Equipotential Surfaces and Its Properties | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
What is Equipotential Surface?
- The surface which is the locus of all points which are at the same potential is known as the equipotential surface. No work is required to move a charge from one point to another on the equipotential surface.
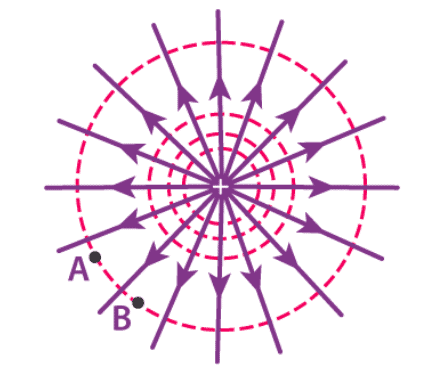 Equipotential Surface
Equipotential Surface - In other words, any surface with the same electric potential at every point is termed as an equipotential surface.
Equipotential Points
- If the points in an electric field are all at the same electric potential, then they are known as the equipotential points. If these points are connected by a line or a curve, it is known as an equipotential line.
- If such points lie on a surface, it is called an equipotential surface. Further, if these points are distributed throughout a space or a volume, it is known as an equipotential volume.
Work Done in Equipotential Surface
- The work done in moving a charge between two points in an equipotential surface is zero. If a point charge is moved from point VA to VB, in an equipotential surface, then the work done in moving the charge is given by:
W = q0(VA –VB)
As VA – VB is equal to zero, the total work done is W = 0.
Properties of Equipotential Surface
- The electric field is always perpendicular to an equipotential surface.
- Two equipotential surfaces can never intersect.
- For a point charge, the equipotential surfaces are concentric spherical shells.
- For a uniform electric field, the equipotential surfaces are planes normal to the x-axis
- The direction of the equipotential surface is from high potential to low potential.
- Inside a hollow charged spherical conductor the potential is constant. This can be treated as equipotential volume. No work is required to move a charge from the centre to the surface.
- For an isolated point charge, the equipotential surface is a sphere. i.e. concentric spheres around the point charge are different equipotential surfaces.
- In a uniform electric field, any plane normal to the field direction is an equipotential surface.
- The spacing between equipotential surfaces enables us to identify regions of a strong and weak field i.e. E= −dV/dr ⇒ E ∝ 1/dr
Equipotential Lines in a Constant Field
- In a conducting plate-like in a capacitor, the electric field lines are perpendicular to the plates and the equipotential lines are parallel to the plates.
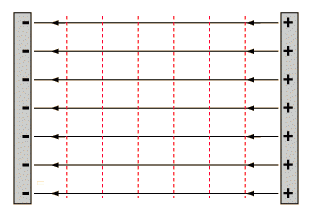
- The illustration below shows the electric field of a positive point charge.The electric field is fixed away from the charge and potential is positive at any set distance from the charge. If the charge moves in the direction of the electric field it will move towards the lower values of potential.
- If the charge moves towards the direction opposite to that of electric field we move towards the higher values of potential.
- The illustration below shows the electric field of a point negative charge.
- Limited distance is negative at any point from the charge. If the charge moves toward the direction of the electric field and in the direction of decreasing U thus, becoming move negative. If a charge moves in the direction opposite to electric field, the increasing value of V thus, become less negative.
- Hence, the moving with the direction of electric field means moving in the direction of decreasing V and moving against the direction of electric field means moving in the direction of increasing V. Therefore, potential difference canbe expressed in terms of electric field as:
- Electric field (E) as a function of potential can be expressed as
where Er is the component of electric field along the direction of dv/dr is known as the potential gradient and the negative sign infers that electric field acts in a direction of decrease of potential.
- The expression above indicates that E is not certainly zero if V is zero.
Properties of Equipotential Surfaces
To gain a comprehensive understanding of equipotential surfaces, let's explore their key properties:
- Perpendicular Electric Field: The electric field is always perpendicular to an equipotential surface.
- Non-intersecting Surfaces: Two equipotential surfaces can never intersect.
- Point Charge: For a point charge, the equipotential surfaces manifest as concentric spherical shells.
- Uniform Electric Field: In a uniform electric field, the equipotential surfaces take the form of planes perpendicular to the x-axis.
- Directional Flow: The direction of the equipotential surface extends from high potential to low potential.
- Hollow-Charged Spherical Conductor: Inside a hollow-charged spherical conductor, the potential remains constant, turning it into an equipotential volume.
- Effortless Charge Movement: No work is required to move a charge from the center to the surface of a hollow-charged spherical conductor.
- Isolated Point Charge: For an isolated point charge, the equipotential surface takes the shape of a sphere, with concentric spheres representing different equipotential surfaces.
- Uniform Electric Field (Continued): In a uniform electric field, any plane perpendicular to the field's direction serves as an equipotential surface.
- Field Strength Identification: The spacing between equipotential surfaces aids in identifying regions of strong and weak electric fields. This can be determined through the formula E = -dV/dr, suggesting that E is inversely proportional to the spacing 1/dr.
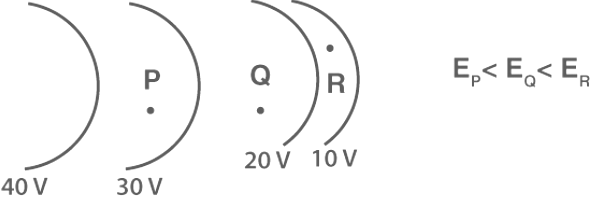
Problems on Equipotential Surface
Q.1: A charged particle (q =1.4 mC) moves a distance of 0.4 m along an equipotential surface of 10 V. Calculate the work done by the field during this motion.
Solution: The work done by the field is given by the expression
W = -qΔV
Since ΔV = 0, for equipotential surfaces, the work done is zero, W = 0.
Q.2: A positive particle of charge 1.0 C accelerates in a uniform electric field of 100 V/m. The particle started from rest on an equipotential plane of 50 V. After t = 0.0002 seconds, the particle is on an equipotential plane of V = 10 volts. Determine the distance travelled by the particle.
Solution: The work done in moving a charge in an equipotential surface is given by
W = -qΔV
Substituting the values, we get
W = (-1.0, C) (10V – 50V) = 40 J
We know that the work done in moving a charge in an electric field:
W = qEd
40 = (1.0) (100)d
d = 0.4m
Q.3: An electron of mass (m) and charge (e) is released from rest in a uniform electric field of 106 newton/coulomb. Compute its acceleration. Also, find the time taken by the electron to attain a speed of 0.1 c, where c is the velocity of light. (m = 9.1 × 10–31 kg, e = 1.6 × 10–19 coulomb and c = 3 ×108 metre/sec).
Solution: The force experienced by the electron is
F = Ee = 106 (1.6 × 10–19)
= 1.6 × 10–13 newton
The acceleration of the electron is given by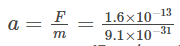
= 1.8 × 1017 m/sec2
The initial velocity = zero.
Let t be the time taken by the electron to attain a final speed of 0.1 c.
Now v = u + at or v = at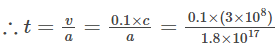
= 1.7 × 1010 sec.
Relation Between Field and Potential
Consider two surfaces, A and B, that are very close to each other, called equipotential surfaces. Equipotential surfaces have the same electric potential across them. In this case, surface A has a potential V and surface B has a potential of V+δV, where δV is a small change in potential in the direction of the electric field E. The perpendicular distance between surfaces A and B is δl.
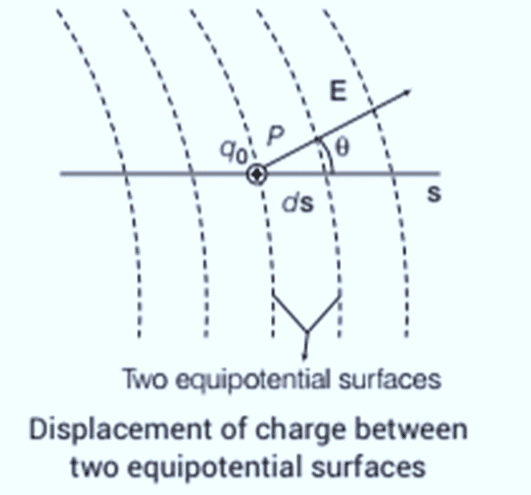
Imagine moving a small positive charge from surface A to B along this perpendicular line. To move this charge against the electric field, we need to do work. This work, represented as ∣E∣δl, equals the difference in potential between A and B, which is VA−VB. Therefore, we can write this relationship as: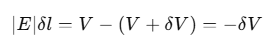
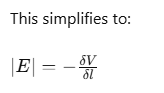
Since δV is negative (because it decreases in the direction of the field), we can rewrite it as:
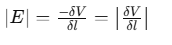
From this, we can conclude two important points:
- The Electric Field Direction: The electric field points in the direction where the electric potential decreases the most.
- Electric Field Magnitude: The strength of the electric field at any point is determined by how quickly the potential changes over a small distance perpendicular to the equipotential surfaces.
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Equipotential Surfaces and Its Properties - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is an equipotential surface in physics? |  |
| 2. What are equipotential points? |  |
| 3. How is work done in an equipotential surface? |  |
| 4. What are the properties of equipotential surfaces? |  |
| 5. How can problems on equipotential surfaces be solved? |  |
















