Nucleophilic Substitution, Elimination Reactions & Polyhalogen Compounds | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
The reactions of haloalkanes may be divided into the following categories:
1. Nucleophilic substitution
2. Elimination reactions
3. Reaction with metals.
Chemical reactions of alkyl halide:
Those organic compounds in which an sp3 hybridized carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group can undergo two types of reaction e.g. substitution reactions in which the electronegative atom or group is replaced by another atom or group. The second is the elimination reaction in which the electronegative atom or group is eliminated along with hydrogen from an adjacent carbon. The electronegative atom or group which is substituted or eliminated is known as leaving group. 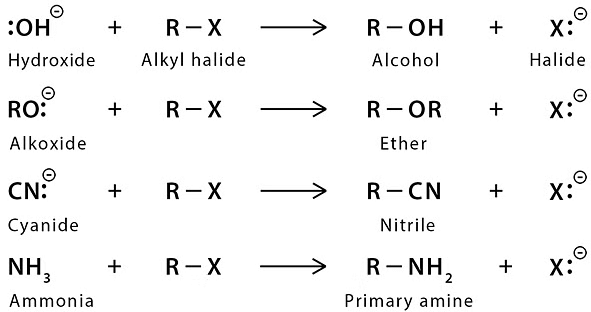 Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction
Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction

Because of more electronegativity of the halogen atom, it has a partial negative charge and partial positive cha develops on the carbon atom.
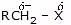
X = F, Cl, Br, I
Due to this polar carbon - halogen bond alkyl halides shows nucleophilic substitution and elimination reaction.
There are two important mechanisms for the substitution reaction:
- A nucleophile is attracted to the partially positively charged carbon. As the nucleophile approaches the carbon, it causes the carbon - halogen bond to break heterolytically (the halogen keeps both of the bonding electrons.)
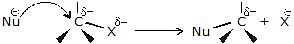
- The carbon-halogen bond breaks heterolytically without any assistance from the nucleophile, with the help of polar protic solvent and carbocation is formed (solvolysis). Formed carbocation then reacts with the nucleophile to form the substitution product.
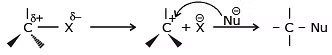
(i) Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction (SN2)
The mechanism of SN2 reaction
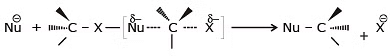
transition state
Characteristic of SN2
It is bimolecular, unistep process
- It is the second-order reaction because in the Rds two species are involved
- Kinetics of the reaction → rate ∝ [alkyl halide] [nucleophile]
rate = k[alkyl halide] [nucleophile]
If the concentration of alkyl halide in the reaction mixture is doubled, the rate of the nucleophilic substitution reaction is double. If the concentration of nucleophile is doubled the rate of reaction is also double. If the concentration of both is doubled then the rate of the reaction quadruples. - Energetics of the reaction:
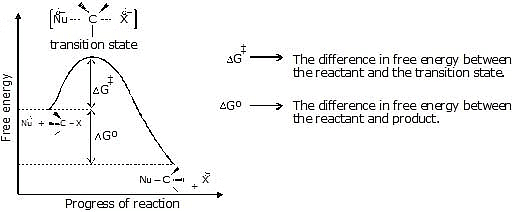
Figure: A free energy diagrams for a hypothetical SN2 reaction that takes place with a negative DGº - No intermediates are formed in the SN2 reaction, the reaction proceeds through the formation of an unstable arrangement of atoms or group called transition state.
- Stereochemistry of SN2 reaction: As we saw earlier, in an SN2 mechanism the nucleophile attacks from the backside, that is from the side directly opposite to the leaving group. this mode of attack causes an inversion of configuration at the carbon atom that is the target of nucleophilic attack. This inversion is also known as Walden inversion.

Factors affecting the rate of an SN2 reaction
A number of factors affect the relative rate of SN2 reaction, the most important factors are:
- Structure of the substrate
- Concentration and reactivity of the nucleophile
- Effect of the solvent
- Nature of the leaving group
1. Effect of the structure of the substrate:
Order of reactivity in SN2 reaction : - CH3 > 1º > 2º >> 3º (unreactive)
the important factor behind this order of reactivity is a steric effect. Very large and bulky groups can often hinder the formation of the required transition state and crowding raises the energy of the transition state and slows down the reaction.
Relative rates of reactions of an alkyl halide in SN2 reaction
Substituent | Compound | Relative rate |
Methyl | CH3X | 30 |
1° | CH3CH2X | 1 |
2° | (CH3)2CHX | 0.02 |
Neopentyl | (CH3)3CCH2X | 0.00001 |
3° | (CH3)3CX | ~0 |
2. Concentration and reactivity of the nucleophile
According to the kinetics of SN2 increasing the concentration of the nucleophile increases the rate of an SN2 reaction. The nature of nucleophile strongly affects the rate of an SN2 reaction. A stronger nucleophile is much more effective than a weaker one. For example, we know that a negatively charged nucleophile is more reactive than its conjugate acid e.g. HO- > H2O, RO- > ROH.
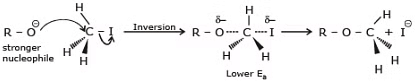
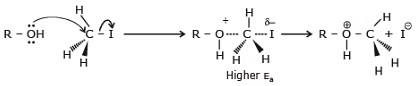
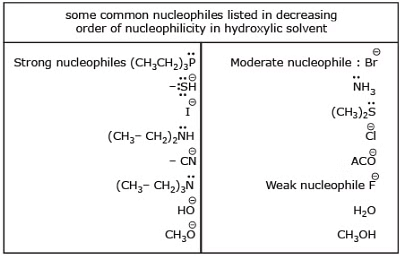 Steric effects on nucleophilicity
Steric effects on nucleophilicity
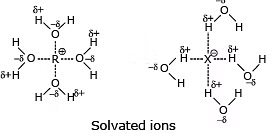
3. The effect of the solvent: In polar protic solvent large nucleophiles are good, and the halide ions show the following order: I- > Br- > Cl- > F- (in polar protic solvent)
This effect is related to the strength of the interaction between nucleophile and solvent molecules of polar protic solvent forms a hydrogen bond to nucleophiles in the following manner. Because small nucleophile is solvated more by the polar protic solvent thus its nucleophilicity decreases and the rate of SN2 decreases
Relative nucleophilicity in a polar protic solvent:
SH+ > CN- > I- > OH- > N3- > Br- > ACO- > Cl- > F- > H2O
So, polar protic solvents are not useful for the rate of SN2, if the nucleophile is anionic. But polar aprotic solvent does not have any active hydrogen atom so they can not forms an H bond with nucleophiles. Polar aprotic solvent has a crowded positive centre, so they do not solvate the anion appreciably therefore the rate of SN2 reactions increased when they are carried out in a polar aprotic solvent.
Examples of a polar aprotic solvent.
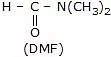
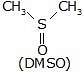
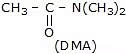
In DMSO, the relative order of reactivity of halide ions is: F- > Cl- > Br- > I-
4. The nature of the leaving group: The best-leaving groups are those that become the most stable ion after they leave because leaving group generally leave as a negative ion, so those leaving groups are good, which stabilise negative charge most effectively and weak base do this best, so weaker bases are good leaving groups. A good leaving group always stabilize the transition state and lowers its free energy of activation and thereby increases the rate of the reaction.
Order of leaving ability of halide ion: I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
Other leaving groups are 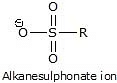
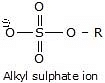
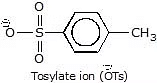

Strongly basic ions rarely act as leaving group:
Examples of SN2 reactions of alkyl halide →
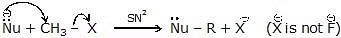
| Nucleophile | Product | Class of Product | |
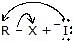 |  | R -  | Alkyl halide |
 |  | R - 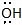 | Alcohol |
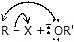 |  | R -  | Ether |
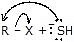 |  | R -  | Thiol(mercaptan) |
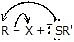 |  | R - 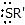 | Thioether (sulphide) |
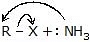 |  | R - 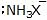 | Amine |
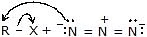 |  | R - 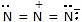 | Azide |
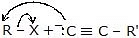 |  | R - 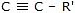 | Alkyne |
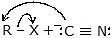 |  | R - 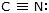 | Nitrile |
 |  | R - COO - R | Ester |
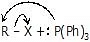 |  | [R - PPh3]+ 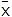 | Posphonium salt |
Question 1: Complete the following reactions with mechanism
(a) 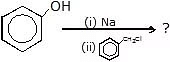
Sol. 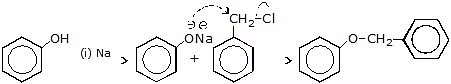
(b) 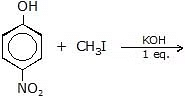 ?
?
Sol.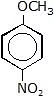 (p-Nitroanisole)
(p-Nitroanisole)
(c) Ph - CH2Cl
Ph - CH2Cl 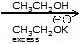
Sol. CH3-CH2-O! is present in excess and it is stronger nucleophile than Ph - O! so the product is Ph-CH2 - OEt
(d) CH3 - C ≡ CH 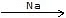 X
X 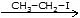 Y
Y
Sol.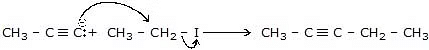
(e) 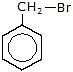 Ph3 → Salt
Ph3 → Salt
Sol. 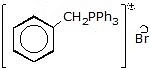
Question 2: When the concentration of alkyl halide is tripled and the concentration of OH- ion is reduced to half, the rate of SN2 reaction increases by :
(A) 3 times (B) 2 times (C) 1.5 times (D) 6 times
Ans: c
(ii) Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction (SN1)

Characteristics of SN1 reactions
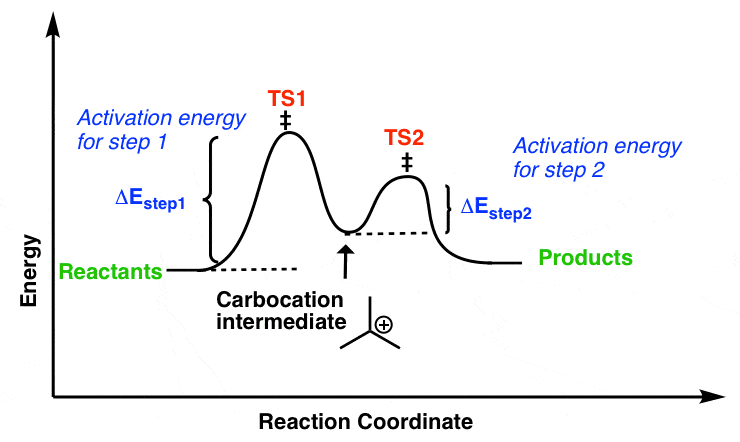
- It is a unimolecular, two-step process and intermediate is formed, (intermediate is carbocation)
- It is a first-order reaction
- Kinetics of the reaction, Rate ∝ [Alkyl halide]
Rate = k[(CH3)3C-X]
The rate of SN1 reaction is independent of the concentration and reactivity of nucleophile. - Stereochemistry of SN1 reaction:
In the SN1 mechanism, the carbocation intermediate is sp2 hybridized and planar. A nucleophile can attack the carbocation from either face if the reactant is chiral than after the attack of nucleophile from both faces gives both enantiomers of the product, which is called recemization.Mechanism of recemization (SN1):
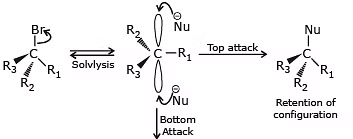
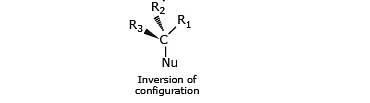
- Energetics of the SN1
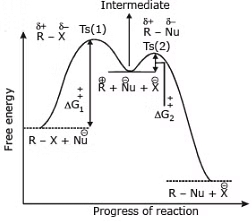
Figure: free energy diagram for the SN1 reaction.
Factors affecting the rates of SN1
The structure of the substrate:
The Rds of the SN1 reaction is an ionization step, in this step form a carbocation. This ionisation is a strongly endothermic process, rate of SN1 reaction depends strongly on carbocation stability because carbocation is the intermediate of SN1 reaction which determines the energy of activation of the reaction.
SN1 reactivity : 3º > 2º > 1º > CH3 - X- Concentration and reactivity of the nucleophile:
The rate of SN1 reactions are unaffected by the concentration and nature of the nucleophile - Effect of the solvent:
Because to solvate cations and anions so effectively the use of polar protic solvent will greatly increase the rate of ionization of an alkyl halide in any SN1 reaction. It does this because solvation stabilizes the transition state leading to the intermediate carbocation and halide ion more than it does the reactant, thus the energy of activation is lower.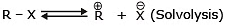
- The nature of the leaving group:
In the SN1 reaction, the leaving group begins to acquire a negative charge as the transition state is reached the stabilisation of this developing negative charge at the leaving group stabilizes the transition state and: this lowers the free energy of activation and thereby increases the rate of reaction.
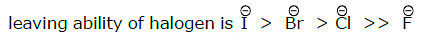
Comparison of SN1 and SN2 reactions :
|
| SN1 | SN2 |
(i) | Effect of the nucleophile | Nucleophile strength is not important | A stronger nucleophile is required |
(ii) | Effect of the substrate | 3° > 2° > 1° > CH3X | CH3X > 1° >2° |
(iii) | Effect of solvent | Good ionizing solvent required | It goes faster in a less polar solvent if Nud is present |
(iv) | Kinetics | Rate = k [R-X] | Rate = k[R-X] [Nu°] |
(v) | Stereochemistry | Racemisation | Walden inversion |
(vi) | Rearrangement | common | Impossible |
Question 3: Predict the compound in each pair that will undergo solvolysis (in aqueous ethanol) more rapidly.
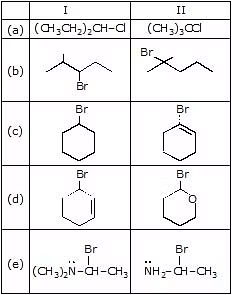
Sol. (a) II > I (b) II > I (c) I > II (d) II > I (e) II > I
Question 4: Give the solvolysis products expected when each compound is heated in ethanol
(a)  (b)
(b) 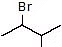 (c)
(c) 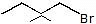 (d)
(d) 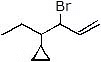
Sol. (a) 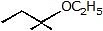 (b)
(b) 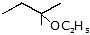 (c)
(c) 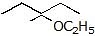 (d)
(d) 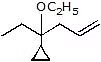
Question 5: The rate of SN1 reaction is fastest with
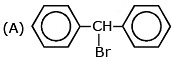
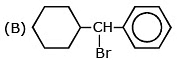
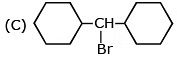
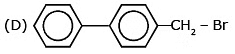
Ans. (A)
The reaction of RX with aq. KOH
-
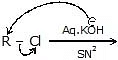 R - OH + KCl
R - OH + KCl - CH3-CH2-Cl
 CH3-CH2-OH
CH3-CH2-OH - CH3-CH
 CH3-CH
CH3-CH 
 CH3-CHO
CH3-CHO - CH3-C
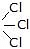
 CH3-C
CH3-C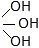
 CH3COOH
CH3COOH - C - C - C - C - Br
 C - C - C - C - OH
C - C - C - C - OH 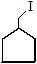
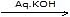
- 14C = C - C - I
 14C = C - C - OH + C = C - C14 - OH
14C = C - C - OH + C = C - C14 - OH 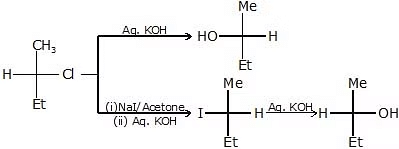
Other Nucleophilic reaction of R - X :-
WillionSon's Ether Synthesis: (SN2)

- EtONa + Me - Cl
 EtOMe
EtOMe 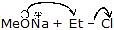
 EtOMeRate (2) > (3) 2 is better method. (Due to less steric hindrence)
EtOMeRate (2) > (3) 2 is better method. (Due to less steric hindrence)- MeONa + PhCl
 No reaction
No reaction 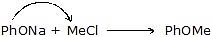 + NaCl
+ NaCl- Me3CO!NaÅ + MeCl
 Me3COMe + NaCl
Me3COMe + NaCl - MeO!NaÅ + Me3C - Cl

 + MeOH + NaCl
+ MeOH + NaCl - PhONa + Me3C-Cl

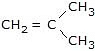 + PhOH + NaCl
+ PhOH + NaCl - Me3CONa + Ph-Cl
 No. reactionMe3CO-Ph can not be prepared by Williamson's ether synthesis.
No. reactionMe3CO-Ph can not be prepared by Williamson's ether synthesis. -
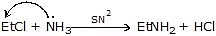
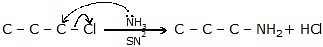
-
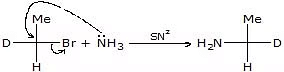 + HCl
+ HCl 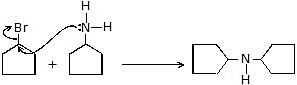 + HBr
+ HBr-
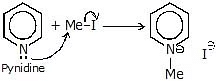 (Pyridinium salt)
(Pyridinium salt)
Hydrolysis of Ether
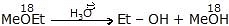
- MeOEt
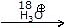 Et -
Et - 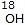 + Me - OH
+ Me - OH 
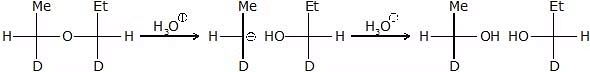
Reaction of ether with HI :
- Me - O - Et
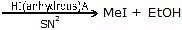
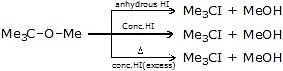 (Due to formation of more stable carbocation)
(Due to formation of more stable carbocation)
With moist and dry Ag2O :
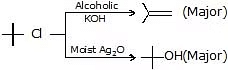
- 2Me - Cl
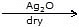 Me - O - Me + 2AgCl
Me - O - Me + 2AgCl - Me - Cl + EtCl
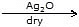 Me - O - Et + Me - O - Me + EtOEt
Me - O - Et + Me - O - Me + EtOEt
(iii) SN1 (Nucleophilic substitution intramolecular )
Darzon's process:
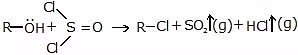
Mechanism:
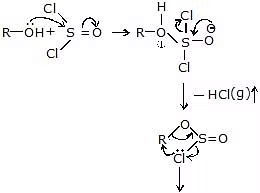
R - Cl + O = S = O (g)
Note : (1) In SNi retention of the configuration takes place.
(2) In presence of pyridine above reaction follow the SN2 reaction mechanism.
(iv) SN NGP (Neighbouring Group Participation)
An increase in the rate of SN reaction due to attack of internal nucleophile is called SNNGP is also known as Anchimeric assistance.
For SNNGP
- Internal nucleophile must be present
- Internal nucleophile must be anti to lg.
During NGP:
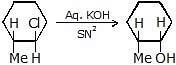
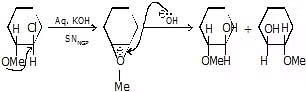 (enantiomers)
(enantiomers)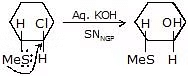 + (enantiomer) Rate 3 > 2 > 1
+ (enantiomer) Rate 3 > 2 > 1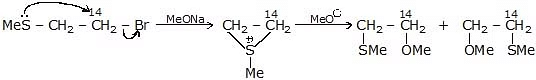
Elimination Reactions
In an elimination reaction, two atoms or groups (YZ) are removed from the substrate with the formation of a pi bond.
Depending on the reagents and conditions involved, elimination may be a first-order (E1) or second-order (E2).
Dehydration of Alcohol (E1)
Characteristics of E1 reaction
- It is a unimolecular, two-step process
- It is a first-order reaction
- Reaction intermediate is carbocation, so rearrangement is possible
- In the second step, a base abstracts a proton from the carbon atom adjacent to the carbocation and forms alkene.
- Kinetics → Rate ∝ [Substrate]
Rate = k[Substrate]
E2- elimination:
Bimolecular reaction, second-order kinetic:
- Leaving group leads when the base is taking proton from adjacent carbon.
- It is a single step reaction
- It shows elemental as well as kinetic isotopic effect with lg as well as at b-position.
- Normally Saytzaff product is major.
- Transition state mechanism therefore rearrangement is not possible.
- The orientation of the proton & leaving group should be antiperiplanar for E2.
- Positional orientation of elimination: In most E1 and E2 eliminations gives two or more possible elimination products, the product with the most highly substituted double bond will predominate. This rule is called the Saytzeff or Zaitsev rule (i.e., most stable alkene will be the major product)
- E2-elimination is favour by:
- Strong base (RO-, Alc. KOH)
- Polar aprotic solvent.
- High conc. of base.
- High temperature
Reactivity towards E2: R - I > R - Br > R - Cl > R - F
Question 1: Predict the elimination products of the following reactions.
(a) Sec. butyl bromide +
(b) 3-Bromo-3-ethylpentane + CH3OH
(c) 2-Bromo-3-ethylpentane + MeONa
(d) 1-Bromo-2-methylcyclohexane + EtONa
Sol. (a) CH3 - CH = CH -CH3
(b)
(c)
(d)
Question 2: major + minor
Write the structure of major and minor product.
Sol. (minor)
(major)
Question: Compare rate of elimination (Dehydro-halogenation in presence of alcoholic KOH) i.e., E2 reaction in the following:
1. (a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Ans: c > b > a > d
2. (a) (b)
(c)
Ans: c > b > a
3. (a) (b)
(c)
Ans: c > b > a
4. (a) (b)
(c)
Ans: b > a > c
Dehalogenation : - (-X2) E2
Dehalogenation : - (-X2) E2
Ec or Ei (Intramolecular or cyclic elimination mechanism):
(1) Lg and Base present in same molecule.
(2) It proceeds by cyclic transition state.
(3) Overall it is syn elimination.
(4) Hoffmann is major product as it is obtained by least hindered site of cyclic transition state.
(5) No rearrangement.
Example of Ec/Ei:
Pyrolysis of Ester:
1.
2.
Comparison of E1 and E2 elimination:
Promoting factors | E1 | E2 |
(i) Base | Weak base | Strong base required |
(ii) Solvent | Good ionizing solvent | Wide variety of solvent |
(iii) Substrate | 3° > 2° > 1° | 3° > 2° > 1° |
(iv) Leaving group | Better one required | Better one required |
Characteristics |
|
|
(i) Kinetics | K[R- X], I order | K[R - X] [Base], IIst order |
(ii) Orientation | Saytzeff alkene | Saytzeff alkene |
(iii) Stereochemistry | No special geometry is required | transition state must be co-planar |
Question 3: P + Q + R
Sol.
P is
Q is
R
Question 4: Arrange the compounds of each set in order of reactivity towards dehydrohalogenation by a strong base
(a) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
(b) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-bromo-2-methylbutane-2-Bromo-3-methylbutane
(c) 1-Bromobutane,1-Bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane, 1-bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane
Haloalkanes Reactions with Metals
Haloarenes undergo few reactions with metals. Two primary reactions are:- Wurtz-Fittig Reaction
- Fittig Reaction
Wurtz-Fittig Reaction:
In this reaction, a mixture of alkyl halide reacts with an aryl halide in the presence of dry ether and sodium. The resultant product is alkyl arene.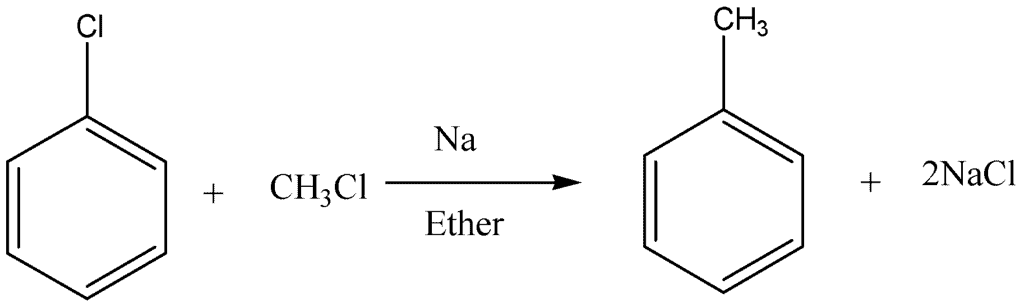
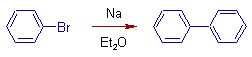
Fittig Reaction:
In this reaction, a mixture of haloarenes reacts with sodium in the presence of dry ether. The resultant product is diaryl.
What is Polyhalogen Compounds?
The hydrocarbons or any carbon compounds containing more than one halogen atom (group 17 elements of the modern periodic table) are known as polyhalogen compounds.
Many of these compounds are useful in industry and agriculture. Some notable polyhalogen compounds are described below:
Polyhalogen derivatives:
1. Trichloromethane (Chloroform), CHCl3
Chloroform, also referred to as trichloromethane is an organic compound. Chloroform is an organic chemical compound initially employed as an ideal anaesthetic. It was first prepared in 1831. The chemical formula is CHCl3. It is a colourless, sweet-smelling dense liquid produced on a large scale.
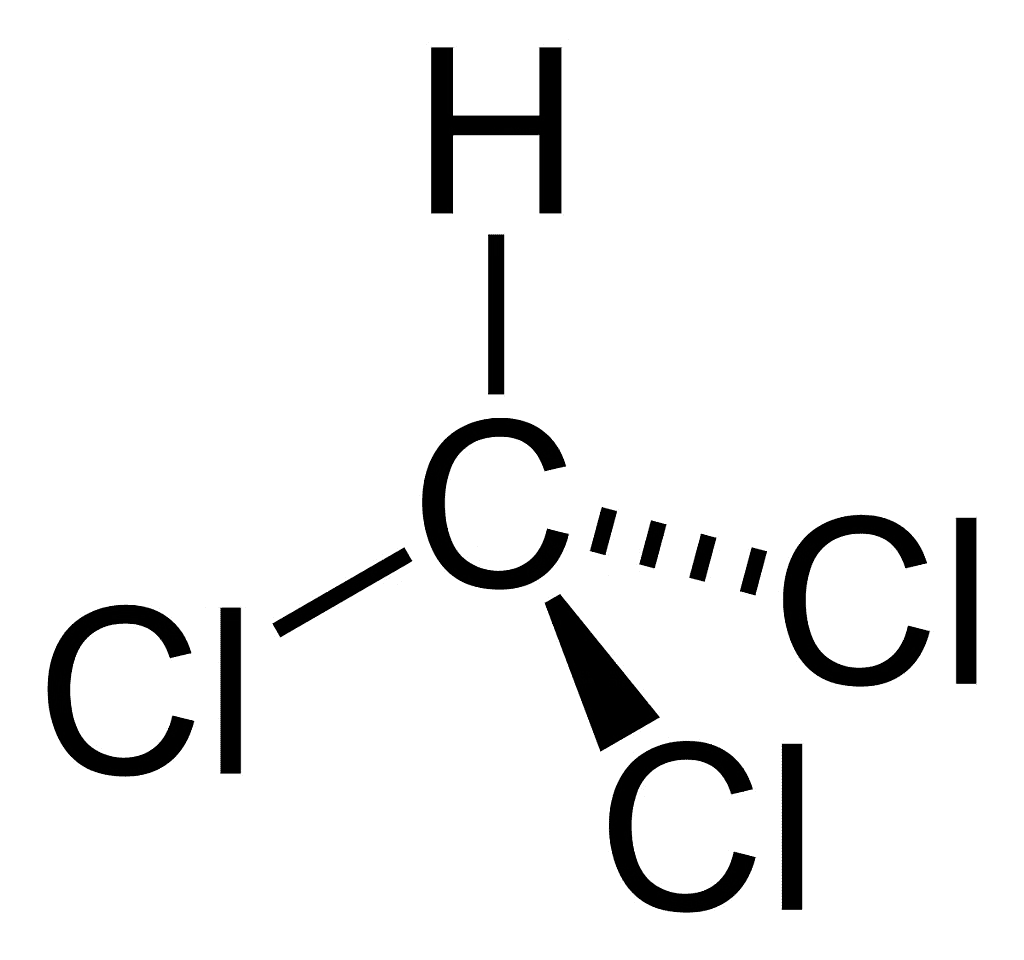
Preparation:
CH4 + Cl2 CH3Cl + HCl
Chloromethane
CH3Cl + Cl2 CH2Cl2 + HCl
Dichloromethane
CH2Cl2 + Cl2 CHCl3 + HCl
Trichloromethane
CHCl3 + Cl2 CCl4 + HCl
Tetrachloromethane
The mixture of CH3Cl, CH2Cl2, CHCl3 and CCl4 can be separated by fractional distillation.
Uses of Chloroform:
- Used as an anaesthetic and used in dentistry during root canal procedures.
- The spectrum of pure chloroform is used as the reference or background, and pure cholesterol powder or cholesterol extract from milk products is dissolved in chloroform and used for FTIR analysis.
- Chloroform was utilized in the past as an extraction dissolvable for fats, greases, oils, and different items; as a laundry spot.
- Used as an indirect food additive in food packaging materials for adhesive components and as a component of food contact materials.
2. Triiodomethane (iodoform)
- It was used earlier as an antiseptic but the antiseptic properties are due to the liberation of free iodine and not due to iodoform itself.
- Due to its objectionable smell, it has been replaced by other formulations containing iodine.
3. Tetrachloromethane
- Carbon tetrachloride is used extensively in refrigerant and aerosol propellant production. It's also a key ingredient in making chlorofluorocarbons and various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals.
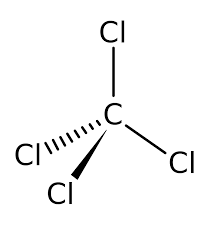
- Until the mid-1960s, it served as a popular cleaning solvent in industry, homes, and as a fire extinguisher. However, exposure to it may cause liver cancer, dizziness, nausea, and nerve cell damage.
- Severe cases can lead to coma or death, with potential heart irregularities upon exposure. It can also irritate the eyes. When released into the air, it depletes the ozone layer, potentially increasing UV exposure and related health risks,
4. Freons
- Freons, made from methane and ethane, are stable, non-toxic gases.
- Freon 12, a common type, is produced from tetrachloromethane via the Swarts reaction. It's used in aerosols, refrigeration, and air conditioning.
- About 2 billion pounds were produced annually by 1974. Most Freon ends up in the atmosphere, where it can harm the ozone layer by causing radical chain reactions
5. DDT
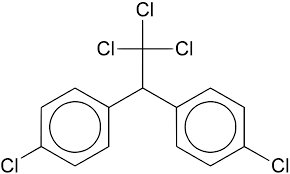
- DDT, the first chlorinated organic insecticide, was created in 1873.
- Its insecticidal properties were discovered by Paul Muller of Geigy Pharmaceuticals in Switzerland in 1939. He received the Nobel Prize in Medicine and Physiology for this in 1948. DDT's global use surged after World War II due to its effectiveness against malaria-spreading mosquitoes and typhus-carrying lice.
- However, problems arose in the late 1940s due to insect resistance and its toxicity to fish. DDT's chemical stability and fat solubility worsened the issue. It accumulates in animals' fatty tissues rather than being quickly metabolized.
- The US banned DDT in 1973, but it's still used in some areas worldwide.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Nucleophilic Substitution, Elimination Reactions & Polyhalogen Compounds - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is a nucleophilic substitution reaction? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between SN1 and SN2 reactions? |  |
| 3. What is NGP (Neighbouring Group Participation) in nucleophilic substitution reactions? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between E1 and E2 elimination reactions? |  |
| 5. How do haloalkanes react with metals? |  |






















