Euler’s Equation: The Equation of Motion of an Ideal Fluid | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Euler’s Equation: The Equation of Motion of an Ideal Fluid
This section is not a mandatory requirement. One can skip this section (if he/she does not like to spend time on Euler's equation) and go directly to Steady Flow Energy Equation.Using the Newton's second law of motion the relationship between the velocity and pressure field for a flow of an inviscid fluid can be derived. The resulting equation, in its differential form, is known as Euler’s Equation. The equation is first derived by the scientist Euler.
Derivation:
Let us consider an elementary parallelopiped of fluid element as a control mass system in a frame of rectangular cartesian coordinate axes as shown in Fig. 12.3. The external forces acting on a fluid element are the body forces and the surface forces.
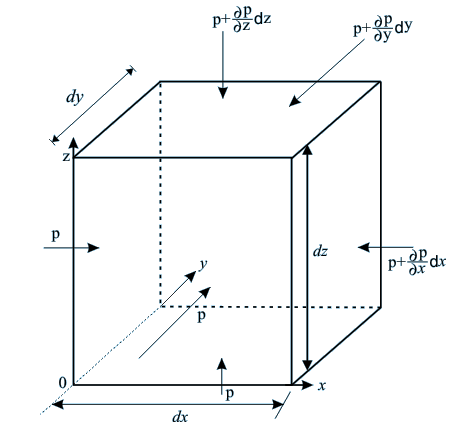
Fig 12.2 A Fluid Element appropriate to a Cartesian Coordinate System used for the derivation of Euler's Equation
Let Xx, Xy, Xz be the components of body forces acting per unit mass of the fluid element along the coordinate axes x, y and z respectively. The body forces arise due to external force fields like gravity, electromagnetic field, etc., and therefore, the detailed description of Xx, Xy and Xz are provided by the laws of physics describing the force fields. The surface forces for an inviscid fluid will be the pressure forces acting on different surfaces as shown in Fig. 12.3. Therefore, the net forces acting on the fluid element along x, y and z directions can be written as
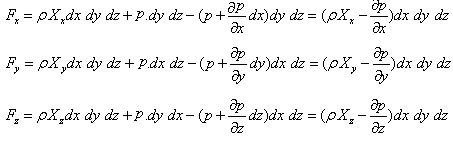
Since each component of the force can be expressed as the rate of change of momentum in the respective directions, we have
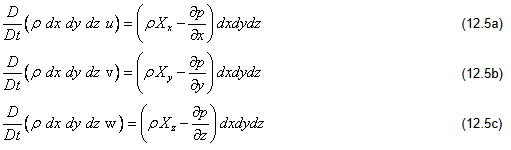
the mass of a control mass system does not change with time, 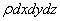 is constant with time and can be taken common. Therefore we can write Eqs (12.5a to 12.5c) as
is constant with time and can be taken common. Therefore we can write Eqs (12.5a to 12.5c) as

Expanding the material accelerations in Eqs (12.6a) to (12.6c) in terms of their respective temporal and convective components, we get
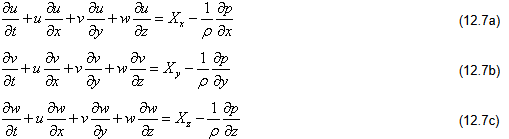
The Eqs (12.7a, 12.7b, 12.7c) are valid for both incompressible and compressible flow. By putting u = v = w = 0, as a special case, one can obtain the equation of hydrostatics .
Equations (12.7a), (12.7b), (12.7c) can be put into a single vector form as

where 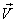 the velocity vector and the body force vector per unit volume
the velocity vector and the body force vector per unit volume 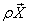 are defined as
are defined as
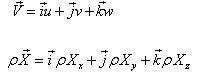
Equation (12.7d) or (12.7e) is the well known Euler’s equation in vector form, while Eqs (12.7a) to (12.7c) describe the Euler’s equations in a rectangular Cartesian coordinate system.
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on Euler’s Equation: The Equation of Motion of an Ideal Fluid - Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is Euler's Equation and how is it related to the motion of an ideal fluid? |  |
| 2. What are the key components of Euler's Equation? |  |
| 3. How is Euler's Equation different from Navier-Stokes Equation? |  |
| 4. How can Euler's Equation be used in practical applications? |  |
| 5. What are the assumptions made in deriving Euler's Equation for ideal fluids? |  |
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















