral area. The formula to calculate the curved surface area of a cone is given by:
Curved Surface Area (CSA) = πrl
Here,
r = Radius of the circular base of the cone
l = Slant height of the cone
When the cone is in the form of an unrolled lateral area, r is referred to as the length of the arc of a sector and l is referred to as the radius of the sector.
Total Surface Area of a Cone
The total surface area of a cone is defined as the total area of the cone occupied in a three-dimensional area. It is equal to the sum of the curved surface and the base of the cone. The formula to calculate the total surface area of a cone is given by:
Total Surface Area (TSA) = CSA + Area of Circular Base
TSA = πr(r + l)
Slant Height of Cone
The slant height of the cone is the distance from the vertex to the edge of the circular base of the cone. The vertical height is the distance from the vertex to the center of circular base of cone. The formula to find slant height of cone is given by:
Slant height of the cone, L = √(h2 + r2)
where ‘h’ is the vertical height and ‘r’ is the radius of circular base of cone.
Example: Determine the curved surface area of a cone whose base radius is 7 cm and slant height is 15 cm.
Curved surface area of a cone = πrl
= (22/7)× 7 ×15
= 330 cm2
Volume of a Cone
The volume of a cone defines the space or the capacity of the cone. A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape having a circular base that tapers from a flat base to a point called apex or vertex. A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines or lines connecting a common point, the apex, to all the points on a base that is in a plane that does not contain the apex.
A cone can be seen as a set of non-congruent circular disks that are stacked on one another such that the ratio of the radius of adjacent disks remains constant.
Volume of a Cone Formula
In general, a cone is a pyramid with a circular cross-section. A right cone is a cone with its vertex above the center of the base. It is also called right circular cone. You can easily find out the volume of a cone if you have the measurements of its height and radius and put it into a formula.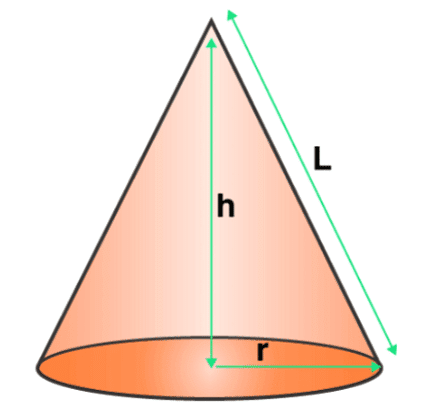
Therefore, the volume of a cone formula is given as
The volume of a cone = (1/3) πr2h cubic units
Where,
‘r’ is the base radius of the cone
‘l’ is the slant height of a cone
‘h’ is the height of the cone
As we can see from the above cone formula, the capacity of a cone is one-third of the capacity of the cylinder. That means if we take 1/3rd of the volume of the cylinder, we get the formula for cone volume.
Note: The formula for the volume of a regular cone or right circular cone and the oblique cone is the same.
Derivation of Cone Volume
Cone as a triangle which is being rotated about one of its vertices. Now, think of a scenario where we need to calculate the amount of water that can be accommodated in a conical flask. In other words, calculate the capacity of this flask. The capacity of a conical flask is basically equal to the volume of the cone involved. Thus, the volume of a three-dimensional shape is equal to the amount of space occupied by that shape. Let us perform an activity to calculate the volume of a cone.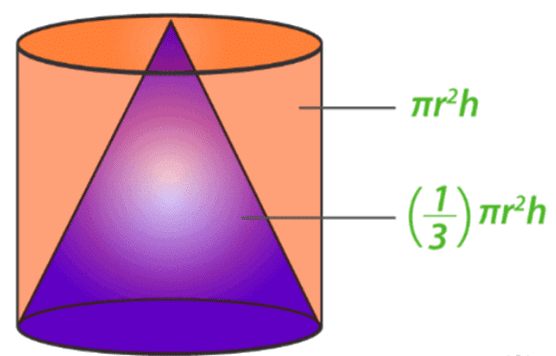
Take a cylindrical container and a conical flask of the same height and same base radius. Add water to the conical flask such that it is filled to the brim. Start adding this water to the cylindrical container you took. You will notice it doesn’t fill up the container fully. Try repeating this experiment for once more, you will still observe some vacant space in the container. Repeat this experiment once again; you will notice this time the cylindrical container is completely filled. Thus, the volume of a cone is equal to one-third of the volume of a cylinder having the same base radius and height.
Now let us derive its formula. Suppose a cone has a circular base with radius ‘r’ and its height is ‘h’. The volume of this cone will be equal to one-third of the product of the area of the base and its height. Therefore,
V = 1/3 x Area of Circular Base x Height of the Cone
Since, we know by the formula of area of the circle, the base of the cone has an area (say B) equals to;
B = πr2
Hence, substituting this value we get;
V = 1/3 x πr2 x h
Where V is the volume, r is the radius and h is the height.
Example: Calculate the volume if r= 2 cm and h= 5 cm.
Given:
r = 2
h= 5
Using the Volume of Cone formula
The volume of a cone = (1/3) πr2h cubic units
V= (1/3) × 3.14 × 22 ×5
V= (1/3) × 3.14 × 4 ×5
V= (1/3) × 3.14 × 20
V = 20.93 cm3
Therefore, the volume of a cone = 20.93 cubic units.
|
433 videos|220 docs|166 tests
|
















