Equilibrium in Chemical Processes: Dynamic Equilibrium | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Equilibrium in Chemical Processes |

|
| What is Dynamic Equilibrium? |

|
| Dynamic Equilibrium in Haber's Process |

|
| Difference Between Static and Dynamic Equilibrium |

|
Equilibrium in Chemical Processes
Chemical reactions, like physical systems, reach a balance known as equilibrium. These reactions can go in two directions: forward and backward.
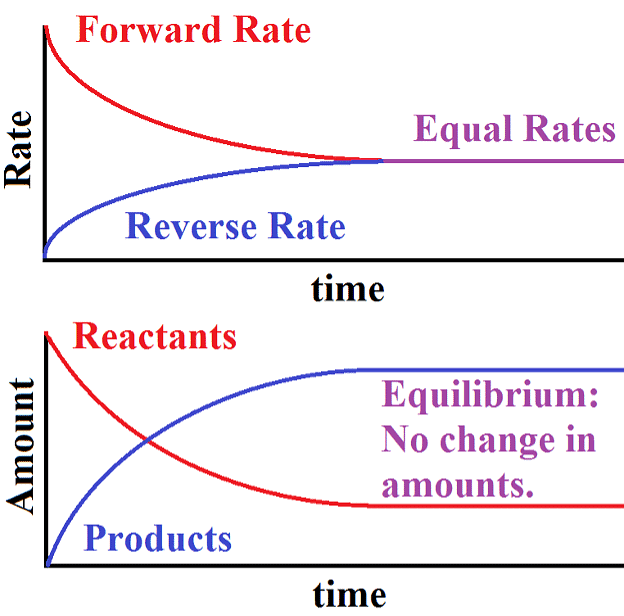
- When the rates of both directions are equal, the concentrations of the starting materials and the resulting products stop changing. This stable situation is called chemical equilibrium.
- It's dynamic because it involves an ongoing process where the forward reaction transforms reactants into products, and the reverse reaction turns products back into the original reactants.
What is Dynamic Equilibrium?
Dynamic Equilibrium can be defined as the state of a given system in which the reversible reaction taking place in it stops changing the ratio of reactants and products, but there is still a movement of substances between the reactants and the products.
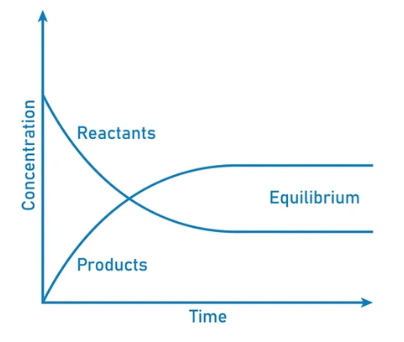
- This movement occurs at an equal rate and there is no net change of the reactant and product ratio.
- For these types of equilibria, the equilibrium constants are represented with the help of the rate constants for the forward and backward reactions. Systems maintaining a dynamic equilibrium are examples of systems in steady states.
Dynamic Equilibrium in Haber's Process
In the process of making ammonia using Haber’s method, the dynamic nature of chemical equilibrium is evident. Initially, known amounts of nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) are combined at high temperatures and pressure. Over time, the amounts of ammonia (NH3), unreacted hydrogen, and nitrogen are measured at regular intervals.
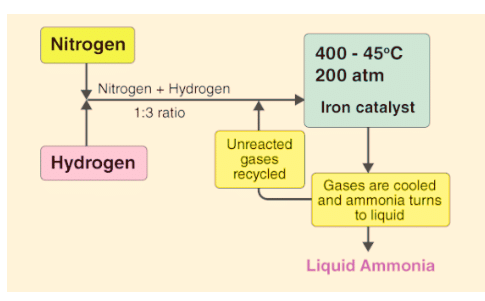
- After a while, a specific composition is reached where the mixture remains constant, indicating equilibrium.
- To understand the dynamic aspect, the synthesis is repeated using deuterium (D2) instead of hydrogen. The equilibrium is achieved with the same composition but with deuterium-containing compounds.
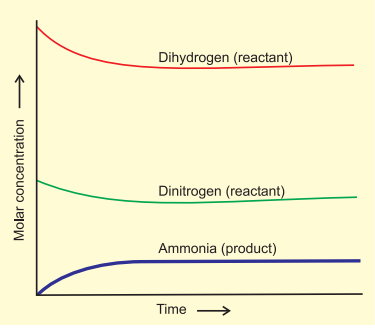 Attainment of Chemical Equilibrium
Attainment of Chemical Equilibrium
- In an intriguing experiment, mixtures from both reactions (H2, N2, NH3, and D2, N2, ND3) are combined. Despite the initial equilibrium composition, further analysis using a mass spectrometer shows a mix of ammonia and its deuterated forms, along with hydrogen and its deuterated forms.
- This reveals that H and D atoms continue to rearrange within the molecules due to ongoing forward and reverse reactions.
- The use of deuterium highlights that chemical reactions reach dynamic equilibrium, where the rates of forward and reverse reactions are balanced, resulting in no net change in composition.
- Equilibrium can be achieved whether starting with H2 and N2 to produce NH3 or starting with NH3 and decomposing it back into N2 and H2.
The balanced chemical equations for the reactions are:
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g) ⇌ N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Difference Between Static and Dynamic Equilibrium
- Static equilibrium refers to a condition where the reaction occurring in a system is completely halted and there exists no movement between the reactants and the products corresponding to the chemical reaction.
- If the forces acting on an object cancel each other, in addition to the constancy of content and composition, no movement of the object takes place. This is static equilibrium.

However, the resultant force acting on both of these types of equilibria in a system is zero. Generally, neither of these types of equilibrium display visible changes.
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Equilibrium in Chemical Processes: Dynamic Equilibrium - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is dynamic equilibrium in chemical processes? |  |
| 2. How does dynamic equilibrium differ from static equilibrium? |  |
| 3. What factors can affect the establishment of dynamic equilibrium in chemical processes? |  |
| 4. How does Le Chatelier's principle relate to dynamic equilibrium? |  |
| 5. Can dynamic equilibrium be reached in all chemical reactions? |  |
















