Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Electroplating
Electroplating | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
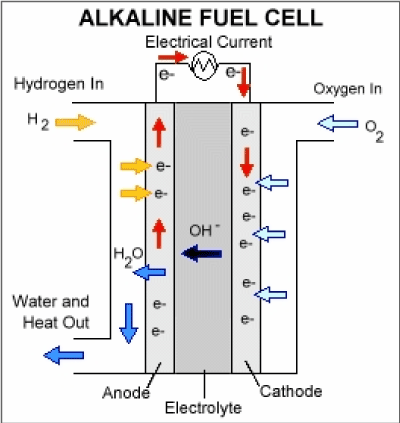
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
- A fuel is a substance that releases energy when burned.
- Hydrogen serves as a fuel in rocket engines and fuel cells for powering certain vehicles.
- A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell where a fuel provides electrons at one electrode and oxygen receives electrons at the other electrode.
- Hydrogen: H2 → 2H+ + 2e–
- Oxygen: O2 + 4e– → 2O2–
- The hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell generates electricity by combining both elements, producing energy and water.
- The comprehensive equation for the reaction in a hydrogen fuel cell is:
hydrogen + oxygen → water - The hydrogen fuel cell configuration involves the intake of hydrogen and oxygen.
- Oxygen is provided by the incoming air while hydrogen serves as the fuel.
- The sole byproduct generated in this process is water.
Question for ElectroplatingTry yourself: What is the purpose of a hydrogen fuel cell?View Solution
Advantages & Disadvantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Increasing Usage in Automotive Industry
- Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells are progressively being employed in vehicles to supplant traditional petrol or diesel engines.
Advantages
- They generate no pollution, with water being the sole byproduct, unlike petrol engines that emit carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
- They yield higher energy output per kilogram compared to both petrol and diesel.
- They incur no power loss during transmission since they lack moving components, unlike internal combustion engines.
- They operate quietly, resulting in reduced noise pollution when compared to petrol engines.
Disadvantages
- The materials required for manufacturing fuel cells are costly.
- Storing hydrogen is more challenging and expensive than storing petrol due to its high flammability, which can lead to explosions under pressure.
- Fuel cells experience reduced efficiency in low temperatures.
- There is a limited availability of hydrogen filling stations nationwide.
- Hydrogen is often obtained through processes involving the combustion of fossil fuels, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere.
Question for ElectroplatingTry yourself: What is one advantage of hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells compared to petrol engines?View Solution
The document Electroplating | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Electroplating - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the main advantages of using hydrogen fuel cells? |  |
Ans. Hydrogen fuel cells offer the advantages of being environmentally friendly, producing zero emissions, providing high energy efficiency, and offering a quiet operation compared to traditional combustion engines.
| 2. What are the main disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells? |  |
Ans. Some of the main disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells include the high cost of production, the lack of infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations, and the challenges of storing and transporting hydrogen gas.
| 3. How do hydrogen fuel cells work in the process of electroplating? |  |
Ans. Hydrogen fuel cells can provide a clean and efficient source of power for electroplating processes by converting hydrogen gas into electricity through an electrochemical reaction, which can then be used to power the electroplating equipment.
| 4. Can hydrogen fuel cells be used for other applications besides electroplating? |  |
Ans. Yes, hydrogen fuel cells have a wide range of potential applications beyond electroplating, including powering vehicles, providing backup power for buildings, and supplying electricity to remote locations where traditional power sources are not available.
| 5. Are there any safety concerns associated with the use of hydrogen fuel cells in electroplating? |  |
Ans. While hydrogen fuel cells are generally considered safe, there are some safety concerns related to the handling and storage of hydrogen gas, which is highly flammable. Proper safety measures, such as proper ventilation and training for handling hydrogen, are essential to minimize the risks associated with using hydrogen fuel cells in electroplating processes.
Related Searches
















