Respiration in Plants Chapter Notes | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introduction
- All living organisms need energy to carry out their daily activities like absorption, transport, movement, and reproduction. This energy comes from food, which is broken down with the help of oxygen to release energy.
- This process of breaking down food to release energy is called respiration.
Photosynthesis: The Source of Food
- Only green plants and cyanobacteria can make their own food through a process called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, these organisms trap light energy and convert it into chemical energy, which is stored in carbohydrates like glucose, sucrose, and starch.
- Photosynthesis happens in special cell parts called chloroplasts, which are usually found in the upper layers of green plant cells. However, not all parts of a plant can do photosynthesis. Non-green parts of the plant also need food, so nutrients from photosynthesis are transported to these areas.

How Do Animals Get Their Food?
- Animals cannot make their own food, so they are called heterotrophs. They get their food in different ways:
- Herbivores eat plants directly.
- Carnivores eat other animals, which indirectly means they are also getting energy from plants because plants are at the base of the food chain.
- Saprophytes, like fungi, feed on dead and decaying matter.
- No matter how animals get their food, all the food they eat ultimately comes from photosynthesis, either directly or indirectly.
Cellular Respiration: Breaking Down Food for Energy
- This chapter is about cellular respiration, which is the process of breaking down food inside the cell to release energy. This energy is then trapped in a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which acts like an energy currency for the cell.
- ATP is used for various energy-requiring processes in the cell, and the carbon skeleton produced during respiration can be used to make other molecules the cell needs.
Where Does Respiration Happen?
- In eukaryotic cells (cells with a nucleus), photosynthesis happens in the chloroplasts, while the breakdown of food to release energy occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell.
- During cellular respiration, the bonds between carbon atoms in complex organic molecules are broken through a process called oxidation. This process releases a lot of energy. The substances that are oxidised during respiration are called respiratory substrates.
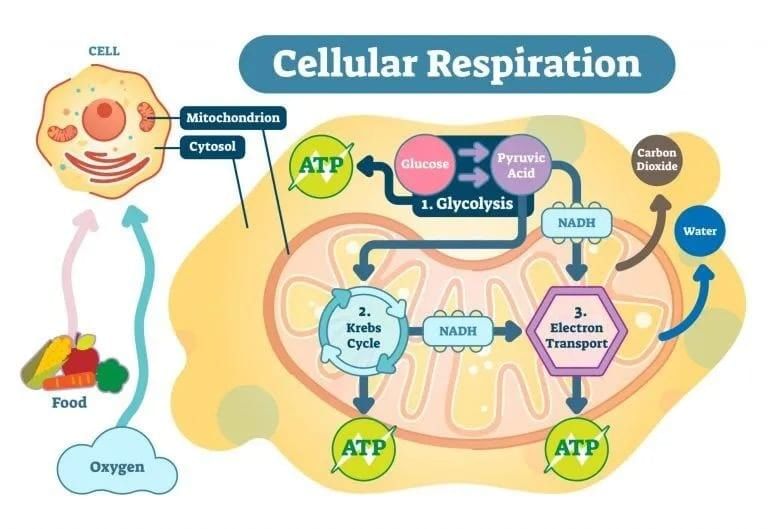
What Do Cells Use as Respiratory Substrates?
- Usually, cells oxidise carbohydrates to release energy, but under certain conditions, proteins, fats, and even organic acids can also be used as respiratory substrates.
- During the oxidation process in a cell, the energy is not released all at once. Instead, it is released slowly in a series of controlled reactions with the help of enzymes. This energy is trapped as chemical energy in the form of ATP.
- Therefore, the energy released during respiration cannot be used directly. It is first used to make ATP, which is then broken down whenever the cell needs energy.
ATP: The Cell's Energy Currency
- ATP acts as the energy currency of the cell. The energy stored in ATP is used for various processes that require energy in the cell.
- The carbon skeleton produced during respiration can be used as building blocks for making other molecules in the cell.
Do Plants Breathe?
The question of whether plants breathe is not as simple as it seems. Yes, plants do need oxygen (O₂) for respiration, and they also release carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the process. However, plants have their own ways of ensuring they have the necessary oxygen without needing specialized organs for gas exchange like animals do. Instead, plants use tiny openings called stomata and lenticels to take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
Why Plants Don’t Need Respiratory Organs
- Self-Sufficient Gas Exchange: Each part of the plant, whether it’s the roots, stems, or leaves, takes care of its own gas exchange needs. There’s not much need for gases to be transported from one part of the plant to another.
- Lower Gas Exchange Demands: Plants have a much lower requirement for gas exchange compared to animals. The rate of respiration in roots, stems, and leaves is significantly lower in plants.
- Photosynthesis and Gas Exchange:. large volume of gases is exchanged during photosynthesis. Each leaf is well-equipped to handle its own gas exchange during this process. While photosynthesis is happening, there’s no issue with oxygen availability because it is produced within the cells.
- Short Diffusion Distance: Even in large plants, the distance that gases need to diffuse is not very far. Each living cell in a plant is located close to the surface, which makes gas exchange efficient.
Gas Exchange in Different Parts of Plants
1. In Leaves:
- Gas Exchange: Leaves have a unique structure that allows for efficient gas exchange. The cells in leaves are packed loosely, creating a network of air spaces. This means that most plant cells, at least partially, are in contact with air, facilitating the exchange of gases.
- Photosynthesis: During photosynthesis, leaves take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. This process is crucial for the plant’s energy production and growth.
2. In Stems:
- Gas Exchange: In stems, living cells are found in thin layers inside and beneath the bark. These cells also play a role in gas exchange through openings called lenticels.
- Structure: The interior cells of the stem are dead and provide mechanical support to the plant. Most plant cells have a part of their surface in contact with air, which aids in gas exchange.
3. In Roots:
- Gas Exchange: Similar to stems, roots also have living cells that are arranged in a way that allows for gas exchange. The loose packing of cells in roots creates air spaces, facilitating the exchange of gases.
- Oxygen and Anaerobic Conditions: While roots generally take in oxygen, some cells can survive in environments without oxygen. These are called facultative anaerobes. Evidence suggests that the first cells on Earth existed in an oxygen-free atmosphere, and some living organisms today are adapted to life without oxygen.
The Process of Respiration in Plants
- Respiration in plants is the process of breaking down glucose to release energy, with the help of oxygen. The chemical reaction can be summarized as: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
- During this process, plants produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. However, not all the energy released is used immediately. Some of it is stored in the form of ATP, which is used for various cellular activities.
- The key to efficient respiration is to oxidize glucose in small steps, allowing some energy to be captured for ATP synthesis. This process is known as respiration.
Glycolysis
- Glycolysis is the process by which living organisms partially oxidize glucose to pyruvic acid, and it does not require oxygen.
- Origin of the term. The word "glycolysis" comes from Greek, meaning sugar splitting.
- Pathway description. The glycolysis pathway, often called the EMP pathway, was described by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and J. Parnas.
- Occurrence in organisms. In anaerobic organisms, glycolysis is the only method of respiration. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of cells and is present in all living organisms.
- Glycolysis process. During glycolysis, glucose is partially oxidized to produce two molecules of pyruvic acid. In plants, this glucose is derived from sucrose, which is produced during photosynthesis or from stored sources.
Note: The breakdown of complex molecules for energy occurs in the cytoplasm and, in eukaryotes, in the mitochondria.
Glucose (6C) converts to:
- Glucose-6-phosphate (6C)
- Fructose-6-phosphate (6C)
- Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate (6C)
- Triose phosphate (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate) (3C)
- Triose phosphate (dihydroxyacetone phosphate) (3C)
- 2 × Triose bisphosphate (1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid) (3C)
- 2 × Triose phosphate (3-phosphoglyceric acid) (3C)
- 2 × 2-phosphoglycerate
- 2 × phosphoenolpyruvate
- 2 × Pyruvic acid (3C)
Along with: ADP, ATP, NADH, H+ , NAD+ , H2O
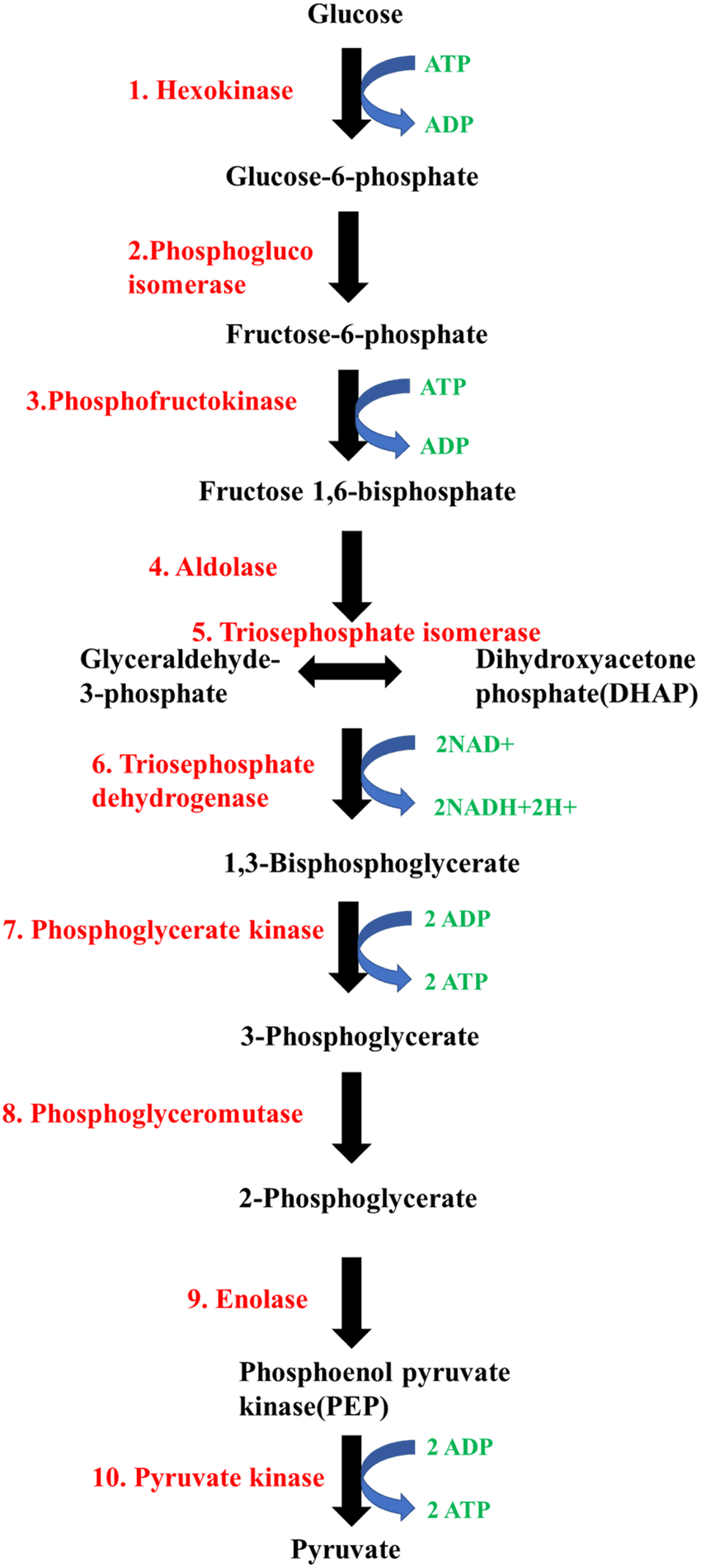 Steps of Glycolysis
Steps of Glycolysis
Detailed Steps of Glycolysis:
- Conversion of Sucrose: Sucrose is broken down into glucose and fructose by the enzyme invertase. These monosaccharides then enter the glycolytic pathway easily.
- Phosphorylation of Glucose and Fructose: The enzyme hexokinase phosphorylates glucose and fructose to form glucose-6-phosphate. This form of glucose is then converted into fructose-6-phosphate. The subsequent steps for processing glucose and fructose are similar.
- Steps of Glycolysis: Glycolysis consists of ten reactions controlled by various enzymes to convert glucose into pyruvate. Here are the key steps:
Use of ATP: ATP is used in two steps of glycolysis:
- When glucose is converted to glucose-6-phosphate.
- When fructose-6-phosphate is transformed into fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate.
Splitting of Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate: Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate splits into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL).
- Production of NADH: In one step, NADH is produced from NAD+ when PGAL is converted to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPGA). This involves the oxidation of PGAL and the addition of inorganic phosphate.
- Conversion of BPGA: BPGA is converted to 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA), producing ATP in the process.
- Formation of ATP: Another ATP is generated when phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is converted into pyruvic acid.
Overall ATP Production: The total number of ATP molecules produced from one glucose molecule during glycolysis is two.
Fate of Pyruvic Acid: Pyruvic acid, the main product of glycolysis, can be further processed in different ways depending on the cell's needs.
Metabolic Pathways for Pyruvic Acid
- Lactic Acid Fermentation: In this process, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid. This occurs in muscle cells and some bacteria under anaerobic conditions.
- Alcoholic Fermentation: Pyruvic acid is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process is common in yeast and some types of bacteria. It involves the enzymes pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase.
- Aerobic Respiration: In the presence of oxygen, pyruvic acid is fully oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. This process occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and involves the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
Fermentation
Fermentation is a process where organisms break down glucose without the presence of oxygen. In this process, glucose is not completely oxidized, and various reactions occur to convert pyruvic acid into different end products. Yeast, for example, converts pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and ethanol (alcohol) through the action of enzymes like pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase.
Types of Fermentation: There are three main ways cells can deal with pyruvic acid from glycolysis:
1. Lactic Acid Fermentation
2. Alcoholic Fermentation
3. Aerobic Respiration
1. Lactic Acid Fermentation: In animal cells, such as muscle cells during intense exercise when oxygen is limited, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. This process uses NADH + H+ as a reducing agent, which is converted back to NAD+ during fermentation. Lactic acid fermentation releases a small amount of energy, capturing less than seven percent of the energy from glucose as high-energy bonds in ATP.
2. Alcoholic Fermentation: Yeast and some bacteria perform alcoholic fermentation, where pyruvic acid is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process also releases a small amount of energy, similar to lactic acid fermentation.
- Net ATP Production: When one glucose molecule is fermented into alcohol or lactic acid, the net ATP produced is very low, typically around 2 ATP molecules per glucose.
- Alcohol Concentration in Fermented Beverages: Yeasts can tolerate alcohol concentrations up to about 13 percent before they are harmed. This limits the natural alcohol concentration in fermented beverages. Higher alcohol concentrations in drinks are achieved through additional processes, such as distillation, where the alcohol is separated and concentrated.
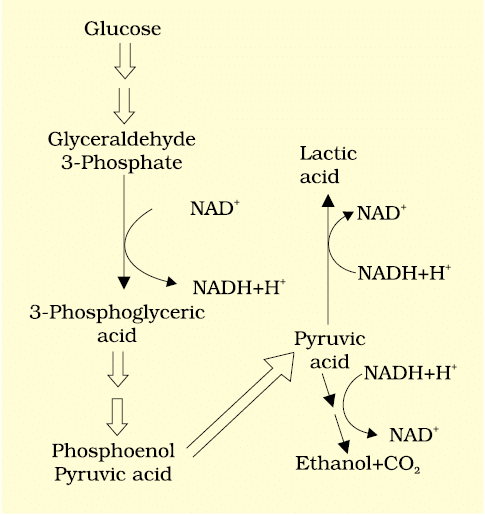 Major Pathways of Anaerobic Respiration
Major Pathways of Anaerobic Respiration
3. Aerobic Respiration: For the complete oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide and water, organisms use aerobic respiration, also known as the Krebs cycle. This process requires a supply of oxygen and results in the release of carbon dioxide, water, and a significant amount of energy stored in the substrate. Aerobic respiration is common in higher organisms and allows for the extraction of more energy from glucose compared to fermentation.
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration takes place in the mitochondria and involves the transport of pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis, from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria. The key events in aerobic respiration include:
- The complete oxidation of pyruvate through the stepwise removal of all hydrogen atoms, resulting in the production of three molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2).
- The transfer of electrons removed from the hydrogen atoms to molecular oxygen (O2), simultaneously producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
It is important to note that the first process occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, while the second process takes place on the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
Pyruvate Decarboxylation and the Krebs Cycle
Pyruvate, produced by the glycolytic breakdown of carbohydrates in the cytosol, undergoes oxidative decarboxylation in the mitochondrial matrix. This process involves a complex series of reactions catalyzed by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase and requires several coenzymes, including nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD + ) and Coenzyme A.
During the decarboxylation of two molecules of pyruvic acid (derived from one glucose molecule during glycolysis), two molecules of NADH are generated. The resulting acetyl CoA then enters the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), also known as the Krebs cycle, named after the scientist Hans Krebs who first described it.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
The TCA cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a crucial part of aerobic respiration that takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. It begins with the combination of an acetyl group from acetyl CoA with oxaloacetic acid (OAA) and water to produce citric acid. This reaction, catalyzed by the enzyme citrate synthase, releases a molecule of CoA.
Respiration and the TCA Cycle
The overall equation for this part of respiration is:
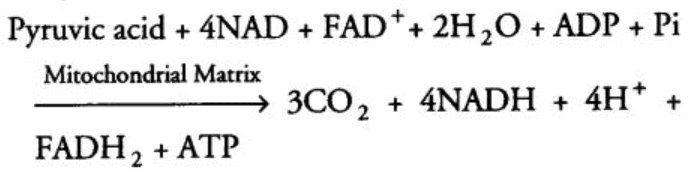 Overall equation of TCA
Overall equation of TCA

In the TCA cycle:
- Succinyl-CoA is converted to oxaloacetic acid (OAA), allowing the cycle to proceed.
- Three instances in the cycle involve the reduction of NAD + to NADH + H + .
- One instance involves the reduction of FAD + to FADH 2 .
- The ongoing oxidation of acetyl CoA in the TCA cycle requires the replenishing of oxaloacetic acid and the regeneration of NAD + and FAD + from NADH and FADH 2 .
During the TCA cycle, glucose breaks down to release CO2 and produce eight molecules of NADH + H + along with two molecules of FADH 2 and just two molecules of ATP.
Role of O2 in Respiration and ATP Generation
The NADH + H + and FADH 2 produced during the TCA cycle play a crucial role in the electron transport chain (ETC), which is where oxygen (O 2 ) comes into the picture. The ETC is a series of protein complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transfer electrons from NADH + H + and FADH 2 to oxygen, the final electron acceptor.
As electrons are transferred through the ETC, protons (H + ) are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space, creating an electrochemical gradient. This gradient drives the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) through a process called oxidative phosphorylation, catalyzed by ATP synthase.
In summary, the TCA cycle produces NADH + H + and FADH 2 , which are essential for ATP production in the ETC. Oxygen is vital in this process as it acts as the final electron acceptor, enabling the production of a large amount of ATP. Overall, the complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose during aerobic respiration can yield up to 38 ATP molecules, including those produced in the TCA cycle, substrate-level phosphorylation, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation
The energy stored in NADH + H and FADH is released and utilized in the following steps of the respiratory process. This happens when they are oxidized through the electron transport system (ETS), and the electrons are passed on to O, resulting in the formation of H O.
The metabolic pathway through which the electron passes from one carrier to another is called the electron transport system (ETS). It is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
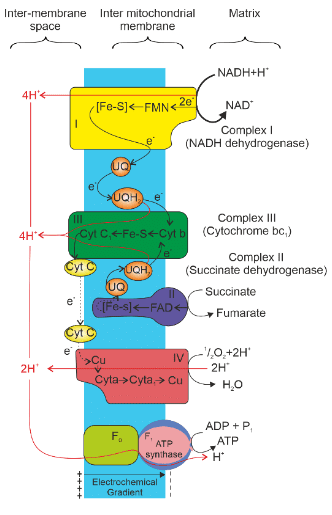 Electron Transport System
Electron Transport System
- Complex I (NADH dehydrogenase): Electrons from NADH, produced in the mitochondrial matrix during the citric acid cycle, are oxidized by complex I. The electrons are then transferred to ubiquinone (coenzyme Q), which is located within the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- Complex II (Succinate dehydrogenase): Ubiquinone also receives reducing equivalents from FADH, generated during the oxidation of succinate in the citric acid cycle.
- Complex III (Cytochrome bc 1 complex): The reduced ubiquinone (ubiquinol) is oxidized, and electrons are transferred to cytochrome c via complex III.
- Cytochrome c: This small protein, attached to the outer surface of the inner membrane, acts as a mobile carrier, transferring electrons between complex III and IV.
- Complex IV (Cytochrome c oxidase complex): This complex contains cytochromes a and a3, along with two copper centers. It facilitates the final transfer of electrons.
- ATP Synthase (Complex V): As electrons pass from one carrier to another through complexes I to IV in the electron transport chain, this process is coupled with ATP synthesis by ATP synthase. ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
ATP Production:
- The number of ATP molecules synthesized depends on the electron donor.
- Oxidation of one molecule of NADH produces 3 ATP molecules.
- Oxidation of one molecule of FADH produces 2 ATP molecules.
Although aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen, oxygen's role is limited to the terminal stage of the process. However, its presence is vital as it drives the whole process by removing hydrogen from the system. Oxygen acts as the final hydrogen acceptor.
In respiration, unlike photophosphorylation where light energy is used to create a proton gradient, the energy of oxidation-reduction is utilized for the same purpose. This is why the process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
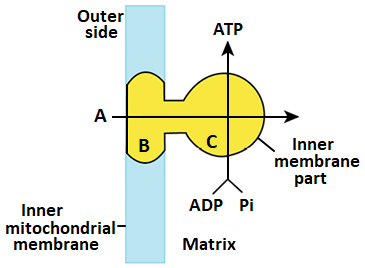 Diagramatic presentation of ATP synthesis in mitochondria
Diagramatic presentation of ATP synthesis in mitochondria
Chemiosmotic Hypothesis and ATP Synthase:
- The mechanism of membrane-linked ATP synthesis, known as the chemiosmotic hypothesis, explains how the energy released during the electron transport system is used to synthesize ATP with the help of ATP synthase (complex V).
- ATP synthase consists of two major components: F1 and F0.
- F1 is a peripheral membrane protein complex that contains the site for ATP synthesis from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
- F0 is an integral membrane protein complex that forms the channel through which protons cross the inner membrane.
- The passage of protons through the F0 channel is coupled to the catalytic site of the F1 component, leading to ATP production.
- For each ATP produced, 4 protons (H ) pass through F0 from the intermembrane space to the matrix, down the electrochemical proton gradient.
The Respiratory Balance Sheet
In theory, it is possible to calculate the net gain of ATP from the oxidation of a single glucose molecule. However, this remains a theoretical exercise due to the need for certain assumptions:
- There is a sequential and orderly pathway where one substrate leads to the next, with glycolysis, the TCA cycle, and the electron transport system (ETS) occurring in succession.
- The NADH produced during glycolysis is transferred to the mitochondria for oxidative phosphorylation.
- Intermediates in the pathway are not used to synthesize other compounds.
- Only glucose is being respired, without any alternative substrates entering the pathway at intermediate stages.
These assumptions are not valid in a living system, as all pathways operate simultaneously, substrates are added and removed as needed, ATP is used as required, and enzymatic rates are regulated by various means. Despite this, it is helpful to make these calculations to appreciate the efficiency of living systems in energy extraction and storage.
Under ideal conditions, there can be a net gain of 38 ATP molecules during the aerobic respiration of one glucose molecule.
Comparison between Fermentation and Aerobic Respiration
- Breakdown of Glucose: Fermentation involves only a partial breakdown of glucose, while in aerobic respiration, glucose is completely degraded to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
- ATP Yield: Fermentation generates a net gain of only two molecules of ATP for each molecule of glucose degraded to pyruvic acid. In contrast, many more ATP molecules are produced under aerobic conditions.
- NADH Oxidation: In fermentation, NADH is oxidised to NAD+ slowly. However, this reaction occurs vigorously in aerobic respiration.
Amphibolic Pathway
- Glucose is the preferred substrate for respiration. Typically, all carbohydrates are first converted into glucose before being used for respiration.
- Other substrates can also be respired, but they do not enter the respiratory pathway at the first step.
- Fats need to be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids first. Fatty acids are degraded to acetyl CoA to enter the pathway, while glycerol is converted to PGAL before entering.
- Proteins are degraded by proteases, and individual amino acids (after deamination) enter the pathway at various stages within the Krebs’ cycle or as pyruvate or acetyl CoA.
- Traditionally, respiration is considered a catabolic process because it involves the breakdown of substrates. However, the respiratory pathway is involved in both anabolism and catabolism.
- For example, when fatty acids are synthesized, acetyl CoA is withdrawn from the respiratory pathway. Similarly, respiratory intermediates link both the breakdown and synthesis of proteins.
- Since the respiratory pathway is involved in both anabolism and catabolism, it is more accurate to consider it an amphibolic pathway rather than just a catabolic one.

Interrelationship among metabolic pathways showing respiration mediated breakdown of different organic molecules to CO2 and H20
Respiratory Quotient
The respiratory quotient (RQ) is the ratio of the volume of carbon dioxide evolved to the volume of oxygen consumed during respiration. It reflects the type of respiratory substrate being used.
RQ = volume of CO2 evolved / volume of O2 consumed
Carbohydrates: When carbohydrates, like glucose, are completely oxidized, the RQ is 1 because equal amounts of CO2 and O2 are involved. For example:

Fats: When fats are used, the RQ is less than 1. For instance, with tripalmitin (a type of fat):


Proteins: When proteins are used as respiratory substrates, the RQ is about 0.9. However, in living organisms, multiple respiratory substrates are used simultaneously; pure proteins or fats are not typically used alone.
|
169 videos|524 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Respiration in Plants Chapter Notes - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is respiration in plants? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of respiration in plants? |  |
| 3. What are the main steps involved in aerobic respiration? |  |
| 4. How does respiration differ from photosynthesis in plants? |  |
| 5. Why is respiration important for plants? |  |

















