Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Distribution of Industrial Zones
Distribution of Industrial Zones | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Distribution & Location of Factories & Industrial Zones
- Companies regularly make choices regarding the placement of their industries.
- Various industries have distinct input requirements, necessitating ready and affordable access to these resources.
- Companies typically seek locations that offer the lowest expenses and the greatest potential for profit.
- Manufacturers must identify the ideal location that will yield the highest profits.
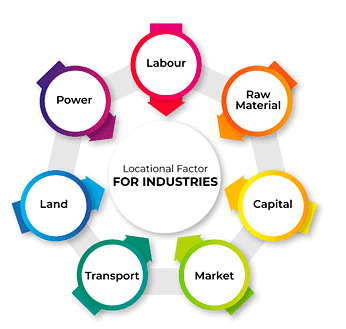
- This determination hinges on multiple factors encompassing physical, human, and economic considerations.
Physical factors
- Raw Materials: Industries requiring heavy or bulky materials tend to situate themselves in close proximity to these resources for cost-effectiveness.
- Site Selection: The availability and affordability of land are crucial. Large factories typically require flat, well-drained land that may allow for future expansion.
- Climate Considerations: Industries like aerospace and film production benefit from sunnier climates. Favorable weather not only reduces energy expenses but also enhances overall quality of life.
- Energy Needs: Energy-intensive industries often relocate to regions with affordable or easily accessible energy sources.
- Natural Routeways: Locations near harbors, motorways, airports, and railways are advantageous for industrial complexes. These areas offer excellent access points for both imports and exports.
- Water Resources: Certain industries such as paper and cotton processing rely heavily on water during manufacturing processes. Hence, proximity to reliable water sources like lakes and rivers is vital.
Human and economic factors
- Capital: Some regions naturally attract investments due to higher returns. For instance, Silicon Valley in the U.S. is renowned for attracting venture capital due to its history of successful tech startups.
- Markets: The size and location of potential markets significantly impact industries. For example, a company producing winter sports gear would likely choose a location near ski resorts for easier market access.
- Government Influence: Government policies, incentives, and grants play a crucial role in attracting industries to specific areas. One such example is China's Special Economic Zones, offering tax benefits and streamlined regulations to encourage investment.
- Transport: The cost and ease of transport are vital factors influencing industrial location decisions. Amazon strategically places fulfillment centers near major highways and airports to optimize delivery efficiency.
- Communications: Efficient communication with customers and suppliers is essential for successful manufacturing. Companies like Apple rely on advanced communication networks to coordinate global supply chains effectively.
- Labour Force: The quality, cost, and availability of labor significantly impact manufacturing operations. Germany's manufacturing sector thrives due to its highly skilled workforce and strong apprenticeship programs.
- Quality of Life: Highly skilled workers prefer locations with a good work-life balance. For instance, tech companies in California offer perks like flexible schedules to attract top talent.
High-Tech Industry
- High-Tech Industry Diversity: High-tech companies operate in various cutting-edge fields like aerospace, medical technology, and software development.
- Cluster Formation: These industries often come together in science parks to enhance collaboration and innovation.
- Proximity to Educational Institutions: Being near universities and research centers ensures a conducive environment for learning and research, often with heightened security.
- Infrastructure for Innovation: Purpose-built facilities encourage research and development, fostering technological advancement and other high-level activities.
- Transport Connectivity: Strategic proximity to transport networks, including airports, facilitates the efficient exchange of knowledge and goods.
- Urban Planning Considerations: Locations are deliberately chosen away from residential and commercial zones to minimize disturbances like noise and pollution.
Question for Distribution of Industrial ZonesTry yourself: What is one of the physical factors that companies consider when choosing the location of their industries?View Solution
Changes to manufacturing and location over time
- Depletion of raw material sources prompts manufacturing relocations.
- Infrastructure diversification enables businesses to operate independently of traditional energy centers like coalfields.
- Escalating costs, including wages and regulatory factors, drive manufacturing shifts away from middle-income countries (MICs).
- Enhanced transportation facilitates easier commuting and migration by reducing travel barriers.
- Technological advancements reduce workforce requirements, exemplified by the utilization of ICT in banking.
- ICT progress fosters telecommuting and increased air travel opportunities.
- Outsourcing initiatives are adopted to cut costs by transferring work to external locations such as call centers.
- Economic progression entails shifts in employment sector compositions.
- Developed nations like the UK and the USA embody "post-industrial societies" where the tertiary and quaternary sectors dominate employment.
- Industrial societies like China and India feature substantial employment within the secondary sector.
- Pre-industrial societies like Bolivia and Mozambique predominantly rely on the primary sector for employment.
Case Study - Manufacturing Industry: Pakistan's Iron & Steel Industry

Question for Distribution of Industrial ZonesTry yourself: What factor prompts manufacturing relocations due to the depletion of raw material sources?View Solution
The document Distribution of Industrial Zones | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
55 videos|68 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Distribution of Industrial Zones - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How has the location of high-tech industries changed over time? |  |
Ans. The location of high-tech industries has shifted over time towards areas with access to skilled labor, research institutions, and infrastructure such as technology parks and business incubators.
| 2. What are the factors influencing the location of industrial zones? |  |
Ans. Factors influencing the location of industrial zones include proximity to raw materials, transportation networks, labor availability, government incentives, and market demand.
| 3. Can you provide an example of a case study in the manufacturing industry related to industrial location? |  |
Ans. One example is Pakistan's Iron & Steel Industry, which has strategically located factories near major ports for easy import of raw materials and export of finished products.
| 4. How has the distribution of industrial zones evolved in recent years? |  |
Ans. The distribution of industrial zones has become more diversified, with a focus on creating specialized clusters for specific industries such as automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
| 5. What role does technology play in shaping the location of factories in the high-tech industry? |  |
Ans. Technology plays a crucial role in determining the location of factories in the high-tech industry by requiring access to advanced infrastructure, skilled workforce, and proximity to research and development centers.
Related Searches















