Events in Sexual Reproduction & Embryogenesis | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Events in Sexual Reproduction: Pre-fertilisation, Fertilisation, Post-fertilisation
Pre-fertilisation- all the events prior to fusion of gametes are included in it. It includes gametogenesis and gamete transfer.
a. Gametogenesis is the process of formation of male and female gametes. Gametes are haploid cells which may be similar or dissimilar in structure. In algae, both gametes are similar in structure called homogametes (isogametes).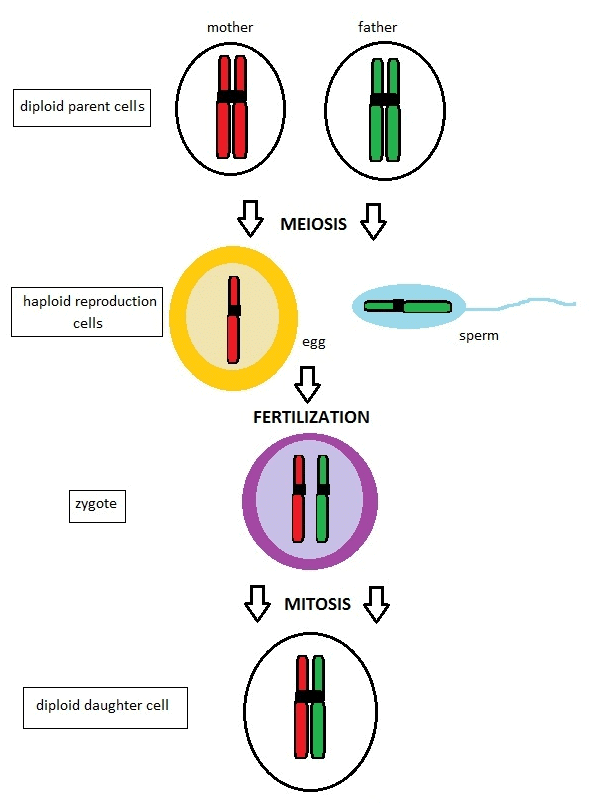 Fig: GametogenesisIn higher organism that reproduces sexually, two morphologically distinct gametes are formed called heterogametes, male gametes are called antherozoid or sperm and female gametes are called ovum or egg.
Fig: GametogenesisIn higher organism that reproduces sexually, two morphologically distinct gametes are formed called heterogametes, male gametes are called antherozoid or sperm and female gametes are called ovum or egg.
Isogametes, heterogametes
In fungi and plants, homothallic and monoecious terms are used to denote the bisexual condition and heterothallic and dioecious are used for unisexual condition. In flowering plants, the unisexual male flower is staminate, i.e., bearing stamens, while the female is pistillate or bearing pistils.
(i) In animals, species which possess both male and female reproductive organs in same individual are called bisexual or hermaphrodites (earthworm, sponges, tapeworm etc.) and both having either male or female reproductive organs are called unisexual (cockroach, human).
(ii) Gametes are always haploid( having half set of chromosome ), although organisms may be haploid and diploid. Diploid organisms form gametes by meiotic division. The organisms belonging to algae, fungi, and bryophytes have haploid plant body and pteridophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms and most of animals are diploid ( having double set of chromosome )
(iii) In diploid organisms, gamete mother cell (meiocyte) undergoes meiosis in which one set of chromosome is present in gametes.
b. Gamete Transfer – in majority of organisms, male gametes are motile and females gametes are non-motile, except in fungi and algae in which both gametes are motile.
(i) In simple plants like algae, fungi, bryophytes and pteridophytes water is the medium through which male and female gametes moves. The number of male gametes are much more than number of female gametes as most of male gametes fail to reach the female gametes.
(ii) In higher plants pollen grains are carrier of male gametes and ovule has eggs. Pollen grains must be transferred from anther to stigma to facilitate fertilisation. The transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is called pollination. Pollination may be self (anther to stigma of same flower) or cross (anther to stigma of different flower).

(iii) Pollen grains germinate on stigma to produce pollen tube that delivers the male gametes near the ovule.
c. Fertilisation – The fusion of male and female gamete is called fertilization or syngamy. It results in the formation of diploid zygote.
The process of development of new organisms without fertilisation of female gametes is called parthenogenesis. For example honey bee, rotifers, and lizards
| EXTERNAL FERTILIZATION | INTERNAL FERTILIZATION |
| Syngamy occurs outside the body of the organism Large numbers of gametes are released in the surrounding medium. | Syngamy occurs inside the body of the organism Numbers of ova produced are less, but large numbers of male gametes are released and they travel towards the ovum. |
| Ex. Bony fishes and Amphibians. | Ex. Birds and Mammals. |
Post Fertilisation Events- events in the sexual reproduction after formation of zygote.
(i) Zygote is the vital link that ensures continuity of species between organisms of one generation and the next. Every sexually reproducing organism, including human beings begin life as a single cell–the zygote.
(ii) In the organisms, having external fertilisation, zygote is formed in external medium (water) and those having internal fertilisation zygote is formed inside the body of female.
(iii) In algae and fungi, zygote develops a thick wall resistant to desiccation and damage. This germinates after a period of rest.
(iv) In the organisms having haplontic life cycle, zygote divides to form haploid spores that germinate to form haploid individual.
Embryogenesis – the process of development of embryo from the zygote. During this, zygote undergoes mitotic division and cell differentiation. Cell division increase the number and cell differentiation help in formation of new group of cells and organs.
| Oviparous | Viviparous |
| Development of zygote takes place outside the body of organisms and lay fertilized of unfertilized eggs. | Development of zygote takes place inside the body of organisms and produces young ones |
| Ex - Reptiles and birds | Ex- Human, dog, horse etc. |
- In flowering plants, zygote is formed inside the ovule. After fertilisation, sepals, petals and stamens of flower fall off. The zygote develops into embryo and ovules into seeds. The ovary develops into fruits which develop a thick wall called pericarp, protective in function.
- After dispersal, seeds germinate under favorable condition to produce new plants.
 Fig: A few kinds of fruit showing seeds (S) and protective pericarp (P)
Fig: A few kinds of fruit showing seeds (S) and protective pericarp (P)
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Events in Sexual Reproduction & Embryogenesis - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What are the main events in sexual reproduction? |  |
| 2. How does embryogenesis occur in sexual reproduction? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of meiosis in sexual reproduction? |  |
| 4. How does fertilization occur in sexual reproduction? |  |
| 5. What is the role of genetic variation in sexual reproduction and embryogenesis? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















