Epithelial Tissue | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
What is Epithelial Tissue?
Epithelial tissues are a type of animal tissue composed of eukaryotic cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. These tissues lack a cell wall, giving them flexibility and allowing cells to take on different shapes for specialized functions. Epithelial tissues are found covering the body's surface, lining internal organs, and body cavities.
 Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Functions of Epithelial Tissue:
- Protection: Safeguards underlying tissues from mechanical injury and blocks germ entry.
- Absorption: Takes in substances.
- Secretion and Excretion: Releases and eliminates substances.
- Regulation: Controls the exchange of chemicals between the tissues and body cavity.
Based on functions & location tissues are classified into four types:
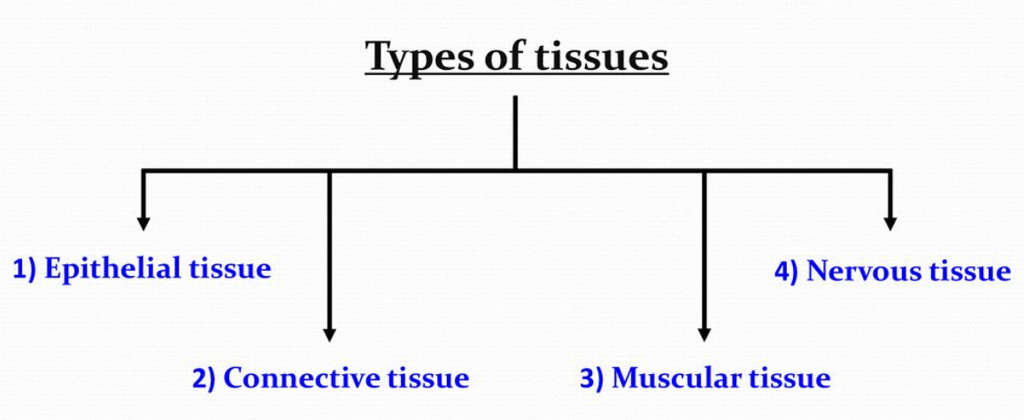
Origin of Epithelial Tissue
It is the only tissue that originated from all three primordial germinal layers.
- Ectodermal – Epidermis (stratified squamous epithelium)
- Mesodermal – Mesothelium (simple squamous Epithelium)
- Endodermal – Endothelium (simple squamous Epithelium)
Types of Epithelial Tissue
 Types of Epithelial Tissue
Types of Epithelial Tissue
1. Simple Epithelium
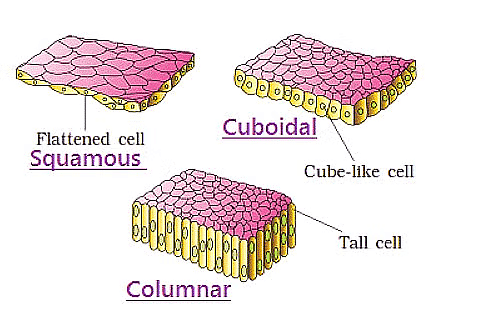
(a) Simple Squamous Epithelium
 Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Structure: Thin, flat cells packed closely together.
- Locations: Lines cavities of the mouth, esophagus, alveoli, and blood vessels.
- Function: Provides protection against mechanical injury and blocks germ entry
(b) Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
 Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- Cells are cube-like in shape
- A basement membrane is present.
- A rounded nucleus is present in the centre of the cell.
- Cells are the same in length & width so they appear square-shaped in vertical sections.
- This epithelium helps in absorption, secretion & exertion.
- It also forms gametes in gonads.
- Mostly cuboidal cells are found in glands.
Example: Vesicles of the Thyroid gland, Pancreatic duct, Secretory unit of sweat glands (secretory unit of salivary glands is composed is the stratified cuboidal epithelium), Iris, Choroid, Ciliary body of the eye, the thick part of ascending limb of the loop of Henle, DCT - In gonads, this epithelium is also called Germinal epithelium (testis & ovaries) where cuboidal cells divide to form egg & sperm.
- It is found in the peripheral region of the ovary & in the wall of seminiferous tubules in the Testis.
Modifications: Brush bordered cuboidal epithelium where microvilli are present on the free surface of cuboidal cells.
Example: PCT of the nephron.
Ciliated cuboidal epithelium when cilia present on the free end of cuboidal cells then Collecting duct / Tubule.
(c) Simple Columnar Epithelium
 Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Columnar epithelial cells are characterized by being taller than they are wide, resembling a stack of columns in an epithelial layer. They are typically found in a single-layer arrangement. In the digestive tract, the nuclei of these cells are aligned at the base. These cells are responsible for absorbing materials from the lumen of the digestive tract and preparing them for entry into the body via the circulatory and lymphatic systems.
(d) Simple Ciliated Epithelium
 Simple Ciliated Epithelium
Simple Ciliated Epithelium
If columnar or cuboidal cells have cilia on their free surface, they are called ciliated epithelium. Cilia are tiny hair-like structures that help in moving particles or mucus in a specific direction over the epithelial surface.
- Function: The main function of ciliated epithelium is to move particles or mucus in a specific direction. This is important for keeping the surfaces of hollow organs clean and clear.
- Location: Ciliated epithelium is mainly found on the inner surfaces of hollow organs such as the bronchioles (small air passages in the lungs) and fallopian tubes (the tubes that carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus).
(e) Pseudo Stratified Epithelium
 Pseudostratified Epithelium
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Pseudostratified epithelium is a special type of tissue that looks like it has multiple layers but actually consists of just one layer of cells. This is because the cells are of different heights, making the nuclei appear at different levels.
- In this epithelium, all cells are attached to the basement membrane, but not all of them reach the top surface (apical surface). This gives it the false impression of being layered.
- Polarity is an important feature of this epithelium. The nuclei of the cells are usually located in the basal two-thirds of the tissue, which is a key difference from true stratified epithelium.
- Most cells in pseudostratified epithelium have cilia, tiny hair-like structures that help move substances along the surface. This feature is not common in true stratified epithelium.
- Pseudostratified epithelium is primarily found in the airways of the respiratory system, where it is often referred to as respiratory epithelium.
(f) Glandular Epithelium
 Glandular Epithelium
Glandular Epithelium

Glandular Epithelium is a specialized type of epithelial tissue where some columnar or cuboidal cells are adapted for secretion. There are two main types of glandular epithelium:
- Unicellular: This type consists of isolated glandular cells, such as goblet cells found in the alimentary canal.
- Multicellular: This type is made up of clusters of cells, like those found in salivary glands.
Glands are categorized into two types based on how they release their secretions:
- Exocrine Glands: These glands secrete substances like mucus, saliva, earwax, oil, milk, and digestive enzymes. Their secretions are released through ducts or tubes.
- Endocrine Glands: Unlike exocrine glands, endocrine glands do not have ducts. They release hormones directly into the fluid surrounding the gland.
2. Compound or Stratified Epithelium
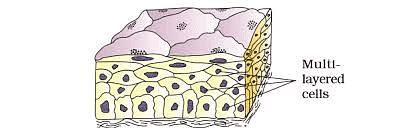 Compound or Stratified Epithelium
Compound or Stratified EpitheliumIn compound epithelial tissue, cells are organized in multiple layers or strata, which is why it is also referred to as stratified epithelium.
Functions of Compound Epithelium
- This tissue has a negligible role in secretion and absorption.
- The primary function of compound epithelium is to protect the organs from chemical and mechanical stress.
- It is present in the lining of the ducts arising from the pancreas, on the dry surface of the skin, moist surface of the cavity of the mouth and pharynx.
(i) Types of Stratified Compound Epithelium
The compound epithelium is classified into the following categories on the basis of types of cells and number of layers:

(a) Stratified Squamous Epithelium
 Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Composed of multiple layers of cells
- Apical surface contains squamous cells
- Deeper layers consist of columnar or cuboidal cells
- Primary function is protection
- Present in areas susceptible to abrasions like mouth, esophagus, and skin
(b) Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
 Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
- Composed of multiple layers of cells
- Outermost layer is of cuboidal cells
- Found in conjunctiva of eyes, lining of ducts of sweat glands, salivary gland, mammary glands, and urethra
- Protects the organ from mechanical and chemical stress
(c) Stratified Columnar Epithelium
 Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
- Composed of multiple layers of cells
- Outermost layer is of columnar cells, middle layer is of cuboidal cells
- Forms lining of vasa-deferentia, respiratory tract, and mammary gland
- Primarily involved in secretion of fluids and protection from mechanical and chemical stress
(d) Stratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
 Stratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Stratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
- Composed of multiple layers
- Superficial layer is ciliated and columnar
- Lines respiratory passages, vas deferens, and epididymis
(ii) Transitional Epithelium
 Transitional epithelium
Transitional epithelium
Transitional epithelium, also known as urothelium, is a type of epithelial tissue composed of multiple layers of epithelial cells that can contract and expand. These cells can change shape depending on the degree of stretch in the tissue, which is why it's called "transitional."
Location: Transitional epithelium is primarily found lining the urinary system's organs, where it is exposed to variable degrees of stretch. This includes: The urinary bladder, Ureters, Part of the urethra, Renal pelvis of the kidneys.

Types of Epithelial Tissues
|
181 videos|361 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Epithelial Tissue - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is epithelial tissue and what are its main functions? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of simple epithelium? |  |
| 3. How does simple squamous epithelium differ from simple cuboidal epithelium? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of ciliated epithelium in the respiratory system? |  |
| 5. What are the characteristics of stratified epithelium, and where is it commonly found? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















