Export-Import Procedures | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Export |

|
| Basic Export Procedures |

|
| Import |

|
| Basic Import Procedures |

|
Introduction
The procedures for exporting and importing play a crucial role as a valuable guide in international trade operations. They encompass examples of nearly every pertinent document utilized in foreign trade (Johnson, 2010).
Export
Export Defined:
- Exporting means transferring ownership of goods from a resident to a non-resident, not necessarily involving physical border crossing.
- National accounts may recognize ownership changes, even without a legal shift, in cases like financial leasing, deliveries between related company branches, or goods sent across borders for processing.
Inclusive Measurement:
- Measurement of exports includes smuggled goods and situations where ownership changes without a physical border crossing.
- Documents such as a 'shipping bill' (for sea or air) or 'bill of export' (for road) must be submitted by exporters, along with relevant paperwork like packing lists, invoices, export contracts, and letters of credit.
Export Process for Companies:
- For businesses, exporting often begins in the sales or marketing department.
- Companies may get inquiries or orders from potential customers through their website, even without specifying the destination.
Order Fulfillment Considerations:
- Sales personnel need to adapt to differences when fulfilling export orders compared to domestic sales.
- The export process involves assessing steps unique to international sales, ensuring a smooth transaction.
Export: Order processing quotation

Export order processing: Order entry
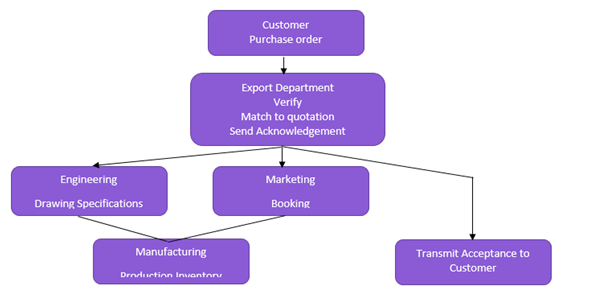
Export order processing: Shipment

Basic Export Procedures
Market Research and Distribution Objectives:
- Identify target markets, export methods, and distribution channels.
- Set foreign market objectives regarding pricing and terms.
Trade Regulations:
- Understand export regulations and requirements.
- Familiarize with overseas import regulations and requirements.
- Address patent, trademark, and copyright considerations.
Making Contacts:
- Conduct investigations with potential overseas buyers.
- Verify buyer backgrounds through organizations like ECIC or banks.
Quotation and Terms:
- Provide offers and quotations to potential buyers.
- Include costs, pro forma invoices, and sales terms.
Sales Contract:
- Confirm sales contract details and transaction terms, including payment terms.
Contract Execution:
- Produce or source goods for export.
- Ensure proper packaging and labeling.
- Arrange shipment logistics.
- Prepare export documentation and secure insurance if necessary.
Customs Clearance:
- Arrange export declaration and obtain export licenses if required.
Getting Paid:
- Present required documents to relevant parties for payment based on the agreed payment terms in the sales contract.
These steps outline the comprehensive process exporters must navigate to successfully conduct international trade.
Export order processing: Collection
Import
What is Import?
- Import means bringing products into your own country from outside its borders.
- It's like buying goods from another country.
Import Procedure:
- Import procedures differ from one country to another, depending on their policies and customs rules.
- Governments often control import trade to manage foreign exchange usage and protect local industries.
Manufacturer's Import Department:
- A manufacturer's import department usually starts from the purchasing department.
- Their job is to buy raw materials or components needed for production.
- Import departments for trading companies might begin when they become distributors for foreign manufacturers.
Import-Export in India:
- In India, import and export are regulated by the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992, and the Export Import (EXIM) Policy.
- The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) oversees EXIM Policy in India.
- Importers need to register with DGFT to get an Importer Exporter Code Number (IEC) against their PAN.
- After getting IEC, importers declare the source of their imports.
- Most goods can be imported freely into India under the Indian Trade Classification – Harmonized System (ITC-HS) without needing a special import license.
Basic Import Procedures
Setting Market Objectives:
- Determine pricing and terms objectives for the target market.
Sourcing Products:
- Identify potential suppliers and distribution channels for sourcing products.
Trade Regulations:
- Understand import regulations and requirements, including the need for import licenses.
- Address patent, trademark, and copyright considerations.
Making Contacts:
- Reach out to suitable suppliers by sending inquiries.
Settling Quotation and Terms:
- Evaluate supplier quotations and offers.
- Consider costs and terms of sale.
Financing the Purchase:
- Arrange working capital for the purchase.
- Explore different types of bank financing, such as exporter credit.
Sales Contract:
- Confirm sales contract details, including payment terms.
Preparing Payment and Insurance:
- Make necessary payments and arrange insurance as specified in the sales contract.
- Submit necessary applications to banks for payment terms like D/C or arrange insurance cover notes when needed.
Acquiring Goods:
- Receive shipping advice and arrival notices.
- Obtain export documents from the exporter.
- Collect goods from the specified shipping company or forwarder.
Customs Clearance:
- Arrange customs clearance and import declaration for the goods.
Import Procedure

Customs Clearance Formalities:
- Importers in India need to go through detailed customs clearance procedures when bringing goods into the country.
- The Indian Directorate of General Valuation's website provides a complete overview of Export-Import (EXIM) procedures.
Specialized Knowledge for Export-Import:
- Efficient exporting and importing require specialized knowledge.
- In some companies, export and import tasks are combined, especially in smaller ones with limited transactions. Larger companies often separate these functions into distinct export and import departments.
Benefits of Manuals:
- Having manuals for export and import procedures is beneficial for companies.
- These manuals serve as effective tools for smooth operations and training resources for new employees.
Record Keeping:
- Companies engaged in international trade transactions must maintain records.
- Record-keeping is crucial for tracking and ensuring compliance with various aspects of the trade process.
Software Solutions:
- Some companies provide software programs to manage the export process.
- These programs help with order processing, generating export documents, ensuring compliance with export regulations, and calculating transportation charges and duties.
Supply Chain Management Software:
- On the import side, companies often use supply chain management software.
- This software assists in efficiently managing the various stages of the import process, ensuring smooth and well-organized operations.
FAQs on Export-Import Procedures - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the basic procedures for exporting goods? |  |
| 2. What is an Export License or Permit? |  |
| 3. How are goods classified for export? |  |
| 4. What are some commonly required export documents? |  |
| 5. What are the key customs regulations and requirements for exporting goods? |  |

















