NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Additional Study Material for NEET > Euglenoids, Slime Moulds & Protozoans
Euglenoids, Slime Moulds & Protozoans | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Division - Euglenophyta - Euglenoids
- Previously euglenoids were placed in plant kingdom due to their photosynthetic ability. But due to the absence of cell wall and animals like nutrition, some scientists placed them in the animal kingdom. But now according to five kingdom classification, they are included in Protista.
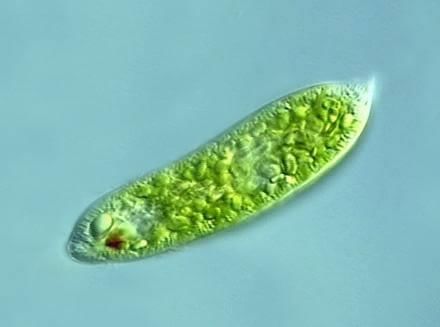
 Euglenoid
Euglenoid - They are found as free-living organisms in freshwater lakes, ponds, etc. But sometimes they are also found in damp soil and brackish water.
- On the basis of their mode of nutrition, they are called as mixotrophic because they have the holophytic, holozoic and saprophytic mode of nutrition.
Example: Euglenoids - Euglena, Paranema.
➢ Structure
- They are unicellular and the cell wall is absent around them. They are surrounded by a cell membrane which is made up of lipoprotein and this cell membrane is covered with a pellicle. The pellicle is made up of lipoprotein and it is elastic in nature.
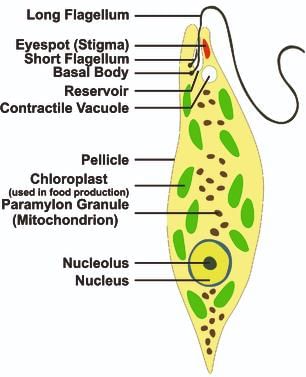
 Structure of Euglenoid
Structure of Euglenoid - At the anterior end of Euglenoids, a cavity is present, which is known as the reservoir. The flagellum is originated from the base of the reservoir. Euglenoids have only one functional flagellum and one non-functional flagellum. One eyespot is present at an anterior position.
- They have a contractile vacuole. These contractile vacuoles help in osmoregulation.
- Euglenoids have a haploid nucleus and chloroplast.
- Chloroplast has the following pigments: Chl. 'a', Chl. 'b' and Xanthophyll (Zeaxanthin).
 View Answer
View AnswerNote: Stored food - Paramylum and fat- Paramylum is a carbohydrate, which is formed by the modification of starch.
- Wriggling movement: Euglenoids are motile. They are of two type - flagellated and Non-flagellated.
- Flagellated Euglenoids locomote with the help of flagella. But non-flagellated Euglenoids are also motile.
- These non-flagellated euglenoids locomote by wriggling movement, which is also called a Euglenoid movement.
- Wriggling movement is due to the wave motion of the pellicle.
➢ Reproduction
- Asexual reproduction by longitudinal binary fission.
 Longitudinal Binary Fission in Euglenoid
Longitudinal Binary Fission in Euglenoid - Also, reproduce by cyst formation during unfavourable conditions.
- Sexual reproduction has not been seen yet.
Slime Moulds
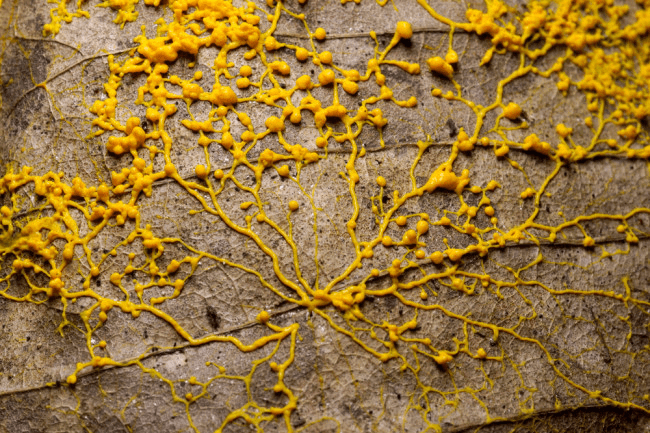
- These organisms develop a slimy mass at the time of their vegetative phase. Therefore they are called slime moulds. They are also called false fungi.
 Slime Mould
Slime Mould - They are found on decaying stem, leaves etc, so these are saprophyte.
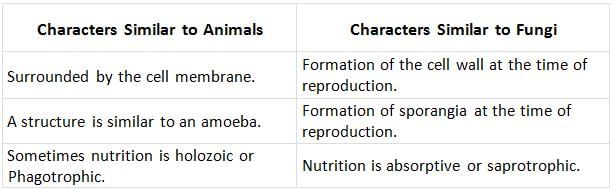
- Slime moulds have characters of both animals & fungus, therefore, they are also called Fungus animals.
- Scientist Anton De Bary placed them in Mycetozoa by relating them with animals. While mycologist 'Ainsworth' placed them in Myxomycota by relating them with fungi.
- But nowadays modern scientists place them in Class - Gymnomycota (Gymnomycota-naked fungi) of Kingdom Protista and now these are known as Protistan fungi.

➢ On the basis of structure, Slime Moulds are of two types:
(i) Acellular Slime Moulds
- Their body is made up of wall-less multinucleated protoplasmic mass. This type of body is known as plasmodium. (Plasmodium = wall-less coenocyte).
- During unfavourable conditions, plasmodium forms fruiting bodies.
- They are diploid, i.e. every nucleus found in the cell is diploid.
Example: Physarum, Stemonitis, Physarella, Fulgio.
(ii) Cellular Slime Moulds
- Their body consists of many wall-less amoeba-like cells (the group of amoeba-like cells is known as cellular slime mould).
- These cells are found in groups but they are not fused. Every cell has a haploid nucleus. This type of body is called as myxamoeba or pseudoplasmodium.
- They are haploid because the nucleus found in each cell is haploid.
Example: Dictyostelium, Protostelium, Acytostelium
➢ Slime moulds have both asexual & sexual type of reproduction:
- Asexual reproduction: It is mainly with the help of spore formation (sporangia). The mucilaginous sporangium of slime moulds is known as capillitium.
- Sexual reproduction: The cells of acellular slime moulds are diploid. So they reproduce by gametic meiosis. Therefore, their life cycle is diplontic. The cells of cellular slime moulds are haploid, so they reproduce by zygotic meiosis. Therefore, their life cycle is haplontic.
Protozoans
All protozoans are heterotrophs and live as predators or parasites. They are believed to be primitive relatives of animals.
There are four major groups of protozoan:
- Flagellated Protozoans: They possess flagella for locomotion. They may be free-living aquatics, parasites, commensals or symbionts. Zooflagellates are generally uninucleate, occasionally multinucleate.
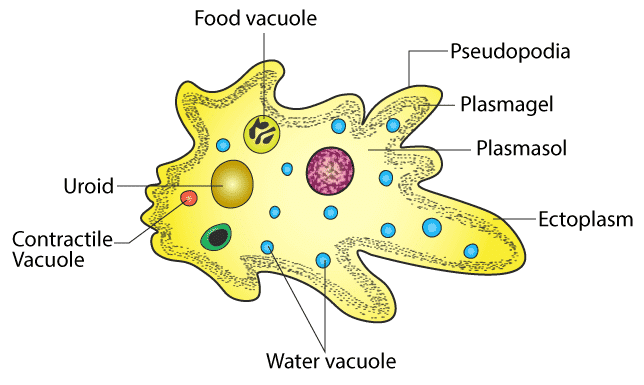
- Amoebid Protozoans: They develop pseudopodia which are temporary protoplasmic outgrowths. These are used for locomotion and engulfing food articles. Sarcodines are mostly free-living, found in freshwater, seawater and on damp soil.
 Amoeba
Amoeba - Sporozoans: All sporozoans are endoparasites. Some sporozoans such as Eimeria cause severe diseases like coccidiosis in the birds. Nutrition is parasitic (absorptive). Phagotrophy is rare.
- Ciliated Protozoans: Ciliates are protozoan protists. These develop a number of cilia during a part or whole of the life cycle. They use cilia for locomotion and driving food. There is a high degree of morphological and physiological specialisation. There are definite regions for ingestion and egestion. The region of ingestion consists of an oral groove, cytostome (mouth) and gullet.
The document Euglenoids, Slime Moulds & Protozoans | Additional Study Material for NEET is a part of the NEET Course Additional Study Material for NEET.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Euglenoids, Slime Moulds & Protozoans - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What are the characteristics of Euglenoids? |  |
Ans. Euglenoids, also known as Euglenophyta, are a group of unicellular organisms that belong to the division Euglenophyta. They are characterized by the presence of flagella, which they use for locomotion. They also have a flexible proteinaceous structure called a pellicle that provides support to their cell membrane. Euglenoids are photosynthetic organisms, containing chloroplasts that enable them to produce their own food through photosynthesis. They are commonly found in freshwater environments.
| 2. What is the role of slime molds in the ecosystem? |  |
Ans. Slime molds are unique organisms that belong to the group known as Myxomycetes. Although they were once classified as fungi, they are now considered to be a separate group. Slime molds play an important role in the ecosystem as decomposers. They feed on dead organic matter, such as decaying plants and tree bark, breaking it down and recycling nutrients back into the environment. This helps in the process of nutrient cycling and contributes to the overall health of the ecosystem.
| 3. What are the major groups of protozoans? |  |
Ans. Protozoans are a diverse group of unicellular organisms that belong to the kingdom Protista. They are classified into several major groups based on their characteristics and mode of locomotion. Some of the major groups of protozoans include amoebas, which move using pseudopodia (temporary extensions of their cell membrane); ciliates, which move using hair-like structures called cilia; flagellates, which move using whip-like flagella; and sporozoans, which are non-motile parasites that reproduce through spores.
| 4. How do Euglenoids obtain their nutrients? |  |
Ans. Euglenoids are photosynthetic organisms, meaning they can produce their own food through photosynthesis. They contain chloroplasts, which contain the pigment chlorophyll, responsible for capturing sunlight energy. Euglenoids also have a specialized organelle called an eyespot, which helps them detect light. However, in the absence of sufficient light, Euglenoids can switch to a heterotrophic mode of nutrition. They can engulf particles of organic matter through a process called phagocytosis, allowing them to obtain nutrients from their environment.
| 5. Can slime molds move? |  |
Ans. Yes, slime molds are capable of movement, although it is quite different from the movement observed in other organisms. During their feeding stage, slime molds move by extending their cytoplasmic streaming, creating a network of threads or pseudopodia. These threads extend towards sources of food, allowing the slime mold to engulf and consume it. Slime molds can also move in response to environmental cues, such as light or chemical gradients. However, it is important to note that slime molds are not considered animals and have distinct characteristics that set them apart from other organisms.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches