Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Enzymes
Enzymes | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
What Are Enzymes?
- Enzymes are protein molecules that act as biological catalysts, accelerating chemical reactions without undergoing any permanent changes themselves.
- These biological catalysts are vital for living organisms as they regulate the speeds of metabolic reactions necessary for sustaining life.
- For instance, digestive enzymes play a crucial role in breaking down food. Without them, the process of digesting a single meal would take approximately 2-3 weeks, whereas with enzymes, it only takes around 4 hours.
Catalysts in Biology
- Definition: Catalysts are substances that accelerate chemical reactions without being altered in the process.
- Role of Proteins: Proteins serve as biological catalysts, being vital for maintaining the speed of metabolic reactions in living organisms.
- Importance: Catalysts are crucial for sustaining life processes. For instance, without digestive enzymes, digestion would take weeks, but with enzymes, it only takes hours.
How Do Enzymes Work?
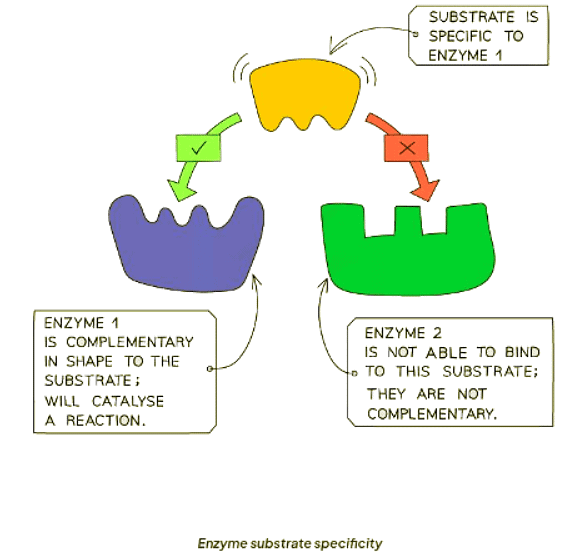
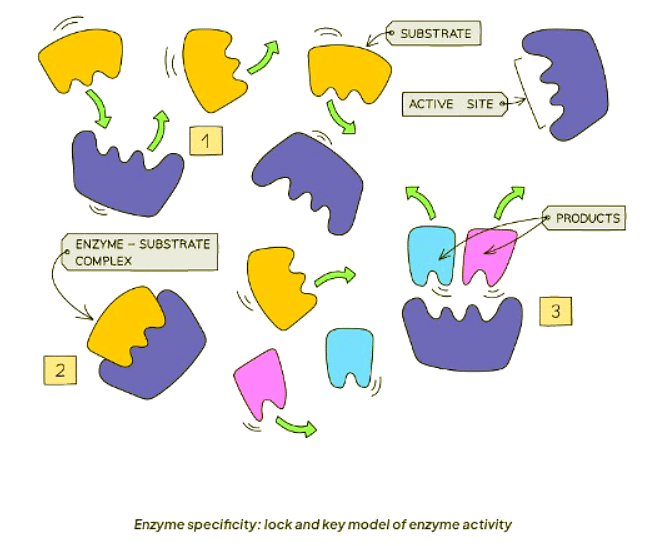
- Enzymes exhibit specificity towards particular substrates because their shapes complement those of the substrates.
- As a result, enzymes can bind only to specific substrates, facilitating the formation of products from the substrates, which are then released.
Question for EnzymesTry yourself: How do enzymes accelerate chemical reactions?View Solution
The document Enzymes | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Enzymes - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are enzymes? |  |
Ans. Enzymes are biological molecules that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. They are usually proteins that help break down or build up molecules in the body.
| 2. How do enzymes work? |  |
Ans. Enzymes work by binding to specific molecules called substrates and facilitating chemical reactions that convert them into different molecules. This process helps the reactions occur faster and more efficiently.
| 3. What factors can affect enzyme activity? |  |
Ans. Factors that can affect enzyme activity include temperature, pH levels, substrate concentration, and the presence of inhibitors or activators. Changes in these factors can alter the enzyme's ability to function properly.
| 4. How are enzymes important in digestion? |  |
Ans. Enzymes play a crucial role in digestion by breaking down food molecules into smaller nutrients that can be absorbed by the body. For example, amylase helps break down carbohydrates, while protease breaks down proteins.
| 5. Can enzymes be used in industrial processes? |  |
Ans. Yes, enzymes are widely used in industrial processes such as food production, textile manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals. They are used to catalyze reactions and improve efficiency in various manufacturing processes.
Related Searches















