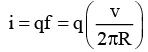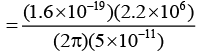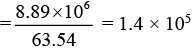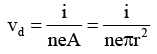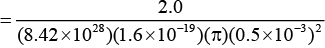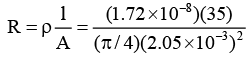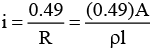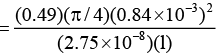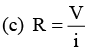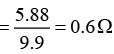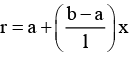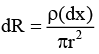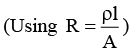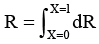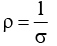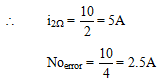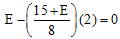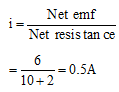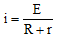DC Pandey Solutions: Current Electricity | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Introductory Exercise 20.1
Q.1. In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electron is pictured to rotate in a circular orbit of radius 5 × 10-11 m, at a speed of 2.2 × 106 m/s. What is the current associated with electron motion?
Ans.
= 1.12 × 10-3A = 1.12mA
Q.2. Copper has one conduction electron per atom. Its density is 8.89 g/cm3 and its atomic mass is 63.54 g/mol. If a copper wire of diameter 1.0 mm carries a current of 2.0 A. What is the drift speed of the electrons in the wire?
Ans.
ρ = 8.89 × 103 kg/m3
Mass of 1 m3 = 8.89 × 103 kg= 8.89 × 103 kg
∴ Number of gram moles
Number of atoms = 1.4 × 105 × 6.02 × 1023
= 8.42 × 1028
One atom emits one conduction electron. Therefore number of free electrons in unit volume (or lm3 volume)
n = 8.42 × 1028 per m3
Now i = neA vd
= 1.9 × 10-4m/s
Q.3. When a steady current passes through a cylindrical conductor, is there an electric field inside the conductor?
Ans. Under electrostatic conditions (when no current flows), E = 0. When current is non-zero, then electric field is also non-zero.
Q.4. Electrons in a conductor have no motion in the absence of a potential difference across it. Is this statement true or false?
Ans. False, there is random or thermal motion of free electrons in the absence of potential difference.
Q.5. In an electrolyte, the positive ions move from left to right and the negative ions from right to left. Is there a net current? If yes, in what direction?
Ans. Current due to both is from left to right. So, the two current are additive.
Q.6. The current through a wire depends on time as, i = (10 + 4t)
Here, i is in ampere and t in seconds. Find the charge crossed through a section in time interval between t = 0 to t = 10 s.
Ans. The resistance of a copper wire and an iron wire at 20°C are 4.1 Ω. and 3.9 Ω respectively. Neglecting any thermal expansion, find the temperature at which resistances of both are equal.
Introductory Exercise
20.2
Q.1. In household wiring, copper wire 2.05 mm in diameter is often used. Find the resistance of a 35.0 m long wire. Specific resistance of copper is 1.72 ×10-8 Ω-m.
Ans.
= 0.18 Ω
Q.2. An aluminium wire carrying a current has diameter 0.84 mm. The electric field in the wire is 0.49 V/m. What is,
(a) the current carried by the wire?
(b) the potential difference between two points in the wire 12.0 m apart?
(c) the resistance of a 12.0 m length of this wire? Specific resistance of aluminium is 2.75 × 10-8 Ω-m.
Ans.
(a) In 1 m, potentials difference,
V = 0.49
V = iR
= 9.9 A
(b) PD between two points, 12 m apart = (0.49 V/m) (12m) = 5.88 V
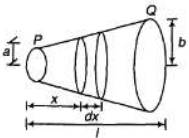
Q.3. A conductor of length l has a non-uniform cross-section. The radius of the cross-section varies linearly from a to b. The resistivity of the material is ρ. Find the resistance of the conductor across its ends.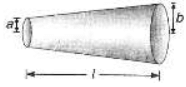
Ans.
Radius at distance x from end P,
Resistance of element of thickness dx is
∴
Q.4. The product of resistivity and conductivity of a conductor is constant. Is this statement true or false?
Ans.
ρσ = constant
Q.5. The resistance of a copper wire and an iron wire at 20°C are 4.1 Ω. and 3.9 Ω respectively. Neglecting any thermal expansion, find the temperature at which resistances of both are equal.
αCu = 4.0 × 10-3K-1. and αFe= 5.0 × 10-3 K-1.
Ans. 4.1[1 + 4.0 × 10-3(θ - 20)]
= 3.9[1 + 5.0 × 10-3(θ - 20)]
Solving we get,
θ = 85°C
Introductory Exercise
20.3
Q.1. Find the current through 2Ω and 4Ω resistance.
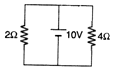
Ans. PD across each resistance is 10V.
Q.2. In the circuit shown in figure, find the potentials of A, B, C and D and the current through 1Ω and 2Ω resistance.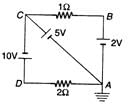
Ans. VA = 0V (as it is earthed)
VC - VA = 5W
KC = 5V VB - VA = 2V
VB = 2V VD - VC = 10V
VD = 10 + VC = 15 V= 3A from C to B as KC > KB
= 7.5A from D to A as VD > VA
Q.3. For what value of E the potential of A is equal to the potential of B?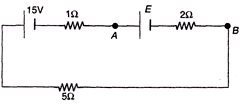
Ans. FA = FB
VAB = 0 or E - ir = 0
Solving this equation we get E = 5V
Q.4. Ten cells each of emf 1V and internal resistance 1Ω. are connected in series. In this arrangement polarity of two cells is reversed and the system is connected to an external resistance of 2Ω . Find the current in the circuit.
Ans. Net emf = (n - 2m)E
= (10 - 2 × 2) (1) = 6 V
Q.5. In the circuit shown in figure, R1 = R2 = R3 = 10Ω. Find the currents through R1 and R2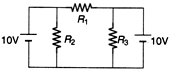
Ans.
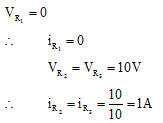
Q.6. Draw:
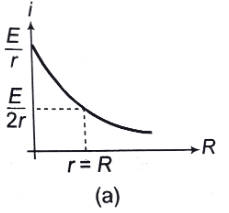
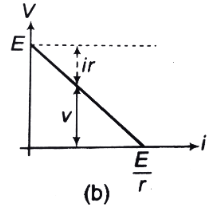
(a) current versus load, and
(b) current versus potential difference graph for a cell.
Ans.
(a)
i versus R graph is shown in answer.
(b) V =E - ir
V versus i graph is shown in answer
Introductory Exercise 20.4
Ques 1: In the circuit shown in figure, a 12 V power supply with unknown internal resistance r is connected to a battery with unknown emf. E and internal resistance 1Ω and to a resistance of 3Ω . carrying a current of 2 A. The current through the rechargeable battery is 1 A in the direction shown. Find the unknown current i, internal resistance r and the emf E.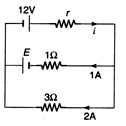
Ans: Applying loop law equation in upper loop we have,
E + 12 - ir - 1 = 0 ...(i)
Applying loop law equation in lower loop we have where i = 1 + 2 = 3A
E + 6 - 1 = 0 ...(ii)
Solving these two equations we get, E = -5Vand r = 2Ω
Ques 2: In the above example, find the power delivered by the 12 V power supply and the power dissipated in 3 W resistor.
Ans: Power delivered by a battery = Ei
= 12 × 3 = 36 W
Power dissipated in resistance = i2R
= (3) (2)2 = 12W
Introductory Exercise 20.5
Ques 1: Find the equivalent emf and internal resistance of the arrangement shown in Fig.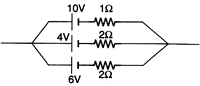
Ans: 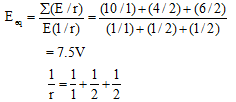
r = 0.5 W
Ques 2: If a battery of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a load of resistance R. Show that the rate at which energy is dissipated in R is maximum when R = r and this maximum power is P = E2/4r.
Ans: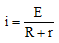
P = power across R = i2R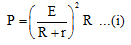
For power to be maximum,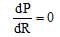
By putting we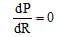 get, R = r
get, R = r
Further, by putting R = r in Eq. (i)
we get,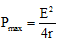
Ques 3: Two identical batteries each of emf E = 2 volt and internal resistance r =1 ohm are available to produce heat in an external resistance by passing a current through it. What is the maximum power that can be developed across an external resistance R using these batteries.
Ans: As derived in the above question,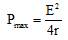
Here, E = net emf = 2 + 2 = 4 V
and r= net internal resistance
= 1 + 1 = 2Ω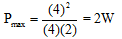
Ques 4: The full scale deflection current of a galvanometer of resistance 1Ω is 5 mA. How will you convert it into a voltmeter of range 5 V ?
Ans: V = ig(G + R)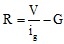 = series resistance connected with galvanometer
= series resistance connected with galvanometer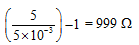
Ques 5: A micrometer has a resistance of 100Ω and full scale deflection current of 50μA. How can it be made to work as an ammeter of range 5 mA ?
Ans: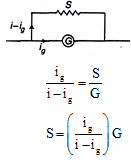
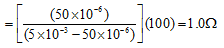
Ques 6: A voltmeter has a resistance G and range V. Calculate the resistance to be used in series with it to extend its range to nV.
Ans: V = igG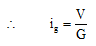
Now, nV = ig(G + R) = V/G (G + R) R = (n - 1)G
Ques 7: The potentiometer wire AB is 600 cm long.
(a) At what distance from A should the jockey J touch the wire to get zero deflection in the galvanometer.
(b) If the jockey touches the wire at a distance 560 cm from A, what will be the current through the galvanometer.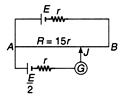
Ans: (a)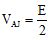 or emf of lower battery
or emf of lower battery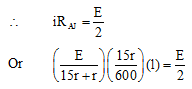
Solving this equation we get,
l = 320 cm
(b) Resistance of 560 cm =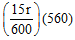
= 14r Now the circuit is as under,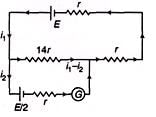
Applying loop law in upper loop we have,
E - 14r(i1 - i2) - i1r - i1r = 0 ...(i)
Applying loop law in lower law loop we have,
-E/2 - i2r + (i:- i2)(14r) = 0 ...(ii)
Solving these two equations we get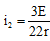
Introductory Exercise 20.6
Ques 1: For the given carbon resistor, let the first strip be yellow, second strip be red, third strip be orange and fourth be gold. What is its resistance?
Ans: Yellow → 4
Red → 2
Orange → 103
Gold → 5
R = (4.2 × 103 + 5%) Ω
Ques 2: The resistance of the given carbon resistor is (2.4 ×106Ω ± 5%)Ω . What is the sequence of colours on the strips provided on resistor?
Ans: 2 → Red
4 → Yellow
106 → Blue
5% → Gold
|
90 videos|420 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Current Electricity - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the important topics covered in DC Pandey Solutions: Current Electricity? |  |
| 2. How can DC Pandey Solutions: Current Electricity help in exam preparation? |  |
| 3. Are the solutions in DC Pandey Solutions: Current Electricity easy to understand? |  |
| 4. Are there any solved examples in DC Pandey Solutions: Current Electricity? |  |
| 5. Can DC Pandey Solutions: Current Electricity be used as a reference for competitive exams? |  |