Direct and indirect speech | English Grammar Basic - Class 10 PDF Download
Introduction
- A Reported Speech is the speech of a person as narrated by himself (Direct), or by someone else (Indirect).
- In Direct speech, we quote the very actual words of the speaker without change, while in Indirect speech, we give his words in the third person, with a reporting verb of saying or thinking, exactly following the sequence of tenses.
- Present or Future tense in the Reporting Verb may be followed by any tense in the Reported Speech.
- Example: Direct: John says, "I did not go and I will not go."
Indirect: John says that he did not go and he will not go.
Change of Tense
A Past Tense in the Reporting Verb is generally followed by a Past Tense in the Reported Verb, with corresponding changes in adjectives and adverbs.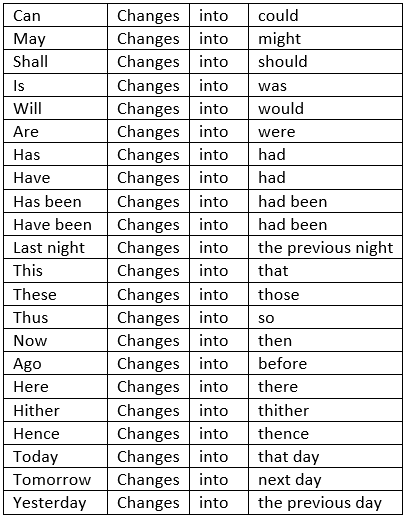
- Direct: John said, "I cannot do it now".
Indirect: John said that he could not do it then. - Direct: Jones said, "I shall go home tomorrow".
Indirect: Jones said that he should go home the next day. - Direct: Meena said, "This is the book I lost".
Indirect: Meena said that was the book she had lost. - Direct: "I came home last night," said he.
Indirect: He said that he had come home the previous night. - Direct: "Twelve years ago," said Rahul, "I came to this world".
Indirect: Rahul said that he had come to that world twelve years before.
Reported Speech: Past Tenses
The Past Indefinite and Past Continuous tenses in the Reported Speech are converted into Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous tenses respectively if the Reporting Verb is in the Past tense.
- Direct: The man said, "The work was done".
Indirect: The man said that the work had been done. - Direct: Frank said, "The train reached at six".
Indirect: Frank said that the train had reached six. - Direct: George said, "The boy was doing his work".
Indirect: George said the boy had been doing his work. - Direct: Tom said, "The man died yesterday".
Indirect: Tom said that the man had died the previous day.
If the Reported Speech states some general, universal, or habitual truth, the Present Tense used there is not changed into the corresponding past form.
- Direct: The teacher said, "Ice floats in water".
Indirect: The teacher said that ice floats in water. - Direct: Father said, "Man is the only animal that cooks his food".
Indirect: Father said that man is the only animal that cooks his food. - Direct: "Man is mortal," he said.
Indirect: He said that man is mortal. - Direct: Madam said, "The earth revolves around the Sun".
Indirect: Madam said that the Earth revolves around the Sun. - Direct: My mother said, "The Sun gives us light".
Indirect: My mother said that the Sun gives us light.
Examples
Let's look at some examples:
Example 1: Direct: "I love playing football," said Tom. How would you convert this into indirect speech?
(a) Tom said that he loves playing football.
(b) Tom said that he loved playing football.
(c) Tom says that he loves playing football.
(d) Tom will say that he loves playing football.
Ans: (b) Tom said that he loved playing football.
The present tense "love" changes to the past tense "loved" because the reporting verb "said" is in the past tense.
Example 2: Direct: "I have never been to Paris," said Maria. How would you convert this into indirect speech?
(a) Maria said that she had never been to Paris.
(b) Maria says that she had never been to Paris.
(c) Maria said that she has never been to Paris.
(d) Maria says that she has never been to Paris.
Ans: (a) Maria said that she had never been to Paris.
The present perfect "have been" changes to past perfect "had been" because the reporting verb "said" is in the past tense.
Example 3: Direct: "I am going to the store," said John. How would you convert this into indirect speech?
(a) John said that he was going to the store.
(b) John says that he was going to the store.
(c) John said that he is going to the store.
(d) John says that he is going to the store.
Ans: (a) John said that he was going to the store.
The present continuous "am going" changes to past continuous "was going" because the reporting verb "said" is in the past tense.
Example 4: Direct: "I will call you tomorrow," said Jane. How would you convert this into indirect speech?
(a) Jane said that she would call me the next day.
(b) Jane says that she would call me the next day.
(c) Jane said that she will call me the next day.
(d) Jane says that she will call me the next day.
Ans: (a) Jane said that she would call me the next day.
The future tense "will call" changes to "would call" because the reporting verb "said" is in the past tense.
Example 5: Direct: "I am learning French," said Peter. How would you convert this into indirect speech?
(a) Peter said that he was learning French.
(b) Peter says that he was learning French.
(c) Peter said that he is learning French.
(d) Peter says that he is learning French.
Ans: (a) Peter said that he was learning French.
The present continuous "am learning" changes to past continuous "was learning" because the reporting verb "said" is in the past tense.
Example 6: Direct: "I have finished my homework," said Lisa. How would you convert this into indirect speech?
(a) Lisa said that she finished her homework.
(b) Lisa says that she finished her homework.
(c) Lisa said that she had finished her homework.
(d) Lisa says that she has finished her homework.
Ans: (c) Lisa said that she had finished her homework.
The present perfect "have finished" changes to past perfect "had finished" because the reporting verb "said" is in the past tense.
|
20 videos|143 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Direct and indirect speech - English Grammar Basic - Class 10
| 1. What is the importance of exam preparation? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively study for exams? |  |
| 3. What are some tips for managing exam stress? |  |
| 4. How can I improve my exam performance? |  |
| 5. How can I stay motivated during exam preparation? |  |

















