Judiciary Exams Exam > Judiciary Exams Notes > Civil Law for Judiciary Exams > Difference Between Coercion and Undue Influence
Difference Between Coercion and Undue Influence | Civil Law for Judiciary Exams PDF Download
Coercion and Undue Influence in Contract Law
Coercion
- Definition: Coercion, within the realm of contract law, involves obtaining consent for an agreement through the use of threats, force, or intimidation against the other party.
- Explanation: In simpler terms, coercion occurs when one party compels another to agree to a contract under the influence of fear or duress.
- Example: For instance, if Party A threatens physical harm to Party B unless Party B signs a contract, this would constitute coercion.
- Legal Implication: Contracts formed under coercion are typically deemed voidable, providing the coerced party with the option to uphold or reject the contract.
- Consequences: If the coerced party opts to void the contract, they can seek release from their obligations due to the involuntary nature of their consent.
Undue Influence
- Definition: Undue influence occurs when one party takes advantage of a position of power over another to manipulate their decision-making.
- Explanation: This influence can arise from a variety of factors such as a fiduciary relationship or the vulnerability of one party.
- Example: If a mentor persuades a mentee to sign a contract that heavily favors the mentor's interests, this could be considered undue influence.
- Legal Implication: Contracts tainted by undue influence are also typically voidable, aiming to protect parties from unfair agreements.
- Remedies: The party subjected to undue influence may seek to have the contract set aside or modified to rectify the imbalance caused by the undue influence.
Understanding Undue Influence
- Undue influence is a key concept in contract law that involves one party exploiting a position of power or trust to manipulate another party's decision-making process, resulting in an unfair or unconscionable agreement.
- Unlike coercion, which typically involves threats or force, undue influence relies on the misuse of a dominant position to control the consent of the other party.
- The party exerting undue influence may not necessarily resort to physical intimidation or explicit threats. Instead, they leverage a special relationship, such as a fiduciary duty or a position of trust, to apply psychological or emotional pressure on the vulnerable party.
- This kind of influence significantly affects the weaker party's capacity to make independent and well-informed decisions.
Examples of Undue Influence
- A doctor pressuring a vulnerable patient into signing a contract that primarily benefits the doctor illustrates a case of undue influence.
- An attorney taking advantage of their client's trust to secure an unfair advantage in a contractual agreement also demonstrates the misuse of undue influence.
Question for Difference Between Coercion and Undue InfluenceTry yourself: Which of the following best describes coercion in contract law?View Solution
Difference Between Coercion and Undue Influence
Meaning
- Coercion: Coercion involves forcing or threatening a party who is unwilling to enter into a contract.
- Undue Influence: Undue influence refers to influencing a person's will through psychological pressure or taking advantage of an existing relationship.
Nature of Offence
- Coercion: Considered a criminal offence involving the use of force or physical violence.
- Undue Influence: Not a criminal offence but renders the contract voidable if proven.
Legal Provisions
- Coercion: Covered under Section 15 of the Indian Contract Act 1872.
- Undue Influence: Addressed under Section 16 of the Indian Contract Act 1872.
Relationship of Contracting Parties
- Coercion: No prior relationship between the parties involved.
- Undue Influence: Requires an established relationship between the parties.
- Actions:
- Coercion: Involves threats, physical violence, or force to obtain consent.
- Undue Influence: Involves psychological pressure or exploiting emotional vulnerabilities.
- Aim:
- Coercion: Aims to force a person into a contract for the coercing party's benefit.
- Undue Influence: Used to take advantage of the other party's weakness or vulnerability.
- Burden of Proof:
- Coercion: The burden of proof lies with the aggrieved party to demonstrate the use of force or threats.
- Undue Influence: The burden of proof lies with the dominating party to show their influence was not improper.
- Examples:
- Coercion: Party "A" threatens harm to party "B" if party "C" does not sell property to "A".
- Undue Influence: A teacher promises a student full marks in exchange for the student selling their car at an unreasonably low price.
Below is a table to distinguish between Coercion and Undue Influence: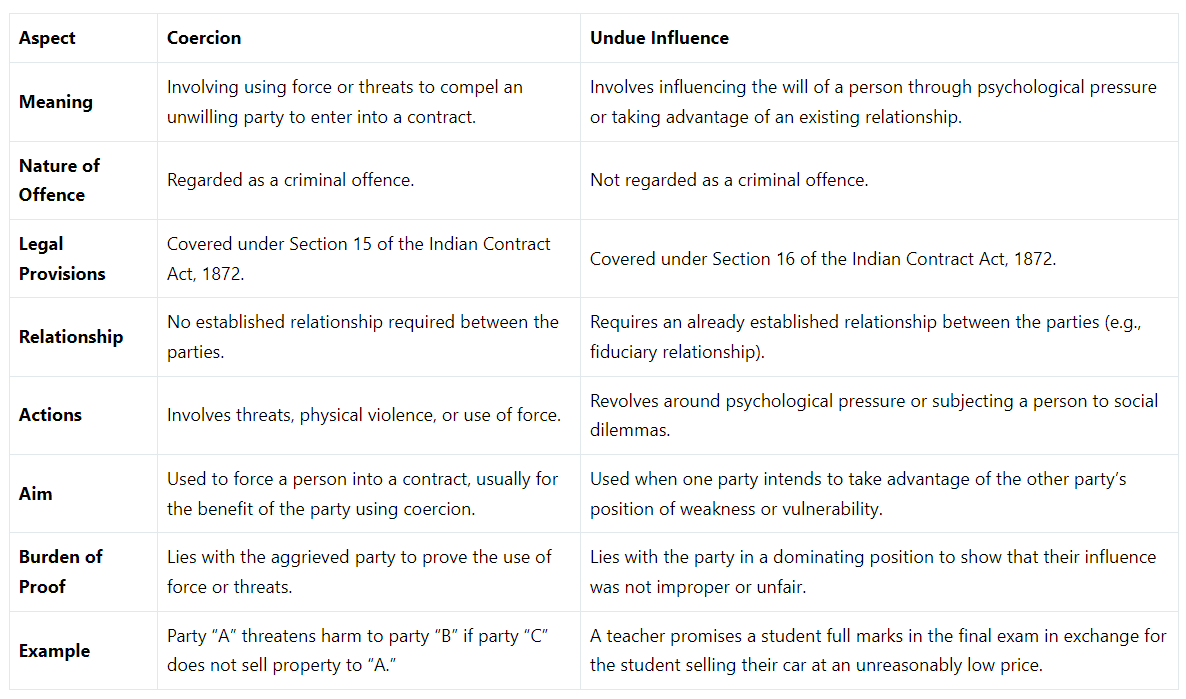
Final Thoughts
- Coercion involves using force or threats to obtain consent, while undue influence is the improper use of power or trust to manipulate someone into an agreement.
- Coercion is a criminal offense, while undue influence is not.
- Both concepts aim to protect the integrity of contracts and ensure that parties enter into agreements willingly and fairly.
- Understanding the differences between coercion and undue influence helps safeguard the rights of parties involved in contractual relationships and promotes fairness in contractual dealings.
Question for Difference Between Coercion and Undue InfluenceTry yourself: Which of the following best describes the nature of coercion and undue influence?View Solution
The document Difference Between Coercion and Undue Influence | Civil Law for Judiciary Exams is a part of the Judiciary Exams Course Civil Law for Judiciary Exams.
All you need of Judiciary Exams at this link: Judiciary Exams
|
363 docs|256 tests
|
FAQs on Difference Between Coercion and Undue Influence - Civil Law for Judiciary Exams
| 1. What is the difference between coercion and undue influence in contract law? |  |
Ans. Coercion in contract law refers to the use of threats or force to make a party enter into a contract, while undue influence involves one party taking advantage of a relationship of trust and confidence to unfairly influence the other party into entering a contract.
| 2. How is undue influence defined in contract law? |  |
Ans. Undue influence in contract law occurs when one party exerts improper pressure on another party, exploiting a relationship of trust and confidence to persuade the other party to enter into a contract that benefits the influencing party.
| 3. What are some examples of coercion in contract law? |  |
Ans. Examples of coercion in contract law include threats of physical harm, blackmail, or other forms of intimidation used to force a party to enter into a contract against their will.
| 4. How can a contract be invalidated due to undue influence? |  |
Ans. A contract can be invalidated due to undue influence if it can be proven that one party took advantage of a relationship of trust and confidence to unfairly influence the other party into entering the contract. The influenced party must demonstrate that they were pressured into the contract and did not freely consent to its terms.
| 5. How can parties protect themselves from coercion and undue influence in contracts? |  |
Ans. Parties can protect themselves from coercion and undue influence in contracts by ensuring that all negotiations are conducted freely and voluntarily, seeking legal advice before entering into any agreement, and being aware of their rights and responsibilities under contract law.
Related Searches
















