Economic Development: July 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
Quality Control Orders
Why in News?
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce & Industry has recently notified two new Quality Control Orders (QCOs) on 'Potable Water Bottles' and 'Flame-Producing Lighters'.
- These QCOs aim to strengthen the quality ecosystem in India and ensure the public health and safety of consumers.
What are the Key Points Related to the QCOs?
- The QCO for ‘Potable water bottles’ mandates compulsory certification under the appropriate IS Standard for the production and import of potable water bottles made of copper, stainless steel, or aluminum.
- The QCO for ‘Flame-Producing Lighter’ mandates compulsory certification under IS Standards for ‘Safety Specification for Lighters’, and ‘Safety Specifications for Utility Lighters’, for the Flame lighters manufactured for domestic market or imported into India.
What are Quality Control Orders?
- QCOs are regulatory measures introduced by the government to establish quality standards for specific products or product categories. These orders are designed to ensure that products meet certain prescribed quality, safety, and performance requirements before they can be manufactured, imported, stored, or sold in the country.
- The main objective of QCOs is to control the import of sub-standard and cheaper items into the domestic market and ensure that customers have access to quality products that meet the necessary standards.
- QCOs cannot be challenged at the World Trade Organization (WTO) if they are imposed on the grounds of health, safety, environment and deceptive trade practices, or national security.
- To ensure compliance with the quality standards set forth in the QCOs, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) play a crucial role.
- BIS is responsible for certifying products that meet the prescribed standards, both for domestic and international manufacturers.
- With the QCOs, manufacturing, storing and sale of non-BIS certified products are prohibited as per the BIS Act, 2016."
50th Meeting of GST Council
Context
The Union Finance & Corporate Affairs Minister chaired the 50th meeting of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council in New Delhi. The meeting discussed various issues related to GST tax rates, trade facilitation and compliance simplification. The GST Council made several recommendations.
Details
Recommendations regarding the GST rates on various goods:
- Uncooked/unfried snack pellets
- Uncooked/unfried snack pellets, which are also known as papad khar, sago fritters, etc., will have a lower GST rate of 5% instead of 18%.
- This will benefit the manufacturers and consumers of these products.
- The GST on these products for the previous period will be paid as per the existing rules.
- Dinutuximab (Quarziba) medicine
- Dinutuximab (Quarziba) medicine, which is used for treating a rare form of cancer in children, will be exempted from IGST when imported for personal use.
- This will provide relief to the patients and their families who need this medicine.
- Medicines and Food for Special Medical Purposes (FSMP)
- Medicines and Food for Special Medical Purposes (FSMP) that are used for treating rare diseases listed under the National Policy for Rare Diseases, 2021 will also be exempted from IGST when imported for personal use, subject to existing conditions.
- FSMP will also be exempted from IGST when imported by Centres of Excellence for Rare Diseases or any person or institution on the recommendation of any of the listed Centres of Excellence.
- This will facilitate the availability and affordability of these products for patients suffering from rare diseases.
- Raw Cotton
- Raw cotton, including kala cotton, supplied by agriculturists to cooperatives will be taxable under the reverse charge mechanism. This means that the cooperatives will have to pay GST on behalf of the agriculturists.
- This will ensure uniformity and compliance in the taxation of raw cotton.
- The GST on raw cotton supplied by agriculturists to cooperatives for the previous period will be regularised as per the existing rules.
- Yarn
- Imitation zari thread or yarn, which is used for making embroidery and decorative items, will have a reduced GST rate of 5% instead of 12%.
- This will benefit the small and medium enterprises engaged in this sector.
- The GST on imitation zari thread or yarn for the previous period will be regularised as per the existing rules.
- Utility Vehicles
- All utility vehicles that have a length exceeding 4000 mm, engine capacity exceeding 1500 cc and ground clearance of 170 mm & above will be covered under entry 52B in compensation cess notification. This means that they will attract a compensation cess of 22% in addition to the GST of 28%.
- Ground clearance refers to the distance between the lowest point of the vehicle and the ground when the vehicle is not loaded. This will bring clarity and uniformity to the taxation of utility vehicles.
- Linz-Donawitz (LD) slag
- The GST rate on LD slag, a by-product of the steel industry, has been reduced from 18% to 5% to promote its use as a soil conditioner and to reduce environmental pollution.
- Fish soluble paste
- The GST rate on fish soluble paste, a product used in the animal feed industry, has been reduced from 18% to 5% and the GST paid on this product during the past period has been regularised on an “as is basis” without any additional liability.
Recommendations relating to GST rates on Services
- Satellite launch services
- Satellite launch services supplied by private sector organisations, in addition to those supplied by ISRO, Antrix Corporation Limited and New Space India Limited (NSIL), will be exempt from GST. This is to encourage start-ups and innovation in the space sector.
- Goods Transport Agencies
- Goods Transport Agencies (GTAs) will have the option to pay GST under forward charge without filing a declaration every year. Once they opt for this option for a particular financial year, they will continue to pay GST under forward charge for the next and future financial years, unless they file a declaration to revert to reverse charge mechanism (RCM).
- The option can be exercised from 1st January of the preceding financial year till 31st March of the preceding financial year.
- Food and beverages in cinema halls
- Supply of food and beverages in cinema halls will be taxable as restaurant service as long as (a) they are supplied by way of or as part of a service and (b) supplied independently of the cinema exhibition service.
- Where the sale of cinema tickets and supply of food and beverages are clubbed together, and such bundled supply satisfies the test of composite supply, the entire supply will attract GST at the rate applicable to the service of an exhibition of cinematograph films.
Group of Ministers (GoM) on Casinos, Race Courses and Online Gaming
- The GoM on Casinos, Race Courses and Online Gaming was formed to examine the tax issues related to these activities. The GoM gave its first report in June 2022 and it was discussed in the 47th GST Council meeting. The GST Council asked the GoM to review all the issues again.
- The GoM gave its second report and it was discussed in the 50th GST Council meeting. The GoM suggested that the GST Council should decide whether to tax these activities at 28% on the full-face value of bets placed or on the GGR, as there was no agreement on this.
The GST Council decided the following:
- Online gaming and horse racing will be added to Schedule III as taxable actionable claims by making changes to the law.
- Casino, Horse Racing and Online gaming will all be taxed at the same rate of 28%.
- The tax will be based on the face value of the chips bought in casinos, on the full value of the bets placed with bookmakers/totalisators in horse racing and on the full value of the bets placed in online gaming.
GST Council has made several recommendations for facilitating trade under the GST regime
- GST Appellate Tribunal Rules, 2023
- These rules will regulate the appointment and service conditions of the President and Members of the GST Appellate Tribunal, which will hear appeals against orders passed by the National Anti-profiteering Authority and the Appellate Authority for Advance Ruling. The Council has suggested that these rules should be notified by the Centre from 01.08.2023.
- The Council has decided to establish State Benches of the Tribunal in a phased manner.
- Input Services Distributor (ISD) mechanism
- The Council has clarified through a circular that the ISD mechanism is not compulsory for distributing input tax credit of common input services procured from third parties to the distinct persons as per the current provisions of GST law and also resolved issues regarding the taxability of internally generated services provided by one distinct person to another distinct person.
- The Council has also proposed that amendment may be made in GST law to make ISD mechanism mandatory from a future date for distributing input tax credit of such common input services procured from third parties.
- State-level coordination Committee
- The GST Council has also recommended forming a State level coordination Committee comprising GST officers from both State and Central GST administrations for knowledge sharing on GST matters and coordinated efforts towards administrative and preventive measures.
White Label ATMs
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has taken significant steps to promote ATM penetration, especially in Tier III to VI centres, by permitting non-bank companies to set up, own and operate White Label ATMs (WLAs).
- These WLAs provide various banking services to customers based on cards issued by banks, and the RBI has implemented measures to improve their viability and functioning.
- As of now, four authorised non-bank entities are operating White Label ATMs in the country.
What are White Label ATMs (WLAs)?
About
- ATMs set up, owned and operated by non-banks are called WLAs.
- Non-bank ATM operators are authorised under the Payment & Settlement Systems Act, 2007 by the RBI.
- They provide banking services to customers using debit/credit/prepaid cards issued by banks.
- Besides dispensing cash, WLAs offer services like account information, cash deposit, bill payment, mini statements, PIN change, and cheque book requests.
Steps to Enhance WLA Presence and Viability
- Cash Sourcing Flexibility:
- WLAs are allowed to source cash from retail outlets to address cash sourcing constraints.
- Following the demonetization (Rs 500 & Rs 1000 Bank Notes), as WLAs are having difficulties in sourcing cash from their sponsor bank(s).
- WLA operators can buy wholesale cash directly from the Reserve Bank and currency chests.
- They can also source cash from any scheduled bank, including Cooperative Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- Expanded Services and Partnerships
- WLAs are permitted to offer bill payment and interoperable cash deposit services.
- They can display advertisements for non-financial products/services, enhancing revenue streams.
- Banks can issue co-branded ATM cards in partnership with authorized WLA operators.
- This allows WLAs to facilitate 'on-us' transactions, increasing their attractiveness to customers.
- On-Tap Authorization
- RBI introduced on-tap authorization for WLAs to encourage more non-bank players to enter the ATM industry.
- This streamlined approval process simplifies WLA establishment and fosters greater competition.
- Driving ATM Penetration
- The focus is on expanding ATM penetration in Tier III to VI centres to improve banking accessibility in underserved areas.
- WLAs play a crucial role in achieving this objective, offering convenient banking services to a broader customer base.
- Facilitating Consumer Complaints and Protection
- The Consumer Education and Protection Department of RBI addresses complaints against WLAs.
- From April 2022 to June 2023, 98 complaints were received and handled by the Consumer Education and Protection Cells (CEPCs) of RBI.
- RBI has undertaken various steps to promote education and financial literacy, with one of the initiatives being the National Strategy for Financial Education (NSFE) 2020-2025.
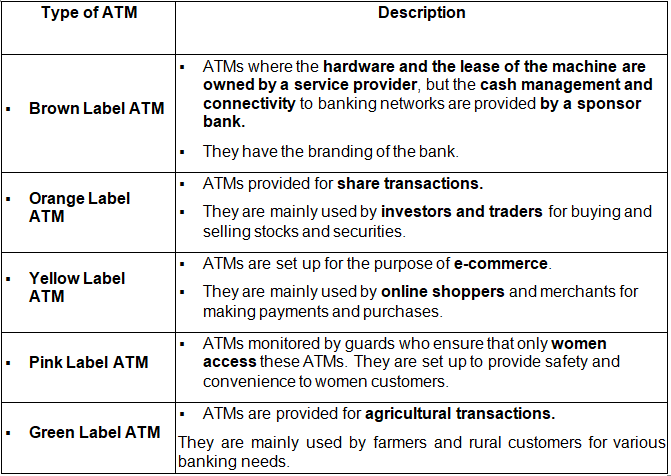
What are the Different types of ATMs?
Ethanol Blending Program
Context
- Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL) has successful launched a groundbreaking pilot study on vehicles using E27 fuel and Ethanol Blended Diesel Fuel.
- HPCL has become the first Oil Marketing Company in India to initiate such a comprehensive research program, in line with the "Roadmap for Ethanol Blending in India by 2025. The roadmap aims to promote the adoption of ethanol blending in gasoline.
Ethanol Blending Program
E27 Fuel
- E27 fuel is a blend of 27 percent ethanol and fossil-based fuel.
Blending of Fuel
- India has already rolled out 20 percent blended fuel, though, in a phased manner, in April 2023 and widespread availability is expected in two years.
- E20 blending in petrol was introduced in the country by the Centre with the aim of reducing the country’s oil import cost, energy security, lower carbon emission, and better air quality, among others.
- Notably, the government had advanced the target of E20 fuel from 2030 to 2025.
- Looking ahead, India’s next milestone in the Ethanol blending program is achieving 27% Ethanol blending beyond E20 fuel. With the success of the ongoing trials and the achievement of E27 fuel, India will proudly stand alongside Brazil on the global platform in the Ethanol blending program.
Tomatoes Price Volatility
Why in news?
- Tomato prices have reached sky-high in two months and yet the inflation rate of its prices is negative.
How is tomato produced in India?
- India grows two major crops of tomato annually
- Kharif - comes to markets from September
- Rabi - hits the market between March and August annually
- Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Odisha, and Gujarat accounts for close to 50% of total production of tomato.
- The production accounts for 90% along with the states Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Bihar, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, and Telangana.
- In the summer, Andhra Pradesh’s Madanapalle region alone accounts for tomato cultivation in the entire country.
- In 2021-22, the tomato production dropped to 20.69MT and 20.62MT in 2022-23.
What is fuelling the price rise?
- There are multiple factors for the drop in overall tomato production this year.
- The two key reasons are extreme weather conditions and low commercial realisation of the crop for farmers in the months before June.
- Weather - The heatwaves and high temperatures in April and May and the delayed monsoon showers in southern India and Maharashtra led to pest attacks in tomato crops.
- Supply crunch - Farmers sold inferior tomatoes at low prices and even some abandoned their crops between last December and April which led to supply crunch.
- Heightening reasons - Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, and Chhattisgarh saw a 20% drop in production, which aggravated tomato supplies in the 2022-23 crop year (July-June).
- The lean production period for tomato (July-August) has compounded the issue.
- Crop shift - Many tomato farmers in the Kolar district of Karnataka shifted to beans owing to the higher prices it fetched last year which reduced sizeable tomato supplies.
- Seasonal price volatility - The data on tomato prices of the last 5 years shows that the rates had risen every year at this time.
Do tomato price volatility impact CPI?
- There are concerns over the high seasonal price volatility of tomatoes and its impact on the overall Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- The contribution of TOP (tomato, onion, potato) to the overall CPI has been quite volatile, even with a low weightage of 2.20.
- In June 2022, at 8.9%, tomato had the largest contribution among 299 commodities in the CPI basket.
Why there is volatility in tomato prices?
- A NABARD study notes that tomato is the most volatile out of all the three TOP (tomato, onion, potato) agri-commodities.
- Reasons for volatility - Tomato is more perishable than onion and potato.
- Supply chain issues in transporting the vegetable from areas where it is grown to regions where it is not grown.
- The cyclical price drop led to a lot of farmers cultivating tomatoes in lesser land area and shifting to other crops.
Why the inflation rate of tomato is negative despite price hike?
- The inflation rate in tomato prices is negative.
- The inflation rate suggests that tomato prices are crashing despite actual soaring in prices.
- The tomato prices have been experiencing ‘deflation’ since November 2022.
- Inflation rate - It is based on the value of an index and is calculated on a year-on-year basis in India.
How can volatility be controlled?
- Produce - Increase tomato yields in India (now at 25 tonnes per hectare (t/ha)) at par with the global average of 37 t/ha.
- Encouraging cultivation in structures called poly houses and greenhouses (like done in European countries) to can control pest attacks.
- Storage and Processing - Since tomato is highly perishable, improved value and supply chains can help with the problem.
- Increasing the processing capacity for tomatoes and building more processing units.
- Farmers’ income - Eliminating middlemen and encouraging Farmer Producers Organisations (FPOs) to sell produce directly to increase farmers’ share.
- Amending rules of Agricultural Produce Market Committees (APMC) to reduce commission and other fees has also been suggested.
Quick Facts
- CPI - Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a comprehensive measure used for estimation of price changes in a basket of goods and services representative of consumption expenditure in an economy.
- Inflation is measured using CPI in India.
- The National Statistical Office (NSO) under Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) releases CPI.
Tomato
- Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) is an annual or short lived perennial herb.
- The flowers are off white bearing fruits which are red or yellow in colour and is a self-pollinated crop.
- The plant is a warm season crop that cannot withstand frost and high humidity.
Bhoomi Samman 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the President of India presented the “Bhoomi Samman” 2023 at a function organised by the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
What is “Bhoomi Samman”?
- The “Bhoomi Samman” is a prestigious award scheme launched by the Union Ministry of Rural Development to recognize and incentivize the achievements of states and districts in the implementation of the Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP).
- The award is presented by the President of India to the state secretaries and district collectors along with their teams who have excelled in achieving saturation of the core components of DILRMP, such as:
- Computerization of land records
- Digitization of cadastral maps
- Integration of textual and spatial data
- Survey/re-survey using modern technology
- Computerization of registration
- Interoperability between registration and land records
What are the Advantages of Digitalisation of Land Records?
- Transparency and Accountability: Digitization increases transparency in land transactions, reducing the scope for unethical and illegal activities related to land.
- Disaster Management: Digital records are more resilient to natural calamities like floods and fires, safeguarding essential land-related documents from loss.
- Land Parcel Identification Number: Similar to Aadhaar Card, the Unique Land Parcel Identification Number provided under the Digital India Land Information Management System allows efficient land utilization and enables the formulation and implementation of new welfare schemes.
- Resolution of Land Disputes: Access to land-related information in a free and convenient manner aids in resolving ownership and land-use disputes, reducing the burden on the administration and judiciary.
What are the Challenges Associated with Digitisation of Land Records?
- Fragmented Land Records: India's land records are maintained by multiple authorities at different levels - village, district, and state.
- The lack of uniformity and integration between these records can create difficulties when attempting to centralize and digitize them.
- Technological Infrastructure and Connectivity: Digitization requires adequate technological infrastructure, including hardware, software, and internet connectivity.
- In rural areas, where most land is located, the availability of such infrastructure can be limited, hindering the digitization process.
- Data Security and Privacy: Land records contain sensitive personal and property-related information.
- Ensuring the security and privacy of this data during digitization and beyond is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and misuse.
Way Forward
- Blockchain-based Land Records: Implement a blockchain-based system to store and manage land records.
- Blockchain's decentralized and immutable nature ensures transparency, reduces the possibility of fraud, and fosters trust in land transactions.
- Drone Surveys and GIS Mapping: Use drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and Lidar technology to conduct accurate surveys of land parcels.
- Integrate the data with Geographic Information System (GIS) mapping to create a dynamic and real-time representation of land records.
- Standardization and Interoperability: Establish uniform data standards and formats to ensure compatibility and seamless integration of land records across different departments and systems.
- This will enable efficient data sharing and retrieval.
UPU to Assess UPI for Cross-Border Remittances
Why in News?
The Universal Postal Union (UPU) has announced plans to evaluate the integration of the Unified Payment Interface (UPI) with cross-border remittances using the global postal network.
- This evaluation aims to explore the potential of UPI in facilitating secure and efficient international money transfers.
What are the Benefits of Integrating UPI with UPU?
- UPI offers a secure, convenient, and real-time payment experience, making it a promising platform for cross-border remittances.
- Leveraging the global postal network, which has extensive reach and infrastructure, can further expand the reach of UPI-enabled remittances.
- The integration of UPI with postal channels can provide a reliable and accessible remittance solution for individuals, particularly in remote areas where traditional banking services may be limited.
- This initiative aligns with UPU's goal of promoting efficient and inclusive postal services globally.
What is Universal Postal Union (UPU)?
- About
- The UPU is a United Nations specialized agency and the postal sector's primary forum for international cooperation.
- UPU is the second oldest international organization.
- Establishment and Structure
- The UPU was established in 1874 through the Treaty of Bern.
- UPU's headquarters are located in Bern, Switzerland.
- The organization consists of four bodies: Congress, the Council of Administration (CA), the Postal Operations Council (POC), and the International Bureau (IB).
- It also oversees the Telematics and Express Mail Service (EMS) cooperatives.
- Membership
- Any member country of the United Nations can become a member of the UPU.
- Non-member countries of the United Nations can join the UPU if approved by at least two-thirds of the member countries.
- The UPU has now 192 member countries.
- India joined the UPU in 1876.
- Role and Functions
- UPU coordinates postal policies among member nations and the global postal system.
- The union sets rules for international mail exchanges and makes recommendations to stimulate growth in mail, parcel, and financial services volumes.
- It aims to improve the quality of service for customers and promote efficiency in international postal operations.
|
63 videos|5407 docs|1145 tests
|
FAQs on Economic Development: July 2023 UPSC Current Affairs - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are Quality Control Orders? |  |
| 2. What was discussed at the 50th Meeting of GST Council? |  |
| 3. What are White Label ATMs? |  |
| 4. What is the Ethanol Blending Program? |  |
| 5. How does price volatility affect tomatoes? |  |

















