Cross-border Mergers and Acquisitions | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
During the era of globalization, there has been a significant surge in cross-border mergers and acquisitions (M&As) over the past twenty years. Theoretical models proposed by Horn and Persson (2001) and Norback and Persson (2004) suggest that foreign companies may acquire domestic targets in M&As, with the acquisition price determined through an endogenous bargaining process. Contrary to the tariff jumping argument, these models reveal that elevated trade costs do not always lead to an increase in foreign M&As.
Definition of Merger: Combining two or more independent businesses into one, usually with a bigger company absorbing smaller ones. Types include Horizontal (similar businesses), Vertical (different stages of production), or Conglomerate (unrelated businesses).
Definition of Acquisition: When one company gets control over another by buying its shares, assets, or management rights.
Cross-Border Mergers and Acquisitions (M&As)
- Increasing Trend: More businesses from different countries are joining together.
- Reasons for Increase: Policies promoting global financial movement and agreements between countries.
- Key Players: Wealthy countries like those in the European Union and the United States are the main ones involved.
- Recent Shifts: Latin America and Africa are becoming more attractive due to political reasons and economic growth.
- Historical Trend: In the 1990s, there was a huge jump in cross-border M&A, especially in Asia Pacific.
- Current Scenario: India's uncertain policies, China's saturation, and Africa's growth contribute to the rise in M&A.
Determinants of Cross-Border M&As
- Unclear Factors: It's not entirely clear why companies engage in cross-border M&As.
- Important Factors: Culture, geography, and industry-specific factors play a role.
- Research Findings: Different studies emphasize various aspects like cultural proximity, industry type, and deal volume.
Motivation for M&As
- Building Value: Companies aim to increase shareholder value through M&As.
- Drivers: Global competition, technology changes, regulations, and financial opportunities push companies to merge.
- Benefits: Access to assets, market dominance, operational synergies, size advantage, risk diversification, and financial gains are some of the benefits.
Relation to Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- Characteristics: Cross-border M&A is a major part of FDI.
- Comparison: While they are related, they differ in terms of investment types and where the money comes from.
- Complex Relationship: Sometimes, cross-border M&A exceeds documented FDI values due to differences in how they are calculated.
Distribution of different types of FDI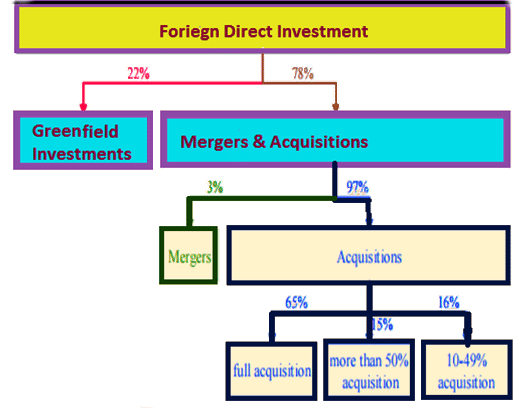
Basic Characteristics of Cross-border M&As
Best Data Source: Thomson's database is the top source for merger and acquisition (M&A) information globally.
Types of Cross-Border M&A:
- Inward M&A: When a foreign investor buys a local company, bringing capital into the country.
- Outward M&A: When a local company buys a foreign one, sending capital out of the country.
Interconnection of Inward and Outward M&A:
- Inseparable: In M&A, both selling and buying are interconnected, forming a complete transaction.
- Mutual Relationship: Inward and outward M&As work together as a part of the overall M&A landscape.
Top companies involved cross-border M&As in 1998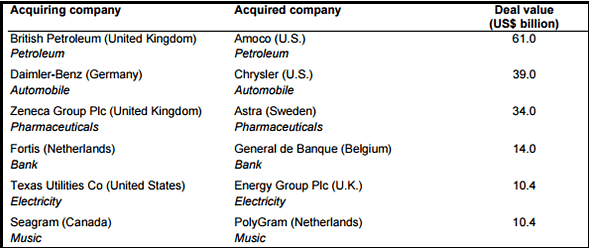
Factors to be considered in Cross Border Mergers and Acquisitions
Incentives for M&As:
- Both the foreign and domestic companies must benefit for a successful cross-border M&A.
- Domestic firms in emerging markets often exaggerate their capabilities to attract M&A deals.
Preparation and Assessment:
- Foreign companies conduct thorough research and get help from consultancies and banks before entering into an M&A deal.
- They assess risks like political, economic, social, and unforeseen events (black swan events) using a risk matrix.
Regulatory and Political Support:
- Cross-border M&As require approvals and political backing to proceed smoothly.
Motivations for Cross-Border M&As
Globalization of Financial Markets:
- Markets are interconnected globally, driving companies to explore opportunities beyond borders.
Market Pressures and Competition:
- International competition and changing market dynamics push companies to seek new avenues.
Technological Advancements:
- Evolving technology prompts companies to explore new markets and innovation opportunities.
Geographical Diversification:
- Companies aim to explore assets and opportunities in different countries to spread risks.
Efficiency and Profitability:
- M&As help companies increase efficiency in production and grow profitably.
Scale of Production:
- Combining forces allows companies to increase their production scale and reach.
Technology Sharing and Innovation:
- Sharing technology and innovative ideas through M&As can reduce costs and improve processes.
Effects of Cross Border Merger and Acquisitions
Global Transformation:
- M&As reshape industrial assets and production structures worldwide.
- Facilitate the global transfer of technology, capital, goods, and services.
Efficiency Gains:
- Lead to economies of scale and scope, enhancing overall efficiency.
Economic Benefits:
- Boost the host country's productivity, contributing to economic growth and development.
- Positive impact if government policies are favorable.
Capital Accumulation:
- Supports long-term capital buildup.
- Investments not only in physical assets like buildings but also in intangible assets like technical know-how.
Employment Impact:
- Short-term downsizing during restructuring may occur.
- Long-term gains with business expansion leading to new job opportunities.
Technology Transfer:
- Fosters transfer of technology and sharing of management skills across borders.
- Investments in intangible assets spur innovation and positively impact company operations.
Cross Border Merger and Acquisitions - Issues and Challenges
Political Hurdles:
- Involves dealing with the impact of politics on mergers, especially in sensitive industries like defense.
- Government agencies, employees, suppliers, and others need to be considered, and sometimes, discussions with labor unions are required.
Cultural Barriers:
- Cultural differences can be a big problem in cross-border deals.
- Issues may arise due to different cultural backgrounds, languages, and business practices, leading to failed mergers.
- Businesses should invest time and effort in understanding local cultures to avoid problems.
Legal Complexities:
- Merging companies must navigate various legal and regulatory challenges.
- Differences in security, corporate, and competition laws can complicate the process.
- Reviewing these issues might reveal incompatibilities, advising against proceeding with the merger.
Tax and Accounting Challenges:
- Tax considerations, such as the mix of debt and equity, can impact the cost of the merger.
- Decisions on asset or stock purchases can be influenced by transfer taxes.
- Understanding financial and accounting terms helps minimize confusion and risk.
Due Diligence Importance:
- Thorough due diligence is crucial in cross-border M&As.
- Beyond legal and regulatory concerns, infrastructure, currency, and local risks must be assessed.
- Failure to conduct proper due diligence can lead to a high risk of failure, often due to cultural differences.
Summary
- Cross-border M&A involves a company from one country buying a significant portion or all of another company in a different country.
- While beneficial, it poses challenges like political influence, cultural clashes, legal complexities, tax issues, and the importance of due diligence.
- Poor cultural fit is a common reason for M&A failures, highlighting the need for careful planning and preparation.
- Success in cross-border M&As requires a commitment of time and resources, learning from past cases like the Daimler-Chrysler merger.
FAQs on Cross-border Mergers and Acquisitions - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the basic characteristics of cross-border mergers and acquisitions? |  |
| 2. What factors should be considered in cross-border mergers and acquisitions? |  |
| 3. What are the effects of cross-border mergers and acquisitions? |  |
| 4. What are the issues and challenges in cross-border mergers and acquisitions? |  |
| 5. How do cross-border mergers and acquisitions impact the global economy? |  |















