Class 10 Civics Chapter 4 Extra Question Answers - Political Parties
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What is the concept of political parties in rural areas?
Ans:
Rural Awareness: Limited education in rural areas may result in unfamiliarity with the constitution, but awareness of political parties is common.
Democratic Role: Political parties, composed of like-minded individuals, contest elections to secure governance in democracies.
Policy Influence: They play a vital role in formulating policies, and influencing laws whether in a ruling or opposition capacity.
Rural Recognition: In rural areas, knowledge about political parties often surpasses awareness of the constitution.
Public Opinion: Beyond elections, political parties significantly shape public opinions by emphasizing key issues.
Q2: What do you understand by 'Partisan' and 'Partisanship'?
Ans: (i) Partisan: A partisan is an individual deeply dedicated to a specific party, group, or faction.
(ii) Partisanship: It involves a strong inclination to take a side, displaying an inability to maintain a
balanced perspective on an issue.
 PartisanshipQ3: Is it true that political parties shape public opinion? Explain.
PartisanshipQ3: Is it true that political parties shape public opinion? Explain.
Ans: Certainly, it is accurate that political parties sometimes lead movements to address the challenges encountered by the public. The perspectives prevailing in society often align with the positions taken by these parties.
Q4: What is an ‘alliance’ or a ‘front’? Name three major alliances of India.
Ans: In a multi-party system, when multiple parties collaborate to participate in elections to secure power, it is referred to as an alliance or a front.
Three major alliances of India:-
(i) The National Democratic Alliance (NDA) formed by BJP.
(ii) The United Progressive Alliance (UPA) formed by Congress I.
(iii) Left Front formed by Communist Parties of India
Q5: What are National Parties? How is a party recognized as a ‘National Party’ by the Election Commission of India?
Ans: Certain parties operate on a national scale and are designated as national parties. These organizations uniformly implement policies, programs, and strategies determined at the national level, fostering consistency across all their units.
A political party attains recognition as a national party when it obtains a minimum of six percent of the total votes in either Lok Sabha or assembly elections in four states and secures at least four seats in the Lok Sabha.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Why is there a lack of internal democracy within the political parties in India? Explain with examples.
Ans:
There is a lack of democracy within the political parties due to the following reasons:
(i) There is a tendency in political parties towards the concentration of power in one or a few leaders at the top.
(ii) Parties do not hold organizational meetings and do not conduct internal elections regularly.
(iii) Parties do not have the means or the connections needed to influence the decisions.
(iv) Parties do not keep membership register.
All these features can be found in India’s parties like the Indian National Congress, BJP, BSP, SP, etc.
 Political PartiesQ2: Mention different types of party systems. Write one merit of each. Which party systems do we have in India?
Political PartiesQ2: Mention different types of party systems. Write one merit of each. Which party systems do we have in India?
Ans: Three types of party systems exist all over the world:
(i) One-party system: There is no choice or competition in this system. The party nominates the candidate and the voters have two choices – Either not to vote or write Yes or No to the candidate. This kind of system existed in communist countries or authoritarian regimes. Example – China, North Korea, and Cuba. Supporters of a one-party system claim that this system helps the government in mobilizing the talents of all citizens towards a common goal.
(ii) Two-party system: In this case, two parties are dominated in the system. The winner required a maximum number of votes. The smaller party usually merges with the bigger one or drops out from the competition. Example – Great Britain and Canada. Supporters of this system believe that this system helps the Government to go smoothly, it also prevents the danger of fragmentation.
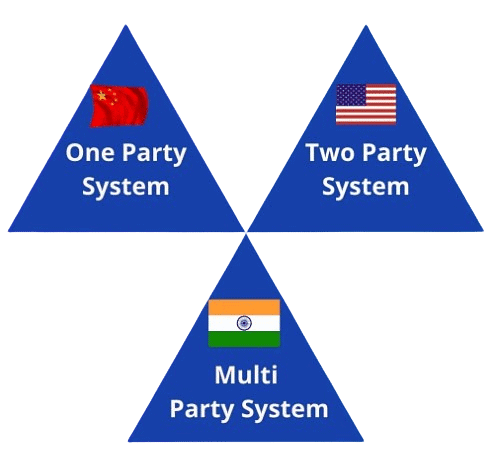 (iii) Multi-party system: In this system, three or more parties compete to gain control of the government separately or in coalition. When not any single party gains majority votes then several parties join and form a coalition government. Example-India. Supporters of this system point out that it allows more points of view to be presented in the government.
(iii) Multi-party system: In this system, three or more parties compete to gain control of the government separately or in coalition. When not any single party gains majority votes then several parties join and form a coalition government. Example-India. Supporters of this system point out that it allows more points of view to be presented in the government.
Q3: State any two advantages of the multi-party system. In what way is an alliance different from a coalition Government?
Ans:
- If several parties compete for power, more than two parties have a reasonable chance of coming to power either on their strength or in alliance with others.
- This system allows a variety of interests and opinions to enjoy political representation. In a coalition government, the government is formed by various parties coming together in a coalition. When several parties in a multi-party system join hands to contest elections and raise power, it is called an alliance or a front.
Q4: Suggest and explain any five measures to reform political parties.
Ans:
(i) The anti-defection law was introduced to counter the rising trend of elected representatives switching parties for ministerial positions or monetary rewards.
(ii) The affidavit requirement was mandated by the Supreme Court to address the issues related to the influence of money and muscle power.
(iii) The Election Commission implemented a third reform measure, making it mandatory for all political parties to conduct regular elections and file income tax returns.
In addition to these measures, several suggestions are often proposed for political party reforms:
(iv) Enforce a mandatory provision for political parties to allocate a minimum number of tickets, approximately one-third, to women candidates. Similarly, there should be a quota for women in the decision-making bodies of the party.
(v) Advocate for state funding of elections, where the government provides financial support to parties for their election expenses. This support could be in the form of resources like petrol, paper, and telephone services or in cash based on the party's performance in the previous election.
Q5: “Political parties are a necessary condition for a democracy”. Analyse the statement with examples.
Ans:
Essential for Democracy: Political parties are a fundamental requirement for the functioning of democracies. Without parties, candidates operate independently, leading to a lack of organized representation.
Promise and Policy Commitments: Political parties facilitate candidates in articulating promises and policy commitments. The absence of parties hampers the communication and implementation of significant policy changes.
Uncertain Government Utility: While a government may form without parties, its effectiveness and utility remain uncertain. Political parties provide a framework for governance, ensuring a systematic approach to addressing societal needs.
Accountability and Responsibility: Political parties enable elected representatives to be accountable at both local and national levels. Parties centralize responsibility for the overall direction and management of the nation.
Representation in Complex Societies: In large and complex societies, political parties serve as crucial agencies. They gather, present, and advocate diverse views on various issues, contributing to informed decision-making.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Civics Chapter 4 Extra Question Answers - Political Parties
| 1. What is the purpose of political parties? |  |
| 2. How do political parties help in the functioning of a democracy? |  |
| 3. How are political parties formed and organized? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges faced by political parties? |  |
| 5. What is the role of political parties in the electoral process? |  |






















