Ecological Issues: Environmental Hazards: Landslides, Earthquakes, Tsunamis, Floods & Droughts -1 | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Natural Hazards
- A hazard is a dangerous condition or threat, natural or man-made that can cause injury, loss of life, or damage to property, livelihood, and environment.
- Natural Hazards may be grouped under the following 2 major categories
- Geological Hazards – Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Tsunami, Landslides, and Avalanches.
- Weather associated Hazards – Cyclones, Thunderstorms, Droughts, Floods and epidemics.
- It has been estimated that the world endures on an average about lakhs of thunderstorms, thousands of floods, hundreds of landslides and earthquakes, and scores of the cyclone and volcanic eruptions every year.
- Natural Disaster versus Natural Hazard – A natural hazard is a threat of a naturally occurring event that will have a negative effect on humans. This negative effect is what we call a natural disaster. In other words, when the hazardous threat actually happens and harms humans, we call the event a natural disaster.
Introduction to Landslides
- Landslide is a rapid movement of rock, soil, and vegetation down the slope under the influence of gravity. It may be induced by natural agencies, e.g., heavy rain, earthquake, or it may be caused by human over- interference with the slope – stability.
- Man breaks rocks for constructing roads, railways, buildings, tunnels, etc. In such cases rocks become loose and landslide occurs.
- Earth flow, mass movement, mudflow, rotational slip, and avalanches are all examples of landslides.
- Landslides are rarely on a scale comparable to seismic or volcanic events. The intensity and magnitude of the landslide, however, depends on the geological structure, angle of dip of the slope, nature of sedimentary rocks, and the human interaction with the slope.
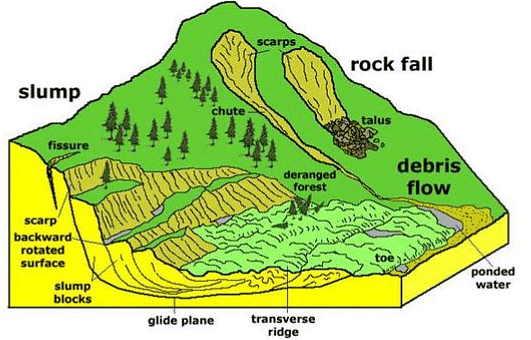
Landslide Dam
When landslides occur on the slopes of a river valley, the sliding mass may reach the bottom of the valley and cause partial or complete blockage of the river channel. This accumulated mass of landslide debris resulting in the blockage of a river is commonly termed as a Landslide dam. Types of landslides
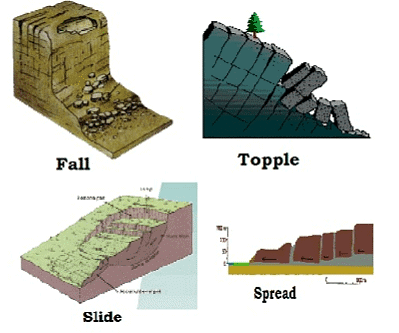
Types of landslides
- Falls: It happens due to the abrupt movements of masses of geologic materials, such as rocks and boulders that become detached from steep slopes or cliffs.
- Topples: It happens due to the forward rotation of a unit or units about some pivotal point, below or low in the unit, under the actions of gravity and forces exerted by adjacent units or by fluids in cracks
- Slides: In this types, rocks, debris or soil slide through slope forming material.
- Spread: It usually occur on very gentle slopes or flat terrain.
Causes of Landslides
The major causes of landslides are –
- Rainfall and Snowfall-
- The occurrence of heavy or continuous rainfall may lead to heavy landslides in the areas of steep slopes where National Highways and roads have been constructed.
- The Nashri area between BatoteRamban- Ramsu, and Banihal (Jammu and Kashmir) is frequently subjected to landslides. The landslides in this region are particularly severe during the rainy and winter seasons when the vehicular traffic is disturbed for several days.
- Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruptions-
- Earthquakes are the most important cause of landslides in the folded mountainous areas. In India, Landslides are more frequent in the folded mountains of the Tertiary Period, like the Himalayas.
- In the Kashmir valley, the earthquake of 1905 resulted into landslides in the lesser and the Greater Himalayas in which several thousand people lost their lives.
- Volcanic eruptions also trigger landslides in the mountainous regions.
- Mining, Quarrying and Road cutting-
- The continuous extraction of coal, minerals, and stones from the mines and quarries and the development of roads by cutting the steep slopes in the folded mountains create conducive conditions for the occurrence of landslides.
- Such landslides may be observed throughout the Himalayas and in the Eastern and Western Ghats.
- Loading by construction of houses-
- The unplanned growth of towns and cities in the hilly areas without testing soil and rocks in also an important cause of landslides.
- The eastern slope of Nanital (Uttarakhand) is sinking because of the heavy load of hotels and residential structures.
- Deforestation-
- Deforestation and other human activities also induce landslides. Most of the landslides are small involving some blocks up to a few meters across. But some are large enough to cause a catastrophe. They may bury roads, buildings, and other structures.
- The adverse effect of landslides can be reduced by checking deforestation on mountain slopes, following building codes for such areas, and by avoiding the construction of buildings on steep slopes.
Impact of Landslides
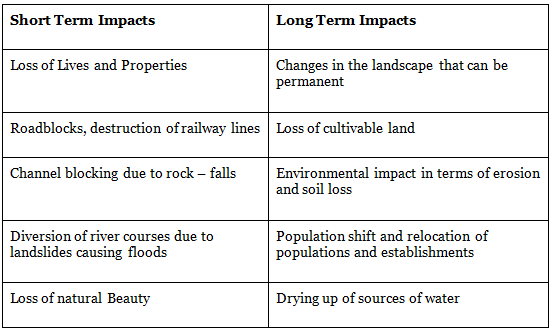
Vulnerability profile of India
In India, this hazard affects at least 15% of the land area of the country ( approx 0.49 million square Km.) It is very frequent in geodynamical active domains in the Himalayan and Arakan- Yoma belt of the Northeastern parts of the country as well as in the relatively stable domains of the Meghalaya Plateau, Western Ghats, and Nilgiri Hills.
The Nilgiri Hills located at the convergence of Eastern and the Western Ghats bear the innumerable scars of the landslides due to their location in a zone of high intensity and protracted rainfall where the overburden is sensitive to over-saturation.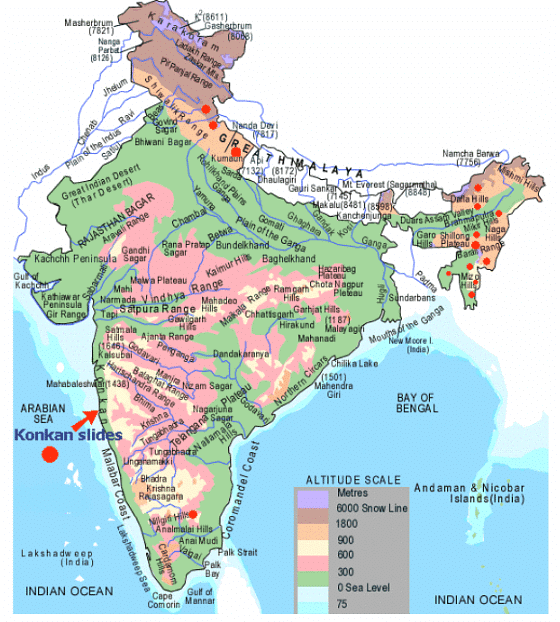
Mitigation Strategy
- Hazard zones have to be identified and specific slides to be stabilized and managed in addition to monitoring and early warning systems to be placed at selected sites.
- Hazard mapping should be done to locate areas commonly prone to landslides. It is always advisable to adopt area-specific measures to deal with landslides.
- Restriction on the construction and other developmental activities such as roads and dams, limiting agriculture to valleys and areas with a moderate slope, and control on the development of large settlements in high vulnerability zones, should be enforced.
- NDMA Guidelines for Landslides –
- Landslide Hazard, vulnerability and Risk Assessment
- Multi – Hazard Conceptualisation
- Landslide Remediation practice
- Research and Development, monitoring, and early warning
- Knowledge network and management
- Capacity building and Training
- Public awareness and Education
- Emergency preparedness and response
- Regulation and Enforcement
Earthquake
- An earthquake is the shaking of the surface of the Earth, resulting from the sudden release of energy in the Earth‘s lithosphere that creates seismic waves.
- Earthquake is the form of energy of wave motion transmitted through the surface layer of the earth.
- It may be due to faulting , folding, plate movement, volcaninc eruptions and anthropogenic factors like dams and reservoirs.
- Earthquake are by far the most unpredictable and highly distructive of all the natural disasters.
- Minor earth tremors caused by gentle waves of vibration within the earth’s crust occur every few minutes while Major earthquakes usually caused by movement along faults, can be very disastrous particularly in densely populated areas.
Terminology Used in the Study of Earthquakes
- Earthquake intensity
- Earthquake magnitude
- Richter Scale
- Mercalli Scale
- Fault
- Focus
- Epicenter
- Seismic wave
- Seismograph
Focus and Epicenter
The point within Earth where faulting begins is the focus, or hypocenter.
The point directly above the focus on the surface is the epicenter. The intensity of the earthquake is highest at the epicenter and decreases with distance from the epicenter.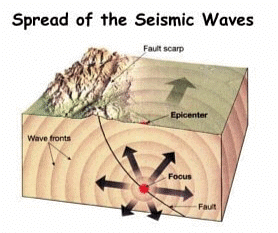
Richter scale
Richter magnitude scale is the scale to measure the magnitude of energy released by an earthquake.
This scale was devised by Charles. F. Richter in the year 1935.
The number indicating magnitude ranges between 0 to 9
An earthquake that registers 5.0 on the Richter scale has a shaking amplitude 10 times that of an earthquake that registered 4.0, and thus corresponds to a release of energy 31.6 times that released by the lesser earthquake.
Mercalli scale
The Mercalli intensity scale is a seismic scale used for measuring the intensity of an earthquake.
It measures the effects of an earthquake
The number indicating intensity ranges between 1 to 12
Seismic Waves
- Seismic waves are the waves of energy caused by the sudden breaking of rock within the earth.
- They are the energy that travels through the earth and is recorded on seismographs.
- The two main types of waves are body waves and surface waves.
Body waves
- Primary waves ( P-waves)
- Secondary waves ( S-waves)
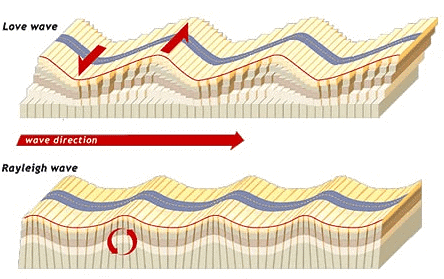
Surface Waves
- Love Waves (L-waves)
- Rayleigh waves
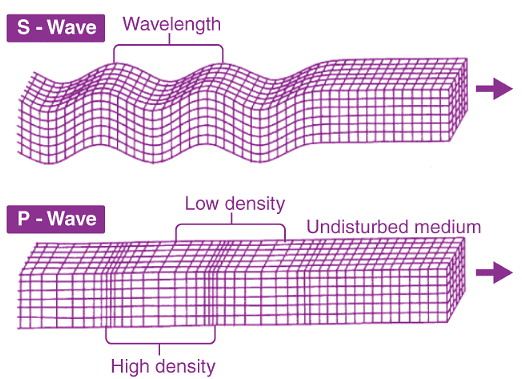
Primary waves (longitudinal wave)-
- The first kind of body wave is the P wave or primary wave.
- This is the fastest kind of seismic wave.
- The P wave can move through gaseous, solid rock and fluids, like water or the liquid layers of the earth.
- It pushes and pulls the rock, it moves through just like sound waves push and pull the air.
 P & S Waves
P & S Waves
Secondary waves (transverse wave)
- The second type of body wave is the S wave or secondary wave.
- An S wave is slower than P wave and can only move through solid rock.
- This wave moves rock up and down, or side-to-side.
- S-waves arrive at the surface with some time Lag.
Love Waves
- The first kind of surface wave is called a Love wave, named after A.E.H. Love, a British
- mathematician.
- It’s the fastest surface wave and moves the ground from side-to-side.
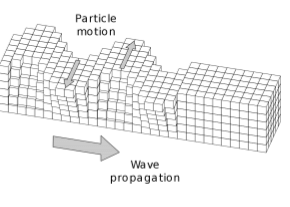
Rayleigh Waves
- The other kind of surface wave is the Rayleigh wave, named after Lord Rayleigh.
- A Rayleigh wave rolls along the ground just like a wave rolls across a lake or an ocean.
- Because it rolls, it moves the ground up and down, and side-to-side in the same direction that the wave is moving.
- Most of the shaking felt from an earthquake is due to the Rayleigh wave, which can be much larger than the other waves.
Earthquake Predicting
Classification of earthquake
- On basis of causative factors
- Natural
(i) Volcanic
(ii) Tectonic
(iii) Isostatic
(iv) Plutonic - Artificial
- Natural
- On basis of depth of focus
- Moderate(0-50km)
- Intermediate(50-250km)
- Deep focus( 250-700km)
- On basis of human casualities
- Moderate (deaths<50,oo)
- Highly hazardous(51,000-1,00,00)
- Most hazardous(>1,00,00)
World Distribution of Earthquakes
- The world’s distribution of earthquakes coincides very closely with that of volcanoes.
- Region of greatest seismicity are Circum-Pacific areas, with the epicenters and the most frequent occurrences along the ‘Pacific Ring of Fire’.
- It is said that as many as 70% of earthquakes occur in the Circum-Pacific belt.
- Another 20% of earthquakes take place in the Mediterranean-Himalayan belt including Asia Minor, the Himalayas, and parts of north-west China.
- The remaining occur in the interiors of plates and on spreading ridge centers.
Earthquake Causes
Earthquakes are caused mainly due to dis-equilibrium in any part of the crust of the earth.
A number of causes have been assigned to caused dis-equilibrium or isostatic imbalance in the earth’s crust.
- Natural Reasons
- Volcanic eruption
- Faulting and folding
- Upwarping and downwarping
- Gaseous expansion and contraction inside the earth.
- Plate Movement
- Landslides
- Man-made/Anthropogenic Reasons
- Deep underground mining
- Blasting of rock by dynamites for construction purposes.
- Deep underground tunnel
- Nuclear explosion
- Reservoir Induced Seismicity (RIS) (E.g. Koyna Reservoir witnessed Earthquake in 1967 due to RIS)
- Hydrostatic pressure of man-made water bodies like reservoirs and lakes.
Plate tectonics provides the most logical explanation of volcanoes and earthquakes.
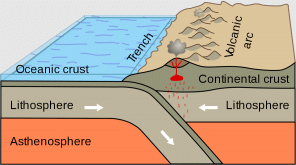
There are 3 types of plate boundaries along which earthquake occurs
- Convergent
- Divergent
- Transform
 Boundaries
Boundaries
Earthquake prone areas in India
- Earthquake of mild intensity takes place daily. Strong tremors causing large scale destructions are, however, less frequent. Earthquakes are more frequent in the areas of plate boundaries, especially along the convergent boundaries.
- In India, the region of convergence of the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate is more vulnerable to earthquakes. E.g. the Himalayan Region.
- The peninsular part of India is considered to be a stable block. Occasionally, however, some earthquakes are felt along the margins of minor plates. The Koyna earthquake of 1967 and the Latur earthquake of 1993 are examples of earthquakes in peninsular regions.
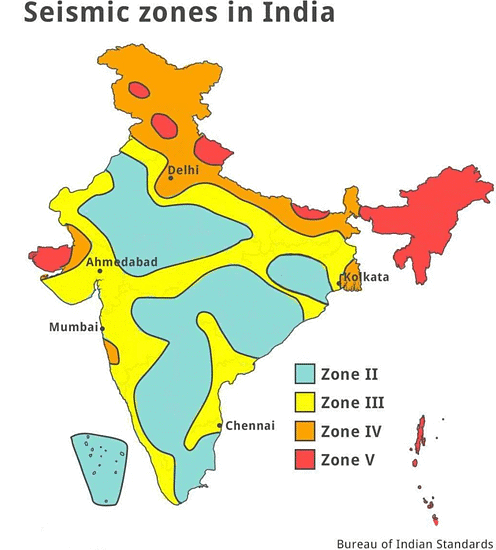
- The experts of Indian Seismology have divided India into Four seismic zones namely Zone-II, Zone-III, Zone-IV, and Zone-V. It may be observed that the entire Himalayan region, the states of North-East India, Western and Northern Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, and parts of Gujarat belong to the highest and the high-risk categories zone, named as zone V and IV.
- The remaining parts of the northern plains and western coastal areas fall in moderate risk zone and a large part of the peninsular region lies in the low-risk zone.
Consequences of Earthquake
Damage to human life and property
- The deformation of the ground surface because of the vertical and horizontal movement of the earth’s crust causes huge damage and destruction to human establishments and structures.
- Example: – An urban disaster case study of the Nepal earthquake of 2015. This earthquake was of 7.8 magnitudes and was 8.2 Km deep. Nepal earthquake caused heavy casualties because of unplanned urban construction; poor designed buildings and unscientifically designed structures.
- Urban areas of Kathmandu suffered heavy damages with a death toll of 8 thousand people and an economic loss of 10 billion USD.
Landslides and Avalanches
- Tremors especially in mountain areas can cause slope instability and slope failure leading to debris down the slope causing landslides.
- The huge masses of ice may fall down snow-covered peaks due to earthquakes causing Avalanches.
- Example: – The Nepal earthquake of 2015 resulted in several avalanches on and around Mount Everest peak. The Sikkim earthquake of 2011 caused landslides and serious damage to life and property, especially the Singik and Upper Teesta hydel projects.
Floods
- The earthquake can lead to devastating disturbances to dams, reservoirs and can cause flash floods. Landslide and Avalanches which may block the river course, leading to floods.
- Example: – The Assam earthquake of 1950 produced a barrier in the Dihang River due to the Accumulation of huge debris causing flash floods in the upstream section.
Tsunami
- Tsunamis are the waves produced due to disruption of ocean basin and displacement of the huge volume of water. Seismic waves of an earthquake can displace sea floor and generate high sea waves as Tsunamis.
- Example: – The Tsunami of 26th December 2004 of the Indian Ocean was caused by an earthquake off coast of Sumatra. It happened because of the subduction of the Indian plate under the Burmese plate. It killed about 2.4 lakh people in the countries in and around the Indian Ocean.
- Fukushima Nuclear Accident – The massive Tohoku earthquake of Japan in 2011 resulted into Tsunami waves of 10m which was caused due to an undersea earthquake of magnitude 9. This destroyed the emergency generators cooling the reactors and led to the nuclear meltdown and the radioactive fallout from the Fukushima Daiichi became a worldwide concern.
Earthquake Management
Earthquake management is the organization and management of the resources and responsibilities for dealing with all humanitarian aspects of emergencies. The aim is to reduce the harmful effects of the hazards. The earthquake management includes steps from pre-earthquake risk reduction to post-earthquake recovery.
- Risk Recognition – Certain areas are more vulnerable to earthquakes than others, so risk recognition is the first step.
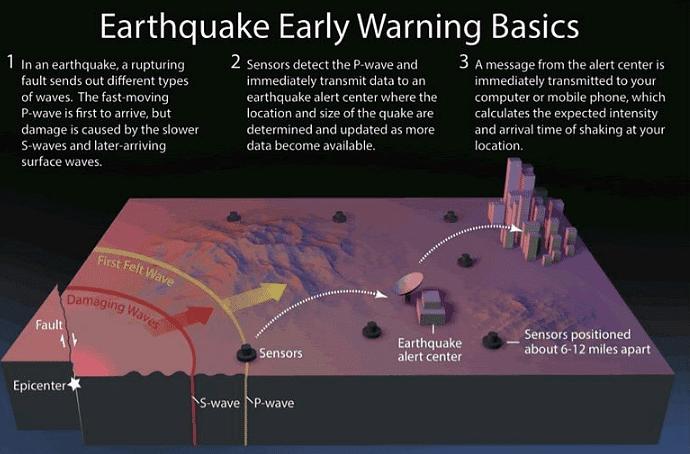
- Earthquake monitoring system/Early warning system– Making a precise forecast about the occurrence of an earthquake in a region is still a difficult proposition. Seismologists are increasingly concentrating on the aspect of earthquake forecasting.
- It will help in reducing the impact of upcoming disasters.
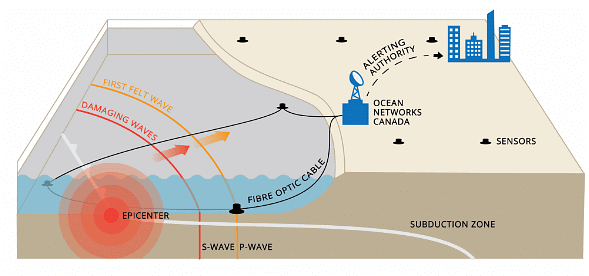
- Example: – Japan has an earthquake early warning system that uses electronic signals that reach faster than earthquake waves.
- Structural Solution– Past earthquakes show that over 95% of the lives lost were due to the collapse of buildings that were not earthquake resistant. But, the construction of such quake-resistant buildings is more expensive than ordinary buildings. Therefore, a cost-effective solution remains a challenge for a country like India. Seismic strengthening can be done through prioritization of structures and to implement this, it is important to have an earthquake hazard map for various zones according to the vulnerability.
|
304 videos|718 docs|259 tests
|
FAQs on Ecological Issues: Environmental Hazards: Landslides, Earthquakes, Tsunamis, Floods & Droughts -1 - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are the main causes of landslides? |  |
| 2. How do earthquakes occur and why are they considered environmental hazards? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a tsunami and a regular ocean wave? |  |
| 4. How do floods occur, and what are their impacts on the environment? |  |
| 5. What are the main causes of droughts, and how do they affect ecosystems? |  |
















