Ecology - Geography | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Fundamental Concepts and Principles of Ecology
 Organisms and the Environment:
Organisms and the Environment:
- Organisms have basic needs for energy and matter obtained from the environment.
- Environment includes abiotic (nonliving) factors like sunlight, soil, temperature, and biotic (living) factors including other organisms.
Niche:
- Niche refers to a species' role in its ecosystem, encompassing its interactions with biotic and abiotic factors.
- Key aspects involve the food it eats and how it acquires food.
Habitat:
- Habitat denotes the physical environment where a species resides and adapts.
- Determined mainly by abiotic factors like temperature and rainfall.
Competitive Exclusion Principle:
- Different species in a habitat must have distinct niches to avoid competition for resources.
- Two species occupying the same niche in the same location will lead to competition and displacement.
The Ecosystem:
- An ecosystem comprises all biotic and abiotic elements in an area, varying in size (e.g., a lake, a log).
- Constant energy inputs (usually sunlight) sustain ecosystems, while matter is recycled (e.g., water, carbon, nitrogen).
Ecosystem Classification:
- Coined by A.G. Tansley, an ecosystem is a self-sustaining unit involving complex interactions between biotic and abiotic components.
- Classified as terrestrial (forests, deserts) and aquatic (ponds, oceans), or manmade (crop lands, aquariums).
Types of Ecosystems:
- Natural Ecosystems:
- Dependent on solar radiation, providing essentials like food, fuel, and medicines.
- Some rely on energy subsidies like wind, rain, and tides, like tropical rainforests and coral reefs.
- Manmade Ecosystems:
- Solar energy-dependent (agricultural fields, aquaculture ponds).
- Fossil fuel-dependent (urban and industrial ecosystems).
Components of an Ecosystem
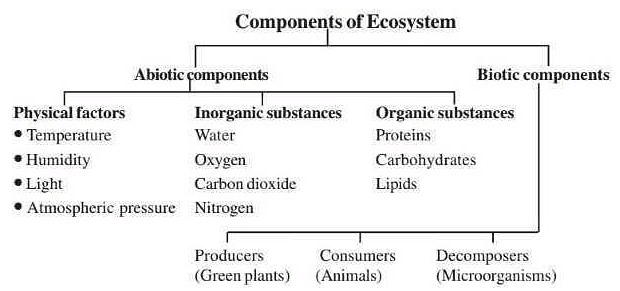
Abiotic Components (Nonliving)
Physical Factors:
- Sunlight, temperature, rainfall, humidity, and pressure.
- Sustain and limit organism growth in an ecosystem.
Inorganic Substances:
- Carbon dioxide, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, Sulphur, water, rock, soil, and minerals.
Organic Compounds:
- Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and humic substances.
- Act as building blocks for living systems, bridging the gap between biotic and abiotic components.
Biotic Components (Living)
Classified into different groups:
Producers:
- Green plants perform photosynthesis, creating food for the ecosystem.
- Termed autotrophs, absorbing water, nutrients, carbon dioxide, and solar energy.
Consumers:
- Heterotrophs, relying on food synthesized by autotrophs.
- Divided into:
- Herbivores (e.g., cow, deer, rabbit) feeding directly on plants.
- Carnivores (e.g., lion, cat, dog) consuming other animals.
- Omnivores (e.g., humans, pigs, sparrows) feeding on both plants and animals.
Decomposers:
- Also known as saprotrophs, mostly bacteria and fungi.
- Break down dead organic matter of plants and animals, secreting enzymes externally.
- Vital for nutrient recycling, also termed detrivores or detritus feeders.
Ecosystem – Structure and Function
Ecosystem Structure
- Interaction between biotic and abiotic components defines the physical structure of an ecosystem.
- Species composition and stratification are vital structural features:
- Species Composition: Identifying and enumerating plant and animal species.
- Stratification: Vertical and horizontal distribution of species across different levels.
- Structural components function collectively, contributing to ecosystem functionality.
Functional Aspects of Structural Components
- Species Composition:
- A community comprises populations living together in a specific place and time.
- Different ecosystems exhibit unique species compositions based on habitat and climate.
- The variety and number of species in a community influence its stability and balance.
- Stratification:
- Refers to the vertical and horizontal distribution of plants within an ecosystem.
- In forests, the top canopy consists of tall trees, followed by shorter trees, shrubs, herbs, and grasses.
- Different layers harbor distinct flora and fauna, forming vertical stratification.
- Deserts display sparse, discontinuous layers with minimal vegetation and animals, showcasing horizontal stratification.
Functions of Ecosystems
- Ecosystems are complex dynamic systems performing several crucial functions:
- Energy Flow: Transferring energy through food chains.
- Nutrient Cycling: Biogeochemical cycles facilitating the movement of nutrients.
- Ecological Succession: Continuous development or change within ecosystems.
- Homeostasis: Mechanisms maintaining ecosystem stability through feedback control.
- Examples of ecosystems include natural environments like ponds, lakes, forests, grasslands, and manmade ones such as aquariums, gardens, or lawns.
Energy Flow through Ecosystem
Ecosystem Dynamics and Food Chains
- Food chains and energy flow are essential ecosystem properties that create dynamism.
- Charles Elton introduced the concepts of Food Chain, Food Web, and Ecological Pyramid.
Food Chain
- It's the transfer of food energy from producers to organisms through repeated consumption.
- Each step in the chain is a trophic level.
- Example: Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk/Eagle.
- Limited steps due to energy loss as heat, typically 4 or 5 trophic levels.
Trophic Levels in Food Chain
- Autotrophs: Producers converting inorganic material into chemical energy via photosynthesis.
- Gross Primary Production (GPP): Total energy stored in photosynthesis; Net Primary Production (NPP) is the available energy to consumers.
- Herbivores: Primary consumers eating plants directly.
- Carnivores: Secondary or tertiary consumers.
- Omnivores: Eating both plants and animals.
- Decomposers: Recycling nutrients from dead organisms.
Types of Food Chains
- Grazing food chains: From plants to herbivores to carnivores.
- Detritus food chains: From dead organic matter to detritivores and further up the chain.
Food Web
- Interconnected trophic levels form a network called a food web.
- Animals can belong to multiple food chains.
- Represents a more realistic model of energy flow in ecosystems.
Energy Flow and Ecological Pyramid
- Linear energy flow in ecosystems with decreasing energy quantity at successive trophic levels.
- Ecological pyramids: Graphic representations of trophic levels in an ecosystem.
Types of Ecological Pyramids
- Pyramid of number: Represents the number of organisms at each trophic level. May sometimes invert.
- Pyramid of biomass: Depicts the total standing crop biomass at each trophic level, sometimes inverted in aquatic ecosystems.
- Pyramid of energy: Illustrates the total energy at each trophic level, never inverted.
Biogeochemical Cycles
Nutrient Cycling (Biogeochemical Cycles)
- Movement of nutrient elements through an ecosystem is known as nutrient cycling or biogeochemical cycles, involving gaseous and sedimentary cycles.
- Energy flow in ecosystems is linear, while nutrient flow is cyclical within the closed system of the biosphere.
Types of Nutrient Cycles
- Gaseous cycles (e.g., nitrogen, carbon) have reservoirs in the atmosphere, while sedimentary cycles (e.g., sulfur, phosphorus) have reservoirs in Earth's crust.
The Carbon Cycle
- Most significant among biogeochemical cycles, influencing life's composition. Human activities have altered this cycle significantly since the Industrial Revolution.
- Carbon flows among storage pools in the atmosphere, oceans, and land. Increased CO2 concentrations result from human activity, impacting the atmosphere.
Processes in the Carbon Cycle
- Photosynthesis: Green plants utilize CO2 in sunlight, converting it into organic matter and releasing oxygen.
- Respiration: All organisms respire, releasing CO2 into the atmosphere.
- Decomposition: Dead organic matter decomposes, releasing CO2 by microorganisms.
- Combustion: Burning biomass releases carbon dioxide.
Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle
- Large-scale deforestation and fossil fuel consumption in industries, power plants, and automobiles contribute to increased CO2 emissions, a major cause of global warming.
The Nitrogen Cycle
- Nitrogen is crucial for protein and is cycled by various organisms.
- Processes include nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, and denitrification.
Water Cycle (Hydrological Cycle)
- Water, essential for life, cycles through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
- Only a small percentage of Earth's water is fresh and available for use, driven by solar radiation and gravity.
Phosphorus Cycle
- Phosphorus, vital for biological structures, is obtained from rocks, absorbed by plants, and passed through the food chain.
- Unlike carbon, phosphorus does not have a significant gaseous exchange with the atmosphere.
Phosphorus in the Environment
- Rocks' weathering releases phosphates, absorbed by plants and further transferred through the food chain, with phosphate solubilizing bacteria aiding in decomposition.
Ecological Succession
Ecological Succession and Definitions
- Hult coined the term "Ecological Succession" referring to orderly community changes. Odum termed it as "Ecosystem Development."
- Ragnar Hult published the first comprehensive study on ecological succession in 1881, recognizing the shift from numerous pioneer communities to stable ones.
Dynamic Nature of Biotic Communities
- Ecological succession involves the replacement of plant and animal communities over time in an area, influenced by both biotic and abiotic factors.
Changes during Succession
- Both plant and animal communities undergo alterations during succession, leading to species colonization and decline.
Sere and Seral Stages
- The sequence of changing communities in an area is termed "sere," with transitional communities known as "seral stages."
Types of Successions
- Primary succession occurs in barren areas, while secondary succession follows disturbances in existing vegetation.
Primary Succession
- Pioneer species colonize bare land, forming a pioneer community. Successive replacement of communities leads to a stable climax community.
Climax Community
- The climax community is mature, complex, and stable, in equilibrium with climate and habitat factors.
Types of Successions based on Moisture
- Xerarch occurs on dry land like bare rock, while hydrarch occurs in water bodies like ponds or lakes.
Secondary Succession
- Results from the disturbance or removal of existing vegetation, often quicker due to the availability of soil nutrients and dormant organisms.
Causes of Ecological Succession
- Initial causes involve habitat destruction by climatic and biotic factors.
- Continuing causes relate to population shifts due to migration, industrialization, and competition.
- Stabilizing causes include land fertility and climatic conditions.
Homeostasis of Ecosystem
- Ecosystems self-regulate and resist changes, maintaining stability through negative feedback mechanisms.
Productivity of Ecosystem
- Ecosystem productivity measures organic matter accumulation over time.
- Types include primary productivity (gross and net), secondary productivity, and net productivity.
Primary Productivity
- Gross primary productivity measures total photosynthesis, while net primary productivity accounts for stored organic matter minus plant respiration.
Secondary Productivity
- Measures energy storage at consumer levels like herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers.
Net Productivity
- Refers to stored organic matter remaining after consumption by heterotrophs, indicating biomass increase in primary producers.
Principles of Ecology
Ecosystem Overview:
- Ecosystems are fundamental units that integrate the physical environment and living organisms, allowing the study of interactions between biotic and abiotic components.
- Autotrophic and heterotrophic components play significant roles within ecosystems.
Interconnected Components: Biotic and abiotic elements within the biosphere's ecosystem are closely related, facilitating energy, water, chemical, and sediment transfer via large-scale cyclic mechanisms.
Sustained Life and Ecosystems: Sustained life is a characteristic of ecosystems rather than individual organisms or populations.
Environmental Principles: Holliman's four environmental principles emphasize material cycles, interrelatedness of systems and problems, finite Earth resources, and nature's refinement of stable ecosystems.
Uniformitarianism in Processes: Physical and biological processes follow the principle of uniformitarianism, operating similarly across time periods but with varying rates due to human-induced environmental changes.
Natural Hazards and Biological Communities: Natural hazards affect biological communities, often creating severe risks to both wildlife and humans.
Organism-Environment Interactions: All living organisms and the physical environment mutually react, with interactions at different levels - positive, negative, or neutral.
Solar Radiation and Energy Flow: Solar radiation, harnessed via photosynthesis by green plants, drives ecosystem energy flow following thermodynamic laws.
Trophic Levels and Energy Transfer: Energy moves from lower to higher trophic levels, but higher levels often receive energy from multiple sources.
Trophic Level Relationships: Principles highlight the relationship between trophic levels, energy transfer, efficiency, and food chain length.
Biogeochemical Cycles: Inorganic and organic substances circulate via closed biogeochemical cycles among biosphere components.
Ecosystem Productivity: Ecosystem productivity relies on solar radiation availability and plant efficiency in converting it to chemical energy.
Ecosystem Stability: Self-regulating mechanisms maintain ecological stability through diversity, complexity, and homeostatic mechanisms.
Ecosystem Instability: Ecosystems become unstable when unable to adapt to environmental changes.
Dynamic Nature of Ecosystems: Charles Darwin's evolutionary concepts exemplify the dynamic nature of ecosystems.
Evolution and Mutation: Concepts of species evolution were challenged by mutation theory, proposing inheritable variations via spontaneous change.
Sere and Climax Vegetation: Transitional stages of vegetation changes culminate in a stable climax community through succession.
Successional Changes: Ecological succession and ecosystem development involve changes leading to increased complexity, structure, productivity, soil maturity, and stability.
Human Impact on Ecosystems: Human activities reduce ecological diversity and complexity by exploiting natural resources.
Preserving Ecosystem Diversity: Urges the application of ecological knowledge to preserve diversity in a world facing rapid resource depletion.
|
175 videos|619 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Ecology - Geography - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is ecology and how does it relate to geography? |  |
| 2. How does geography influence ecological patterns and processes? |  |
| 3. What are the main challenges in studying ecology from a geographic perspective? |  |
| 4. How do human activities impact the ecological dynamics of different geographic regions? |  |
| 5. How can the integration of ecology and geography contribute to solving environmental issues? |  |






















