Cytogenetic Method (Chromosomal and karyo-Type Analysis) | Anthropology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Cytogenesis is the study of Chromosomes & the related disease states caused by abnormal chromosome number and /or structure. Normally chromosomes can't be seen in light microscope, but during cell division they become condensed enough to be easily analysed @ 1000X To collect cells with their chromosomes in this condensed state, they are exposed to a mitotic inhibitor which blocks formation of the spindle and arrests cell division at the metaphase stage. A variety of tissue can be used to obtain chromosome preparations- peripheral blood, bone marrow, amniotic fluid, product of conception etc. Such chromosome preparations are then subjected to various technique to identify possible numerical & structural changes.
A variety of tissue can be used to obtain chromosome preparations- peripheral blood, bone marrow, amniotic fluid, product of conception etc. Such chromosome preparations are then subjected to various technique to identify possible numerical & structural changes.
What are the various method to study Chromosomes
Traditionally observing the chromosomes under the microscope. Here we study their
morphological characteristics such as
- Relative lengths
- Arm ratios
- Presence or absence of secondary constructions.
 Chromosome banding technique
Chromosome banding technique
- Developed during 2nd half of 20th century
- Allow the identification of individual chromosomes that differ morphologically with great degree of accuracy.
- Also allow identification of chromosome that possess similar morphological attributes.
- It also permits us to establish a correlation between linkage maps & cytological maps S This involves staining the chromosome with fluorescent dyes. The staining gives different pattern of bands & inter bands ie stained & unstained regions along the length of chromosome.
- The banding pattern of a particular chromosome remain constant for a particular treatment.
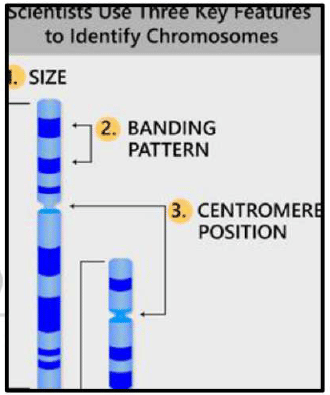 At present four such banding pattern are known, which are represented as Q,G,C and R Patters. Comparing chromosome pattern with normal banding pattern, abnormalities in different chromosomes can be easily identified. In some cases bands can also be used as Markers.
At present four such banding pattern are known, which are represented as Q,G,C and R Patters. Comparing chromosome pattern with normal banding pattern, abnormalities in different chromosomes can be easily identified. In some cases bands can also be used as Markers.
(a) Q bands
- Fluorescent bands observed on human chromosome by staining with quinacrine mustrard & observed under UV light.
- It produce characteristic bright & dark bands on chromosomes.
- In their width, brightness & position there Q bands are so unique that individual chromosomes could be identified & Q band Karyotypes could be constructed.
(b) G bands
- Produced by staining with Giemsa stain.
- The bands occur on the same locations as the Q. bands
- Their staining does not require fluorescent microscope.
 (c) C Banding
(c) C Banding
- Stain all constitutive heterochromatin (that is why C) localized to particular site on the chromosomes, (ex- centromere region of chromosome).
(d) R Banding
- Also known as Reverse Banding.
- Pattern that is reverse of G banding
That is light banded region of G banded chromosome becomes darkly stained & vice versa.


 In-situ hybridization with DNA probes
In-situ hybridization with DNA probes
There are 2 types- Simple and Fluorescence Hybridization
(a) Simple insitu Hybridization In this technique we locate the physical position of a known DNA sequence on a chromosome- helps physical mapping of genes or repeated DNA sequences.
Following Step
- DNA with in the cell is denatured by treating the cells that have been squashed on a cover slip.
- The squashed cells is incubated in solution of labelled DNA whose position on a chromosome we are interested in knowing. (Labelled DNA probe can be either Radioactively labelled or Biotinylated probe (utilize colorimetric detection)
- Wash the hybridization mix and observe them under radiography (in case or radioactively labelled) or by staining with Giemsa (for Biotin labelled probes)
 (b) Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH) Here molecules or labelling probe that have affinity to fluorescence molecules (which will be deposited on it) are used. The sites thus located will exhibit fluorescence & can be photographed with a fluorescent microscope.
(b) Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH) Here molecules or labelling probe that have affinity to fluorescence molecules (which will be deposited on it) are used. The sites thus located will exhibit fluorescence & can be photographed with a fluorescent microscope.
Following advantage
- Higher resolution, sensitivity & speed.
- 2 or 3 colour can be used on the same slide for simultaneous detection & localization of several DNA sequences in the same nucleus
- Entire genomes, whole chromosome, chromosome segment or single copy sequences can be highlighted depending upon complexity of probe used.
- Can also be used for gene mapping in addition to studying structural and numerical changes in chromosomes.

Karyotyping/ldiogram: Karyotype is a systematized array of chromosomes of a single cell prepared either by drawing or by photography, with the extension in meaning that the chromosomes of a single cell can typify the chromosomes of an individual or even a species.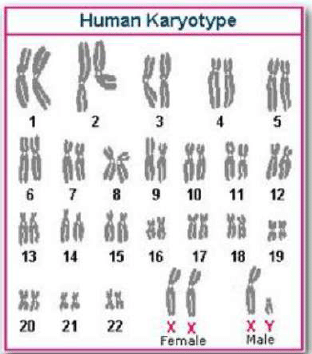 The term ideogram is the diagrammatic representation of a karyotype which may be based on measurements of chromosomes in several or many cells. This sort of arrangement of chromosomes represents relative morphology of chromosomes.
The term ideogram is the diagrammatic representation of a karyotype which may be based on measurements of chromosomes in several or many cells. This sort of arrangement of chromosomes represents relative morphology of chromosomes. Computer Assisted Chromosome Analysis
Computer Assisted Chromosome Analysis
- While preparing karyotypes or ideograms, there may be personal error in measuring chromosomes.
- Similarly difficulties are countered while measuring chromosomes that are not lying straight, but are curved at metaphase state or are over lapping.
- In order to overcome these difficulties, interactive computer assisted image processing systems are now available.
- Insitu hybridization can also be analysed with this computer assisted system.
- This adds precision in chromosome analysis for cytogenetic studies.
Conclusion
Cytogenesis focuses on the study of chromosomes and the diseases caused by abnormal chromosome number and structure. Various methods are used to study chromosomes, such as traditional microscopic observation, chromosome banding techniques (Q, G, C, and R bands), and in-situ hybridization (simple and fluorescence hybridization). Karyotyping and ideograms are used to systematically arrange and represent chromosomes, while computer-assisted chromosome analysis helps to overcome errors and difficulties in measuring chromosomes. These techniques have significantly advanced our understanding of chromosomal abnormalities and contributed to the diagnosis and management of genetic diseases.
|
108 videos|242 docs
|


















