Dalton's Atomic Theory | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
What is Dalton's Atomic Theory?
What is matter made up of? What is the smallest indivisible unit of Matter?
- Democritus, a Greek philosopher tried to answer that. He suggested that all matter is composed of smallest indivisible units called A-tomio, meaning unbreakable.
- This was the Democritus Atomic Theory. Due to the lack of technological set-up back then, scientists had very limited information on this theory.
Tip:Maharishi Kanad an ancient Indian sage, scientist and philosopher who lived in the 6th to 2nd century(actual dates not available ) first gave the atomic theory and called matter as "padarth" and atom as "parmaanu" He explained the creation and existence of universe by his Atomic before much before John Dalton gave one.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- Dalton’s atomic theory was a scientific theory on the nature of matter put forward by the English physicist and chemist John Dalton in the year 1808. It stated that all matter was made up of small, indivisible particles known as ‘atoms’.
- He published this theory in a paper titled “A New Chemical Philosophy”; indeed, the philosophy was new for that era. Let us now look at the postulates of this theory.
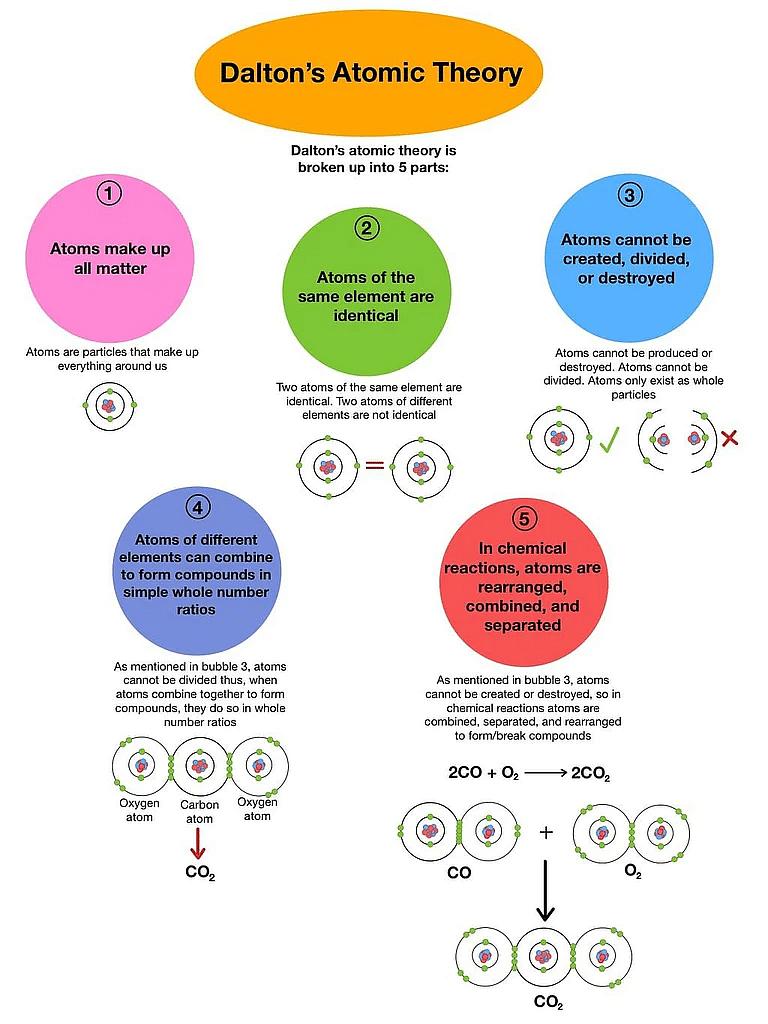
Postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- The matter is made up of indivisible particles known as atoms.
- The properties of all the atoms of a given element are the same, including mass. This can also be stated as all the atoms of an element have identical mass while the atoms of different elements have different masses.
- Atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
- Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. This implies that during chemical reactions, only reorganization of atoms takes place and no atoms are created nor destroyed.
- Atoms of an element are identical in mass, size, and many other chemical or physical properties, but atoms of two different elements differ in mass, size, and many other chemicals or physical properties.
However, this theory is not entirely free of limitations. Let us now look at the drawbacks of this theory.
Drawbacks of Dalton’s Atomic Theory of Matter
- It was proved that an atom is not indivisible. An atom can be subdivided into electrons, protons, and neutrons (Subatomic particles). But an atom is a smallest species which does not lose it’s identity after a chemical reaction.
- According to Dalton Atomic Theory, atoms of an element are identical in mass, size, and many other chemical or physical properties.
- But, practically we observe that atoms of several elements differ in their densities and masses. These atoms with different masses are known as isotopes.
Example: Chlorine (Cl) has 2 isotopes with the mass numbers of 35 and 37. - According to Dalton Atomic Theory, atoms of two different elements differ in mass, size, and many other chemicals or physical properties. However, we observe atoms of different elements having the same number of neutrons and protons and hence having equal masses. Such atoms of different elements having equal masses are called Isobars.
Example: Argon (Ar) and Calcium (Ca) atoms have an atomic mass of 40 AMU. - According to Dalton Atomic Theory, when atoms of different elements (atoms of two or more elements) combine in simple whole-number ratios, we get chemical compounds. But this is not true in the case of complex organic compounds For example- C11H22O11.
- Dalton Atomic Theory fails to explain the existence of allotropes. This implies that the Dalton atomic theory fails to explain the differences in the properties of charcoal, graphite, and diamond (allotropes of carbon).
- Dalton’s Atomic theory explains all the laws of chemical combination except the Gay lussac’s law of gaseous volumes.
- Dalton’s Atomic Theory also suggested that an atom is the smallest part of an atom that can take part in a chemical reaction.
Merits of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- The law of multiple proportions, the law of conservation of mass, and the law of constant proportions are not violated by Dalton’s atomic theory.
- The theory provides a basis to differentiate between elements and compounds.
Solved Examples
Example 1: Give the supporting laws for Dalton’s Atomic Theory.
John Dalton based his theory on two laws. They are explained below:
Law of Conservation of Mass:
According to the law of conservation of mass, the matter is neither created nor destroyed. In a chemical reaction, the amount of elements remains the same in starting when only reactants there and at the completion of the reaction when the product formed. We always use the “Law of conservation of mass” when we balance chemical equations.Law of Constant Composition:
According to the law of constant composition, a pure compound will always have the same proportion of the same elements. For example, table salt with the molecular formula of NaCl holds the same proportions of the elements Na (sodium) and Cl (chlorine). This composition doesn’t depend on where the salt came from and how much salt one should have.
Objective Questions
Example 1: Which of the following is not a postulate of Dalton’s Atomic Theory?
(a) Matter is made up of extremely small particles called atoms or molecules.
(b) Atom is the smallest particle that takes part in a chemical reaction.
(c) Atoms combine together in a simple whole-number ratio to form compound atoms.
(d) Atoms of two different elements may combine to form two or more compound atoms.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Matter is made up of extremely small particles called atoms (not molecules).
Example 2: Which of the following laws could not be explained by Dalton’s Atomic Theory?
(a) Law of constant composition
(b) Law of multiple proportions
(c) Law of reciprocal proportions
(d) Gay Lussac’s law of gaseous volumes
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Gay Lussac’s law of gaseous volumes could not be explained by Dalton’s Atomic Theory.
|
129 videos|238 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Dalton's Atomic Theory - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is Dalton's Atomic Theory? |  |
| 2. What are the postulates of Dalton's Atomic Theory? |  |
| 3. What are the drawbacks of Dalton's Atomic Theory of Matter? |  |
| 4. What are the merits of Dalton's Atomic Theory? |  |
| 5. Can you provide a solved example related to Dalton's Atomic Theory? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|













