Introduction to AI Domain | Artificial Intelligence for Class 10 PDF Download
Domains of AI Overview
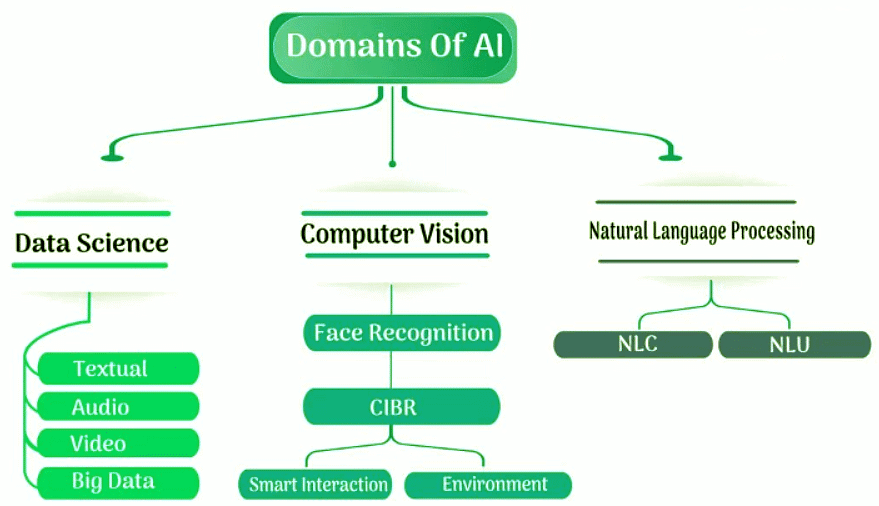
What are Domains of AI?
The domains of AI represent the primary branches of Artificial Intelligence, such as Data, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing.
The flowchart below illustrates these three domains of AI: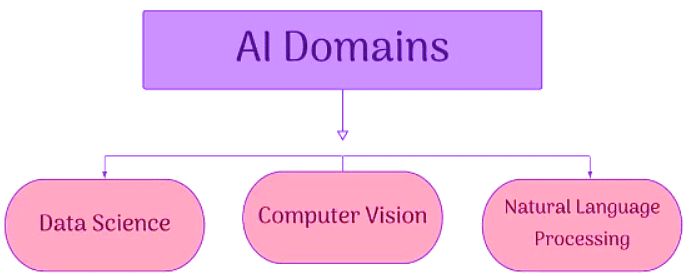
Data Sciences (Data)
"Data Science is about using mathematical and statistical principles to analyze data, essentially making sense of it. This data can be categorized into three types: audio, visual, and textual."
S. Rajeswara Sastry
(Independent Researcher & Certified Data Scientist)
What is Data?
- In today's tech era, we spend much of our time online, where everything is driven by data. For example, when you search for something on Amazon and receive numerous recommendations, it’s due to the recommendation engine principle.
- This engine analyzes vast amounts of data, identifying patterns based on your recent searches and behaviors, to suggest products you might be interested in.
- Data consists of raw facts that can be processed to create meaningful information. It can take various forms, including numbers, words, symbols, or pictures.
Data in different forms
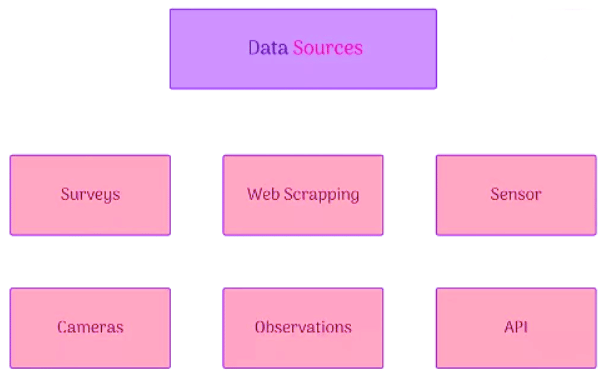
Data Sources
Data Sets
- A dataset is a collection of various types of data.
- For example: When someone posts something on Facebook, they may receive likes, shares, dislikes, comments, etc. All these interactions constitute data, and together they form a single dataset.
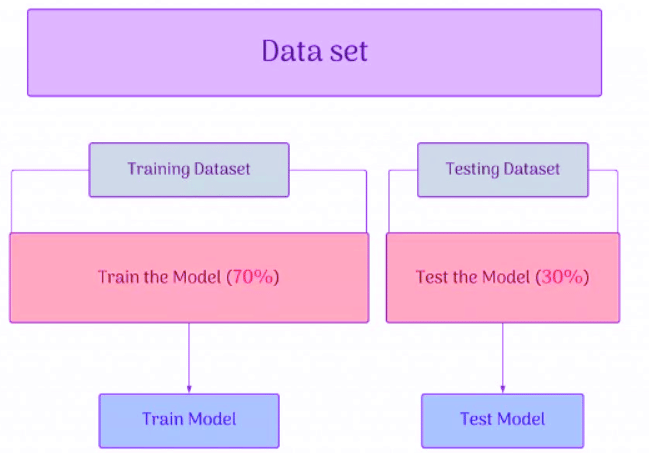
There are two types of data sets: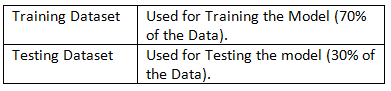
What is Information
Information refers to more detailed data that is arranged in a specific format; it is processed, organized, and structured data.
Data vs Information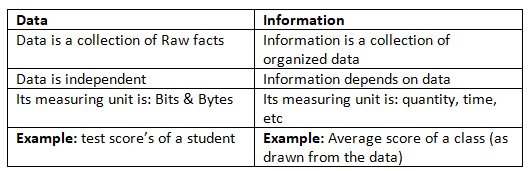
Big Data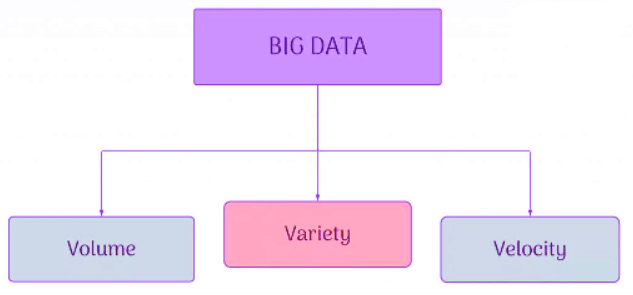
- Big Data was originally associated with three key concepts: Volume, Variety, and Velocity.
- Volume: The amount of data produced.
- Variety: The types of data produced.
- Velocity: The speed at which data is produced.
- Big Data often involves data sets with sizes that exceed the capacity of traditional software to process within an acceptable time frame and value. The term has been in use since the 1990s, with some attributing its origin to John Mashey.
- Big Data usually includes data sets that are too large for commonly used software tools to capture, curate, manage, and process within a reasonable amount of time. The Big Data philosophy encompasses unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data, with a primary focus on unstructured data.
Computer Vision
- Computer Vision, in simple terms, involves identifying symbols from given objects (pictures), learning patterns, and using cameras to alert or predict future objects.
- The goal of computer vision is to understand the content of digital images.
Applications of Computer vision
Computer vision was first introduced in the 1970s, and now its applications are seen everywhere:
- Facial Recognition: Technology capable of identifying or verifying a person from a digital image or video, used by crime investigation agencies.
- Face Filters: Applications like Instagram and Snapchat use computer vision to apply various themes to photographs.
- Google Lens: Uses computer vision to compare features of the input image with a database of images, providing relevant search results.
- Retail Stores: An example is Amazon Go, an innovative store without cashiers or checkout stations, utilizing computer vision and deep learning.
Computer vision tasks
Applications of computers in computer vision are based on various tasks performed on input images to analyze or predict outcomes. These include:
- Image Classification: Classifying the input image into a set of predefined categories.
- Classification + Localization: Identifying the input image and its location within the image.
- Object Detection: Finding instances of objects in an image, identifying real-world objects.
- Instance Segmentation: The next step after object detection, involving the process of detecting instances of objects within the image.
Natural Language Processing
What is NLP?
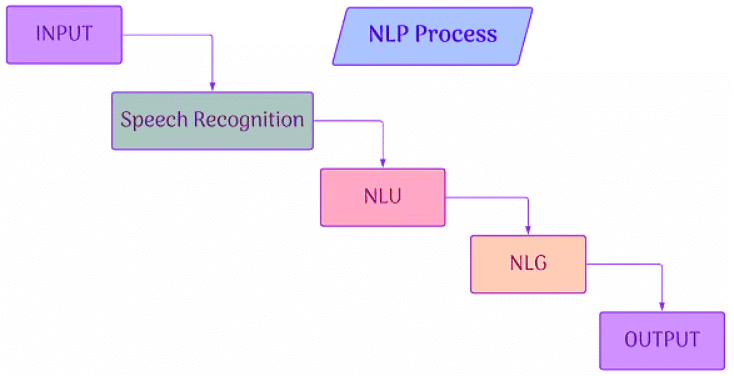
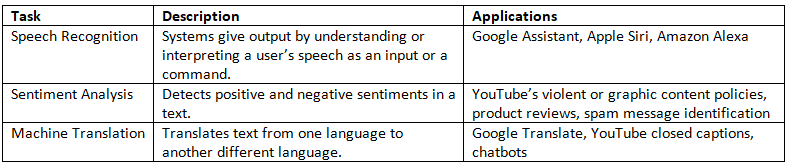
- The ability of a computer to understand human language, whether spoken or written, and to produce an output by processing it, is called Natural Language Processing (NLP). It is a component of Artificial Intelligence.
- Let’s understand it in simple terms! Imagine why you are able to talk with your friend. It's because the words spoken by your friend are taken as input by your ears, your brain processes them, and as an output, you respond. The crucial part is that the language used for communication is known to both of you. That’s NLP in simple words!
Process Of NLP
- Collecting information and understanding it is called Natural Language Understanding (NLU).
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU) uses algorithms to convert data spoken or written by the user into a structured data model. It does not require an in-depth understanding of the input but must handle a much larger vocabulary.
- Two subtopics of NLU:
- Intent Recognition: This is the most crucial part of NLU because it involves identifying the user’s intention in the input and determining the correct meaning.
- Entity Recognition: This process extracts key data from the input, such as names, locations, places, numbers, dates, etc. For example, in the question "What happened on 9/11 (date) in the USA (place)?"
- Thinking of an appropriate output to provide to the user is called Natural Language Generation (NLG).
- Natural Language Generation is the software process of generating natural language output from structured data sets. It searches for the most relevant output from its network and, after arranging and checking for grammatical errors, provides the best result to the user.
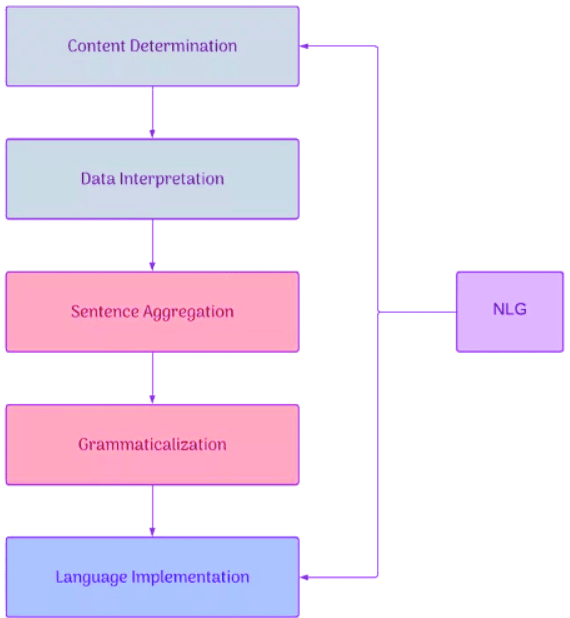
Steps in NLG
- Content Determination: Showing only important information or a summary for the user’s speech. For example, Google shows only a summary for a Wikipedia search.
- Data Interpretation: Identifying the correct data and showing it to the user with the context of the input. For example, in a cricket match, showing winners, the man of the match, and run rates of the teams.
- Sentence Aggregation: The selection of words or expressions in an output sentence. For example, choosing between synonyms such as "brilliant" or "fantastic."
- Grammaticalization: Ensuring the output adheres to grammatical patterns and is free from grammatical mistakes. For example, using commas appropriately in the text.
- Language Implementation: Ensuring the output data aligns with the user’s preferences and organizing it into templates.
- For example, when you ask something to Google Assistant, the words or sentences you speak are taken as input from your microphone. The Google Assistant then recognizes your speech and understands it (NLU), thinks of an answer (NLG), and provides you with the most relevant response (output) for your queries.
Applications of NLP
Challenges in NLU
- Lexical Ambiguity: Some words have several meanings, which can confuse machines when trying to interpret the user's intent. For example, the word "tank" can refer to a water storage tank or an armored military vehicle.
- Syntactic Ambiguity: The machine needs to correctly understand the structure of a sentence. For instance, in "Old man and woman were taken to their home," the phrase suggests that "old" describes only the man, even though it could imply both were old.
- Semantic Ambiguity: This involves understanding the true meaning of a user's statement. For example, "The car hits a pole while it was moving" is unclear whether the car or the pole was moving.
- Pragmatic Ambiguity: This occurs when the user's speech can be interpreted in multiple ways. For example, "The police are coming" doesn't clarify the reason for their arrival.
Challenges in NLG
- It should be Intelligence and Conversational.
- Deal with structured data
- Text/Sentence planning
|
24 videos|33 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to AI Domain - Artificial Intelligence for Class 10
| 1. What are the primary domains of artificial intelligence? |  |
| 2. How does machine learning fit into the domains of AI? |  |
| 3. What is the role of natural language processing in AI? |  |
| 4. Can you explain what computer vision entails in the context of AI? |  |
| 5. What are expert systems, and how do they function within AI? |  |






















