Enter required prob | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
(e)The reaction in which a chemical substance transforms into another new chemical substance is known as a chemical reaction. A chemical change involves the formation of new substances whereas a physical change involves a change in colour or state and no new substances are formed.(e)
Accordingly, the reactions are classified in different types:-(se)
(1) Combination reaction or synthesis reaction
(2) Decomposition reaction/Analysis reaction
(3) Displacement reaction
(4) Double displacement reaction/Metathesis reaction
(5) Oxidation and Reduction reaction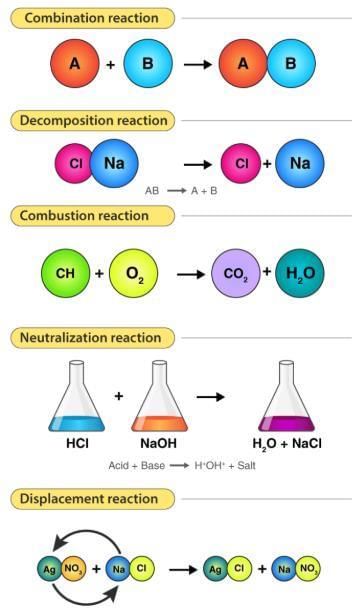 Fig: Types of chemical reaction(1) Combination reaction: The reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single new substance are called combination or synthesis reaction.(e after pic always and before and after equation)
Fig: Types of chemical reaction(1) Combination reaction: The reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single new substance are called combination or synthesis reaction.(e after pic always and before and after equation)
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) (enter)
Combination reactions are of three common types:
(i) Combination of two elements to form a compound. Example:-(se)
H2(g) + Cl2(g)  2HCl(g)
2HCl(g)
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) (shift e)
(ii) Combination of an element and a compound to form a new compound:-(se)
2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g)
(e)(iii) Combination of two compounds to form a new compound:-
NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(g)
(e)(2) Decomposition reaction: The reaction in which a single compound breaks up into two or more simpler substances are known as decomposition reaction. The decomposition reaction generally takes place when energy in some forms such as heat, electricity or light is supplied to the reactants.
(se) (a) Decomposition reactions by heat (Thermal decomposition) (se)
(se)
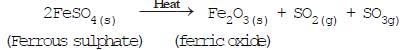 (e)
(e)
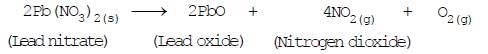
(dse)(b) Decomposition by electricity (Electrical decomposition or Electrolysis)
(e)(c) Decomposition by sunlight (Photochemical decomposition)
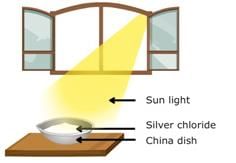 Fig: Decomposition of silver chloride
Fig: Decomposition of silver chloride
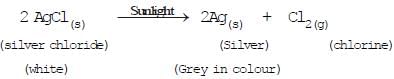
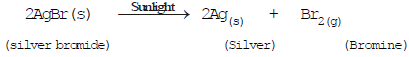
The decomposition of a compound with light is called photolysis.
Note:- All the decomposition reaction requires energy i.e. these reactions are endothermic reactions. These reactions are used in extraction of metals.
A decomposition reaction is called the opposite of combination reaction. This can be supported by the following reactions:
Combination reaction: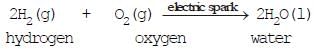
Decomposition reaction :
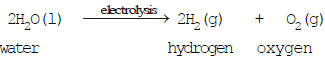
Activity Series of Hydrogen and Common Metals  Fig: Reactivity series
Fig: Reactivity series
(3) Displacement reactions: The chemical reaction in which one element takes the place of another element in a compound, are called displacement reactions e.g. -
(i)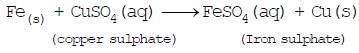
(ii) 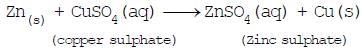
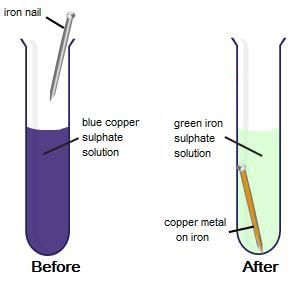 Fig: Displacement reaction
Fig: Displacement reaction
Iron, zinc and lead are more reactive elements than so they displace copper from its compounds.
(iii) Chlorine displaces Bromine from Potassium bromide
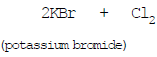
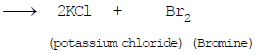
(iv) Copper displaces silver from silver nitrate.
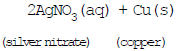
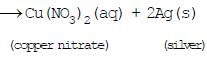
Ques : In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Ans.
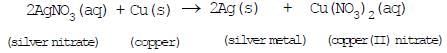
(4) Double displacement reactions: The reactions in which two compounds react to form two different compounds by mutual exchange of ions are called double displacement reactions. These reactions are also called a Metathesis reaction.
Two common types of double displacement reactions are:-
(A) Precipitation reaction: Any reaction that produces a precipitate, (the insoluble substance formed), is called precipitation reaction. e.g.-
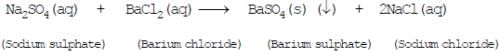
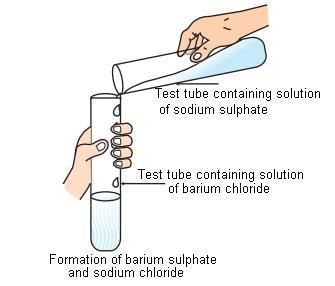 Fig: Precipitation reaction Example
Fig: Precipitation reaction Example
(B) Neutralisation reaction: When an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water by exchange of ions e.g.-
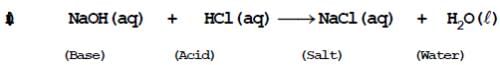
(5) Oxidation and Reduction reactions or Redox reaction:
Oxidation:
(i) The addition of oxygen to an element or compound.
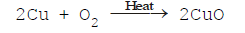
(ii) Removal of hydrogen from a compound is known as oxidation.
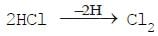
Reduction:
(i) The addition of hydrogen to an element or compound
H2 + O2 → 2H2O
(ii) Removal of oxygen from a compound.

Oxidising agent: The substance which gives oxygen or removes hydrogen for oxidation is called oxidising agent and the substance which gains oxygen during reaction is said to be oxidised.
Reducing agent: The substance which gives hydrogen or removes oxygen for reduction is called the reducing agent. The substance which gains, hydrogen during reaction is said to be reduced.
Those reactions in which oxidation and reduction (both) occur simultaneously are called redox reactions. In the name Redox, the term 'red' stands for reduction and 'ox' stands for oxidation.
Example: 
Ans: SO2 is reduced to sulfur, so it is oxidising agent.
H2S is oxidized to sulphur, so it is a reducing agent.
It should be noted that substance which undergoes oxidation acts as reducing agent whereas the substance undergoes reduction act as oxidising agent.
There is another concept of oxidation and reduction in terms of metals and nonmetals.
(i) The addition of nonmetallic element (or removal of metallic element) is called oxidation.
(ii) The addition of metallic element (or removal of nonmetallic element) is called reduction.
Ques : A shiny brown colored element 'X' on heating in the air becomes black in colour. Name the element 'X' and the black coloured compound formed.
Ans: An element of heating in air changes in its oxide. The brownish element which forms black oxide is copper.
So, Name of the element Copper (Cu)
Name of black compound: Copper(II) oxide, (CuO)
Reaction
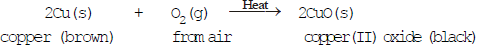
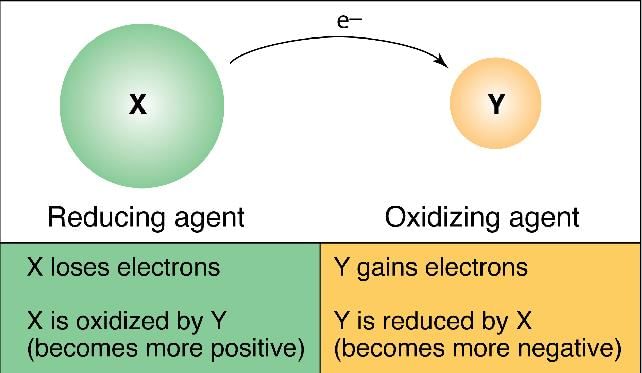
Electronic concept for oxidation and reduction
Oxidation: The loss of an electron by atoms or ions is called oxidation.
Atom → Cation + electrons
A → An+ + ne-
Atom 'A' loses n electrons to become a positively charged ion An+. It is called a cation.
Reduction: The gain of an electron by an atom or ion is called reduction.
B + ne- → Bn-
The atom B gains n' electrons to become negatively charged ion Bn-, it is called anion.
Oxidation and reduction reactions occur simultaneously and are called as redox reactions. Only oxidation or only reduction is called half-reaction. i.e.
A → An+ + ne- - Oxidation
B + ne- → Bn- - Reduction
A + B → A+B- → AB Redox
e.g. Na + Cl → NaCl
In this process, sodium loses one electron and oxidised to Na+, chlorine gains this electron and is reduced to Cl-.
Na → Na+ + e- (loss of an electron is oxidation )
Cl + e- → Cl- (Gain of an electron is reduction)

Effects of oxidation reactions in everyday life: Oxidation has a damaging effect on metals as well as on food. The damaging effect of oxidation on metals is studied as corrosion and that on food is studied as rancidity. Thus there are two common effects of oxidation reactions areas
(i) Corrosion of metals
(ii) Rancidity of food
(i) Corrosion of metals: Corrosion is the process of deterioration of metals as a result of its reaction with air, moisture, and acids. (Present in the environment) surrounding it.
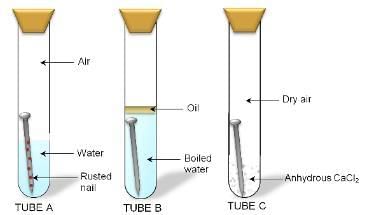 Fig: Different conditions of an iron nail rusting
Fig: Different conditions of an iron nail rusting
The corrosion causes damage to buildings, bridges, ships and many other articles specially made of iron.
Rust: Iron corrode readily when exposed to moisture and gets covered with a brown flaky substance called rust.  Fig: Rusted ChainsIt is called rusting of iron, Rust is a hydrated iron (III) oxide Fe2O3 · 2H2O.
Fig: Rusted ChainsIt is called rusting of iron, Rust is a hydrated iron (III) oxide Fe2O3 · 2H2O.
Rusting of iron takes place under the following conditions -
(a) Presence of air (or oxygen)
(b) Presence of water (or moisture)
It has been observed that
- Presence of impurities in the metal speed up the rusting process. Pure iron does not rust.
- Presence of electrolytes in water also speeds up the process of rusting
- The position of the metal in the electrochemical series determines the extent of corrosion. More the reactivity of the metal, there will be more possibility of the metal getting corroded.
Other examples of corrosion are -
- Copper reacts with moist carbon dioxide in the air and slowly loses its shiny brown surface and acquires a green coating of basic copper carbonate
- Silver articles become black after sometimes when exposed to air because it reacts with sulfur to form a coating of silver sulfide.
- Lead or stainless steel lose their luster due to corrosion.
Unreactive metals such as gold, platinum, palladium, titanium, etc. do not corrode.
(ii)Rancidity: Fresh foods containing fats and oils smell and taste pleasant but when it remains exposed in air for a long time it's smell and taste changes to unpleasant. It is said that food has become rancid. Fig: Rancidity in food productsOR
Fig: Rancidity in food productsOR
It is due to the oxidation of fats and oils, butter, ghee, boiled rice, etc, after prolonged exposure to air i.e. The condition produced by the aerial oxidation of fats and oils in foods marked by unpleasant smell and taste is called rancidity.
Prevention of rancidity:
(i) Rancidity can be prevented by adding antioxidants to foods containing fats and oils. Antioxidants are reducing agents so when they are added to food it does not get oxidised easily and hence do not turn rancid.
The two common antioxidants are -
(a) BHA (Butylated Hydroxy Anisole)
(b) BHT (Butylated Hydroxy Toluene)
Vitamin-E and vitamin-C (ascorbic acid) are the two antioxidants occurring in natural fats.
(ii) Rancidity can be prevented by packaging fat and oil-containing foods in nitrogen gas.
(iii) It can be retarded by keeping food in the refrigerator.
(iv) It can also be retarded by storing food in airtight containers.
(v) It can be retarded by storing foods away from light.
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
















