Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Dispersion of Light
Dispersion of Light | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Dispersion of Light
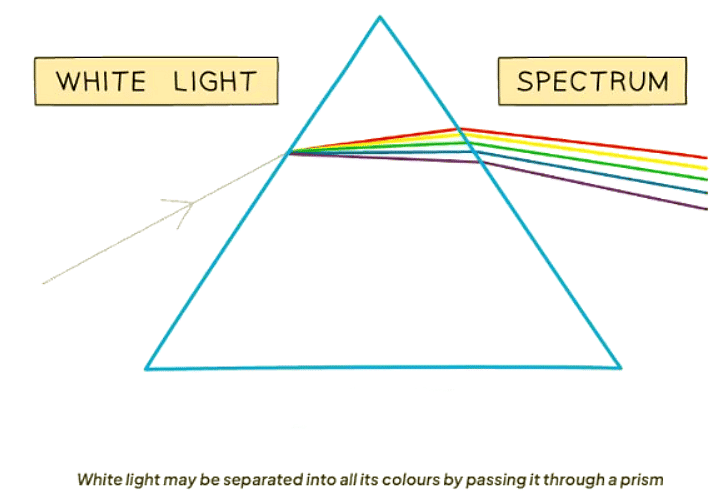
- White light contains all the colors of the spectrum.
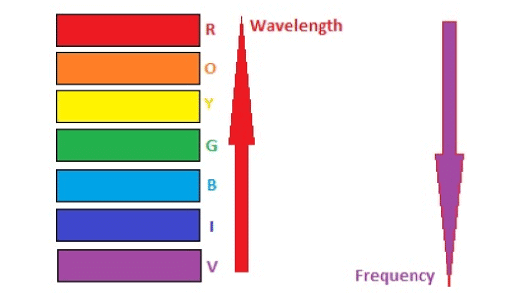
- Each color within white light possesses a unique wavelength and frequency, representing a specific segment of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- When white light is passed through a prism, it separates into its component colors due to refraction. Violet light undergoes the most refraction, while red light experiences the least, leading to the formation of a spectrum.
- The phenomenon of light dispersion through a prism mirrors the creation of a rainbow in nature.
The Visible Spectrum of Light
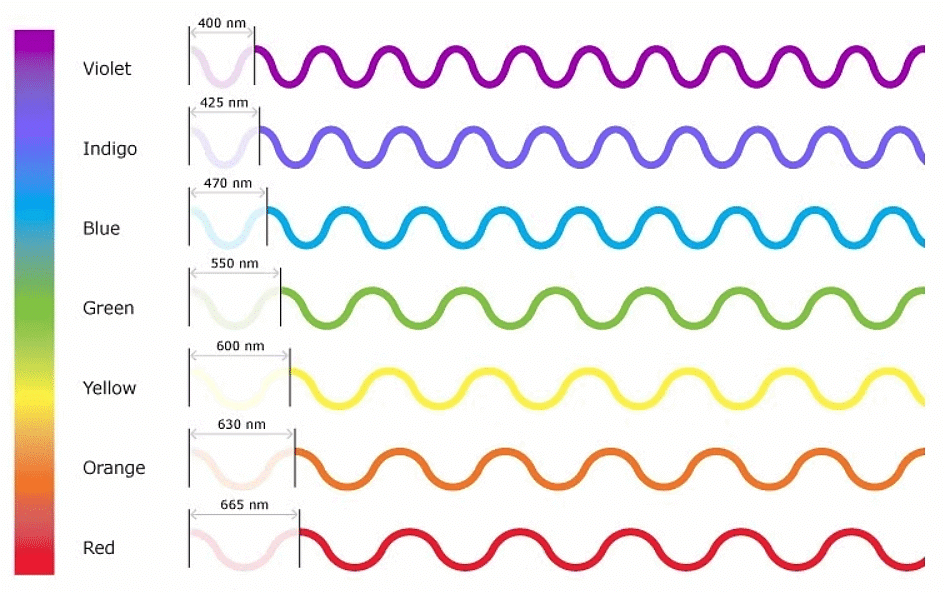
- Visible light encompasses the range of wavelengths detectable by the human eye.
- It represents only 0.0035% of the entire electromagnetic spectrum.
- While humans see only visible light, certain animals like birds, bees, and some fish perceive beyond, including infrared and ultraviolet wavelengths.
- Different colors correspond to different wavelengths: Red has the longest wavelength and lowest frequency, while violet has the shortest wavelength and highest frequency.
Question for Dispersion of LightTry yourself: What happens when white light is passed through a prism?View Solution
Monochromatic Light
- Light is a transverse wave
- The different colors of light all have varying wavelengths and frequencies. Red possesses the longest wavelength while violet has the shortest.
- Light of a single wavelength, or single frequency, is termed monochromatic.
The document Dispersion of Light | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Dispersion of Light - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is dispersion of light? |  |
Ans. Dispersion of light refers to the process by which light is separated into its component colors, or wavelengths, as it passes through a medium. This phenomenon occurs because different colors of light travel at different speeds in a medium, causing them to bend at different angles.
| 2. What is the visible spectrum of light? |  |
Ans. The visible spectrum of light is the range of wavelengths that are visible to the human eye. It consists of colors ranging from violet (shorter wavelengths) to red (longer wavelengths), including blue, green, yellow, and orange in between.
| 3. What is monochromatic light? |  |
Ans. Monochromatic light is light that consists of a single wavelength or color. It is characterized by having a very narrow range of wavelengths, which results in a pure and specific color appearance.
| 4. How does dispersion of light occur in a prism? |  |
Ans. Dispersion of light occurs in a prism due to the phenomenon of refraction. When light enters a prism, it is bent or refracted at different angles based on the wavelength of the light. This causes the different colors of light to separate and form a spectrum.
| 5. How is dispersion of light used in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Dispersion of light is commonly used in optical devices such as spectrometers and prisms to analyze and separate light into its component colors. It is also utilized in technologies like DVD players, where the separation of colors is essential for accurate data reading and playback.
Related Searches















