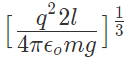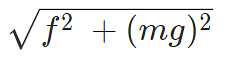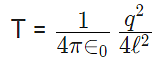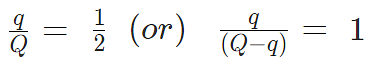Coulomb's Law & Its Applications | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Coulomb's Law |

|
| Coulomb’s Law in Vector Form |

|
| Key Points on Coulomb’s Law |

|
| Application of The Coulombs Law |

|
| Problems on Coulombs Law |

|
| Forces Between Multiple Charges |

|
Coulomb's Law
Charles Augustin de Coulomb, in 1785 through his experiments, found out that the two point charges 'q1' and 'q2' kept at a distance 'r' in a medium exert an electrostatic force 'F' on each other. The value of force F is given by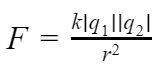
This law gives the net electrostatic force experienced by q1 due to q2 and vice versa.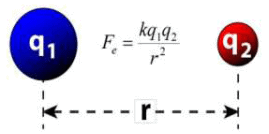 Coulomb's Law
Coulomb's Law
Where,
F gives the magnitude of electrostatic force,
'q1 and 'q2 are the magnitudes of the two interacting point charges,
K is electrostatic constant which depends upon the medium surrounding the two charges. For vacuum, it is equal to 1/4πε0, the symbol ε0 is called ‘epsilon naught’ and it represents permittivity of vacuum.
K = 1/4πε0 = 9 × 109 Nm2/c2
ε0 = 8.854 × 10-12 C2/Nm2
If the point charges are kept in a medium with permittivity ε, then the electrostatic force between the point charges will be: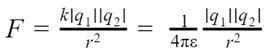
This force F acts along the line joining the two charges and is repulsive if q1 and q2 are of the same sign and it is attractive if they are of opposite sign because like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other.
Coulomb’s Law in Vector Form
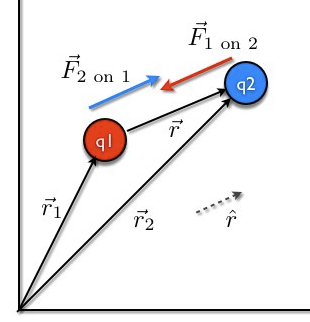 Coulomb's Law in Vector Form
Coulomb's Law in Vector Form
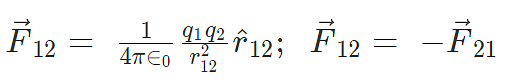 Here F12 is the force exerted by q1 on q2 and F21 is the force exerted by q2 on q1.
Here F12 is the force exerted by q1 on q2 and F21 is the force exerted by q2 on q1.
Coulomb’s law holds for stationary charges only which are point sized. This law obeys Newton’s third law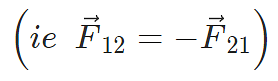
Force on a charged particle due to a number of point charges is the resultant of forces due to individual point charges i.e.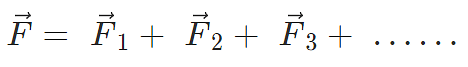
What is 1 Coulomb of Charge?
A coulomb is that charge which repels an equal charge of the same sign with a force of 9 × 109 N, when the charges are one meter apart in a vacuum. Coulomb force is the conservative mutual and internal force.
The value of εo is 8.86 × 10-12 C2/Nm2 (or) 8.86 × 10-12 Fm–1
Note: Coulomb force is true only for static charges.
Coulomb’s Law – Conditions for Stability
- If q is slightly displaced towards A, FA increases in magnitude while FB decreases in magnitude. Now the net force on q is toward A so it will not return to its original position. So for axial displacement, the equilibrium is unstable.
- If q is displaced perpendicular to AB, the force FA and FB bring the charge to its original position. So for perpendicular displacement, the equilibrium is stable.
Key Points on Coulomb’s Law
1. If the force between two charges in two different media is the same for different separations, 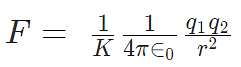 = constant.
= constant.
2. Kr2 = constant or K1r12 = K2r22
3. If the force between two charges separated by a distance ‘r0’ in a vacuum is the same as the force between the same charges separated by a distance ‘r’ in a medium, then from Coulomb’s Law; Kr2 = r02
4. Two identical conductors having charges q1 and q2 are put to contact and then separated after which each will have a charge equal to q1 + q2/2. If the charges are q1 and – q2, then each will have a charge equal to q1 - q2/2.
5. Two spherical conductors having charges q1 and q2 and radii r1 and r2 are put to contact and then separated the charges of the conductors after contact is;
q1 = [r1/(r1 + r2)] (q1 + q2) and q2 = [r2/(r1 + r2)] (q1 + q2)
6. If the force of attraction or repulsion between two identical conductors having charges q1 and q2 when separated by a distance d is F. Also if they are put to contact and then separated by the same distance the new force between them is
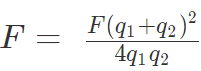
7. If charges are q1 and -q2 then, F = F(q1 + q2)2 / 4q1q2
8. Between two-electrons separated by a certain distance: Electrical force/Gravitational force = 1042
9. Between two protons separated by a certain distance: Electrical force/Gravitational force = 1036
10. Between a proton and an electron separated by a certain distance: Electrical force/Gravitational force = 1039
11. The relationship between the velocity of light, the permeability of free space and permittivity of free space is given by the expression c = 1 / √ (μoεo)
12. If Coulomb’s law is applied to two identical balls of mass m are hung by silk thread of length ‘l’ from the same hook and carry similar charges q then;
- The distance between balls =

- The tension in the thread =

- If the total system is kept in space then the angle between threads is 180° and tension in a thread is given by

- A charge Q is divided into q and (Q – q). Then electrostatic force between them is maximum when

Application of The Coulombs Law
- To calculate the distance and force between the two charges.
- The electric field can be calculated using the coulombs law
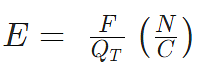
Where E = Strength of the electric field
F = Electrostatic force
QT = Test charge in coulombs
- To calculate the force on one point due to the presence of several points (Theorem of superposition).
Problems on Coulombs Law
Problem 1: Charges of magnitude 100 microcoulomb each are located in vacuum at the corners A, B and C of an equilateral triangle measuring 4 meters on each side. If the charge at A and C are positive and the charge B negative, what is the magnitude and direction of the total force on the charge at C?
Sol. The situation is shown in fig. Let us consider the forces acting on C due to A and B.
Now, from Coulomb’s law, the force of repulsion on C due to A i.e., FCA in direction AC is given by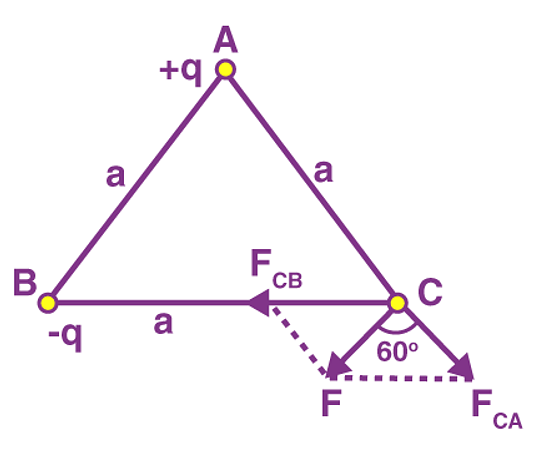
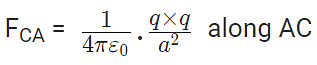
The force of attraction on C due to B i.e., FCB in direction CB is given by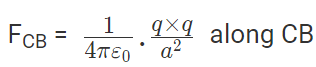
Thus the two forces are equal in magnitude. The angle between them is 120º. The resultant force F is given by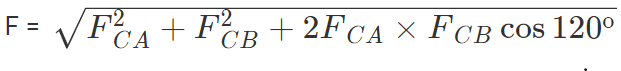
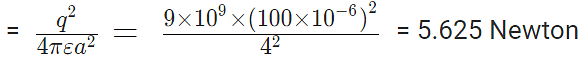
This force is parallel to AB.
Problem 2: The negative point charges of unit magnitude and a positive point charge q are placed along the straight line. At what position and for what value of q will the system be in equilibrium? Check whether it is stable, unstable or neutral equilibrium.
Sol. The two negative charges A and B of unit magnitude are shown in fig. Let the positive charge q be at a distance rA from A and at a distance rB from B.
Now, from coulombs law, Force on q due to A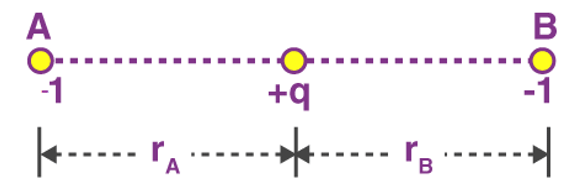
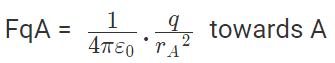
Force on q due to B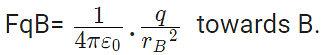
These two forces acting on q are opposite and collinear. For the equilibrium of q, the two forces must also be equal i.e.
|FqA| = |FqB|
or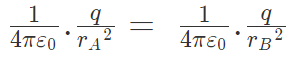 Hence rA = rB
Hence rA = rB
So for the equilibrium of q, it must be equidistant from A & B i.e. at the middle of AB Now for the equilibrium of the system, A and B must be in equilibrium. For the equilibrium of A
Force on A by q = 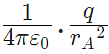 towards q
towards q
Force on A by B = 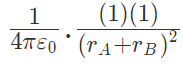
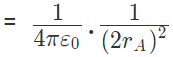 away from q
away from q
The two forces are opposite and collinear. For equilibrium the forces must be equal, opposite and collinear. Hence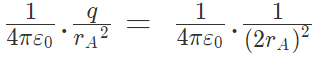
or q = 1/4 in magnitude of either charge.
It can also be shown that for the equilibrium of B, the magnitude of q must be 1/4 of the magnitude of either charge.
Problem 3: A positive charge of 6 × 10-6 C is 0.040m from the second positive charge of 4 × 10-6 C. Calculate the force between the charges.
Given
q1 = 6 × 10-6 C
q2 = 4 × 10-6 C
r = 0.040 m
Sol. 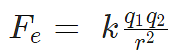
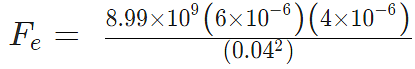
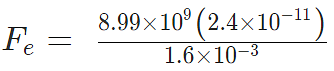
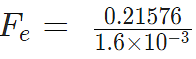
Fe = 134.85 N
Problem 4: Two-point charges, q1 = +9 μC and q2 = 4 μC, are separated by a distance r = 12 cm. What is the magnitude of the electric force?
given
k = 8.988 x 109 Nm2C−2
q1 = 9 ×10-6 C
q2 = 4 ×10-6 C
Sol: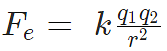
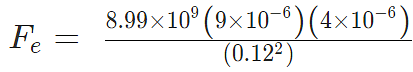
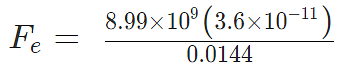
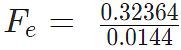
Fe = 22.475 N
Limitations of Coulomb’s Law
Coulomb’s Law is derived under certain assumptions and can’t be used freely like other general formulas. The law is limited to following points:
- We can use the formula if the charges are static ( in rest position)
- The formula is easy to use while dealing with charges of regular and smooth shape, and it becomes too complex to deal with charges having irregular shapes
- The formula is only valid when the solvent molecules between the particle are sufficiently larger than both the charges
Forces Between Multiple Charges
A charge is an inherent property of every atom, an atom is said to be charged if it has an irregular number of electrons and protons, an atom is said to be positively charged if it has less number of electrons than protons, and negatively charged if it has more number of electrons than protons.
The bodies get charged differently, the most common way of charging a body is to rub. If you rub a plastic comb with your hair, the comb attains electrons from hair, now if we get tiny pieces of paper close to the comb attracts the pieces like a magnet attracting iron fillings, this is because the electrons attract the positive charge on the paper. This is the force of charges in action.
How to calculate the magnitude of the force between two charges
We can find the force between any two charges by Coulomb’s law. Coulomb’s law states that two charged bodies will attract or repel each other with a force that proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them,
Let’s get an equation out of this,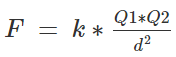
Where F is the force of attraction or repulsion depending upon the charges,
K is the coulombs constant, for air it is 9×109 kg⋅m3⋅s−2⋅C−2.
Q1 and Q2 are the magnitudes of two charges
d is the distance between the two charges,
This is only applicable for two charged particles, how will we find a force on one charge due to multiple charges?
Let’s consider 3 charges QA, QB, and QC.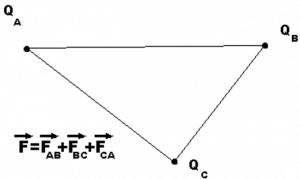
We could get the net force acting on a charge by calculating the vector sum of all the forces acting on the charge, this is called the superposition theorem.
Considering the above example of 3 point charges Qa, Qb and Qc with a position vector of r1, r2 and r3. Then the force experienced by one charge due to the other charges is given by,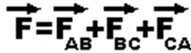
This can be written as,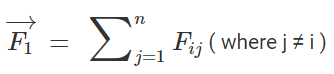
By applying this to our current situation of 3 point charges we will get,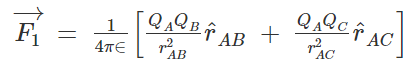
This is a combination of the coulombs law and the superposition theorem, and any electro static force can be derived using coulombs law and the superposition theorem this way.
- The force acting on a charge is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- The force acting on a point charge due to multiple charges is given by the vector sum of all individual forces acting on the charges.
Solved Example
Q.1. Two charges 1 C and – 3 C are kept at a distance of 3 m. Find the force of attraction between them.
Ans. We have q1 = 1C, q2 = – 3C and r = 3m. Then using Coulomb’s Law and substituting above values we get
F = k q1q2/ r2
Or, F = 9 × 109 × 1 × 3/ 32
F = 3 × 109 Newton
Q.2. The electron and proton of a hydrogen atom are separated (on the average) by a distance of approximately 5.3 × 10–11 m. Find the magnitudes of the electric force and the gravitational force between the two particles.
Ans. We can treat the electron and the proton of the hydrogen atoms as two point charges kept at a distance of 5.3 × 10–11 m from each other in vacuum. Also, we know that
Mass of an electron = me = 9.1 × 10-31 Kg
Mass of a proton = mp = 1.67 × 10-27 Kg
Charge of an electron = qe = - 1.6 × 10-19 C
Charge of a proton = qp = +1.6 × 10-19 C
Thus,
By Universal Law of Gravitation,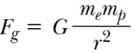
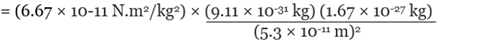
By Coulomb’s Law,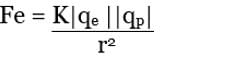
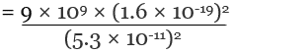
= 8.2 × 10-8 N
Note: The massive difference between the magnitudes of gravitational force and electrostatic force. The electrostatic force between the electron and the proton of the hydrogen atom is around 1039 times stronger than the gravitational force between them. Thus, from now onwards we will consciously neglect the gravitational force of attraction between charged particles.
|
97 videos|370 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Coulomb's Law & Its Applications - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is Coulomb's Law and how is it represented in vector form? |  |
| 2. What are the key points to remember about Coulomb's Law? |  |
| 3. How is Coulomb's Law applied in real-life situations? |  |
| 4. What kind of problems can be solved using Coulomb's Law? |  |
| 5. How can Coulomb's Law be used to determine the forces between multiple charges? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|