UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC > Echinodermata: Feeding and Respiration
Echinodermata: Feeding and Respiration | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Feeding and Excretion
One-Way digestive system
Typically have two stomachs – a cardiac stomach which can be moved outside of the body begin digestion and a pyloric stomach.
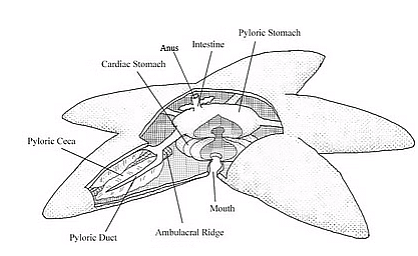 Due to this, sea stars can digest prey much larger than their stomach since they begin digestion outside their body.
Due to this, sea stars can digest prey much larger than their stomach since they begin digestion outside their body.
- Powerful enzymes liquify prey – digested completely within the stomachs.


- Digestive waste exits the anus on opposite side of mouth.
- No distinct excretory organs – nitrogenous waste is removed from the water vascular system via diffusion through tube feet or with digestive waste.
Respiration and Circulation
Respiration:
- Use water vascular system in respiration and circulation.
- Gas exchange occurs through simple gills and diffusion through tube feet.
- Reduced circulatory system.
- All fluids and “blood” circle throughout the hydraulic-like water vascular system. Blood has no pigment (i.e. no colour)
- No heart!
The document Echinodermata: Feeding and Respiration | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
181 videos|346 docs
|
FAQs on Echinodermata: Feeding and Respiration - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the feeding process of echinoderms? |  |
Ans. Echinoderms have a unique feeding process called suspension feeding. They use their tube feet or specialized structures called tube feet to capture food particles from the surrounding water. The tube feet have tiny, hair-like projections called cilia that create a water current to bring in food particles. These particles are then moved towards the mouth using the tube feet and are ingested for digestion.
| 2. How do echinoderms respire? |  |
Ans. Echinoderms respire through a process called cutaneous respiration. They have a thin, flexible body wall that allows gas exchange to occur directly through their skin. Oxygen from the surrounding water diffuses into their body and carbon dioxide diffuses out. Some echinoderms, like sea stars, also have specialized respiratory structures called papulae, which are small projections on their body surface that enhance gas exchange.
| 3. What is the role of the water vascular system in echinoderms' feeding process? |  |
Ans. The water vascular system in echinoderms plays a crucial role in their feeding process. It is a network of water-filled canals connected to tube feet. When echinoderms extend their tube feet to capture food particles, the water vascular system helps in hydraulic pressure regulation, allowing them to control the extension and retraction of their tube feet. It also aids in the movement of food particles towards the mouth by creating a water current through the tube feet.
| 4. How do echinoderms excrete waste? |  |
Ans. Echinoderms excrete waste through small structures called nephridia. Nephridia are found in the body cavity of echinoderms and function as excretory organs. They filter waste products, such as ammonia and urea, from the coelomic fluid and release them into the surrounding water through specialized pores. This process helps maintain the osmotic balance and removes metabolic waste from the echinoderms' bodies.
| 5. How does circulation occur in echinoderms? |  |
Ans. Echinoderms have an open circulatory system, where blood or coelomic fluid flows freely within the body cavity. Circulation in echinoderms is primarily driven by ciliary action and muscular contractions. The coelomic fluid, which contains nutrients, oxygen, and waste products, circulates throughout the body cavity, bathing the internal organs and tissues. This type of circulation allows for the exchange of substances between cells and helps maintain the overall metabolic functions of echinoderms.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















