Financial Administration - 1 - UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Financial administration serves as the backbone of every organization, as it ensures the availability of essential resources, such as personnel and materials, required for the smooth functioning of any office, industry, or enterprise. Money is the lifeblood that enables these resources to be acquired and utilized effectively. The success and efficiency of an organization's operational and maintenance systems largely depend on the effectiveness of its financial system, as every administrative action may have financial implications. Finance plays a crucial role in public administration, as evidenced by Lloyd George's statement, "Government is finance."
- Financial administration has been a vital aspect of public administration throughout history, dating back to the formation of organized governments worldwide. In its early stages, financial administration performed a limited number of functions until the medieval period. During the pre-modern era, it was primarily concerned with establishing legislative control over executive actions. However, the socio-economic forces unleashed by the Industrial Revolution transformed the meaning and purpose of financial administration, imbuing it with a dynamic content. In today's world, financial administration is expected to cater to the dynamic needs of planned development and social change.
- In this unit, we will explore the meaning, importance, nature, and scope of financial administration. Additionally, we will gain an understanding of the various components that make up financial administration.
Financial Administration : Meaning
- The term Financial Administration consists of two words viz. ‘Finance’ and ‘Administration’. The word ‘administration’ refers to organisation and management of collective human efforts in the pursuit of a conscious objective. The word ‘Finance’ refers to monetary (money) resource. Financial Administration refers to that set of activities which are related to making available money to the various branches of an office, or an organisation to enable it to carrying out its objectives. Whether it is the Department of Agriculture, Railways, Road Transport Corporation, Primary Health Centre, Municipality or Gram Panchayat, or for that matter, a family, its day-to-day activities would depend upon the availability of funds with which financial Administration consists.
- Now let us get to know some more accurate definitions of Financial Administration. According to L.D. White, “Fiscal Management includes those operations designed to make funds available to officials and to ensure their lawful and efficient use?'
- According to Jaze Gaston “Financial Administration is that part of government organisation which deals with the collection, preservation and distribution of public funds, with the coordination of public revenue and expenditure, with the management of credit operations on behalf of the State and with the general control of the financial affairs of public household.”
- Though this definition covers some important aspects of fiscal management, it fails to project a comprehensive scope of financial administration. Perhaps, after realising this limitation, G.S. Lall states that financial administration is concerned with all the aspects of financial management of the State. Since public administration is more and more concerned with public affairs and public interest, the frontiers of financial administration are expanding and therefore there is a need for a comprehensive definition of financial administration. As an attempt towards this direction, the following definition is presented.
- “Financial Administration includes all the activities which generate, regulate and distribute monetary resources needed for the sustenance and growth of the members of a political community,”
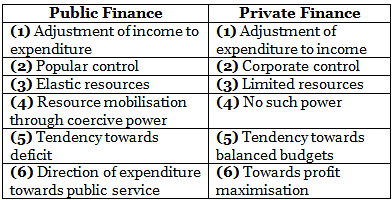
The Distinction between Public Finance and Private Fiance
Finance function appears to be a generic process which takes place in both public and private organisations. But, one should not conclude that the principles and norms which are applicable to private finance are equally applicable to public finance, for despite the challenge to the historic “separate but equal doctrine” from the integrationist movement of recent times, public organisations continue to possess certain distinct characteristics. Dissimilarities between public finance and private finance are quite sharp and clear. ‘According to Sundaram, these dissimilarities can be outlined as follows:
Financial Administration: Importance
- The importance of financial administration was not fully recognized until after the industrial revolution. Prior to this, the concept of minimal government intervention and taxation was dominant due to the laissez-faire doctrine. However, as society became more complex as a result of the industrial revolution, the role of government increased significantly. Moreover, the emergence of the welfare state led to a considerable expansion of state activities. In this changed context, financial administration became crucial for identifying ways to generate resources to meet the growing public expenditure.
- The Great Depression (1929-33) exposed the weaknesses of the neutral economic stance of governments and increased the demand for stability in income, employment, equality, and social justice. Based on the Keynesian perspective, the state assumed an active and positive role in expanding national income and employment and ensuring equity and equality. Fiscal policy became a powerful instrument for influencing the socio-economic life of the people. Defense and administrative expenditure shed their nonproductive label and assumed new importance as a means to stimulate income and employment levels. Financial administration was tasked with formulating effective policies to achieve these new objectives of the state, transforming financial resources into public purposes, and improving the individual's lot through distributive justice.
- With the rise of democracy as a popular social institution, the concept of 'parliamentary control over public purse' gained universal acceptance. The principles of "no taxation without representation" and "no public expenditure without parliamentary sanction" became the guiding canons of modern political communities. Consequently, there was an urgent need to develop a simple and systematic financial procedure to make the financial system comprehensible to the average person. Financial administration thus became an instrument of modern governments for making "popular sovereignty" a social reality.
- The concept of planned development allowed public administrators to play an active and dynamic role in formulating and implementing development schemes and projects. The time and cost of implementing these projects became critically important, and the focus of financial administration shifted from controlling the disbursement of funds to managing various development projects and programs. The rise of performance budgeting and other related budgetary innovations represent significant achievements of financial administration in meeting this challenge.
- From the early 1980s onwards, resource scarcity has become a severe problem for modern governments. While there is immense pressure on governments to increase expenditure to meet the ever-expanding ambitions and demands of the people, taxpayers are either unable or unwilling to bear additional tax burdens. In this dilemma, there is a need for careful prioritization of public expenditure. Hence, the study of financial administration and management, as part of public administration, has become important for seeking ways to eliminate unnecessary expenditure and ensure the optimization of output on a limited resource base. Zero-base budgeting is one such attempt.
To sum up, financial administration is playing a dominant role in modem times.
Nature of Financial Administration
There are two different views regarding the nature of financial administration. These are- Traditional view
- Modern view
Financial administration can be viewed from two perspectives: the traditional view and the modern view. The traditional view focuses on financial administration as a collection of activities aimed at generating, regulating, and distributing monetary resources needed for the growth and maintenance of public organizations. This perspective emphasizes the administrative functions related to the flow of funds and their regulation to ensure proper and productive use. Financial administrators in this view are considered financial managers responsible for planning, organizing, and directing financial activities to achieve efficient implementation of public policy. This view takes a value-neutral stance, focusing solely on the objective aspects of public finance.
On the other hand, the modern view sees financial administration as an integral part of the overall management process of public organizations rather than just raising and disbursing funds. This perspective includes the activities of all individuals involved in public administration, as most decisions made by public officials have direct or indirect financial consequences. The modern view also rejects the value-neutral stance of the traditional theory, incorporating socio-political, functional, and activating theories of public finance. Financial administration, in this view, has several roles, including equalizing wealth distribution, ensuring proper economic functioning through fiscal policies, promoting investment and national income growth, stabilizing price levels and inflationary trends, and maximizing social welfare through state participation in both public and private goods production.
In summary, financial administration can be understood from two different perspectives: the traditional view, which emphasizes the objective aspects of raising and disbursing funds, and the modern view, which considers financial administration as an essential part of overall public management and incorporates various roles and theories. The essence of financial administration may differ depending on the socio-political system and the specific mode of operation of socio-economic and political forces.
Scope of Financial Administration
The scope of financial administration can be understood as encompassing several core areas, which are integral to the effective functioning of a government's financial management system. These core areas include financial planning, budgeting, resource mobilization, investment decisions, expenditure control, and accounting, reporting, and auditing.
- Financial Planning: In a broad sense, financial planning involves the formulation and adoption of policies and programs to achieve the government's goals. This includes considering sources and forms of finance, forecasting expenditure needs, and desirable fund flow patterns. The Planning-Programming-Budgeting System (PPBS) represents an attempt to coordinate planning and budgeting, taking into account the long-term economic consequences of policies and their interrelationships.
- Budgeting: As the core of financial administration, budgeting involves examining and formulating fiscal policy, as well as ensuring equity and social justice. It also deals with the refinement of the budgetary system and its operative processes.
- Resource Mobilization: This area deals with the imposition and collection of taxes, rates, and other forms of revenue. Due to increasing government commitments, budgetary deficits have become a regular feature of public finance. In this context, deficit financing and public debt mobilization become crucial. However, it is vital to ensure that deficit financing is not used recklessly, as it can lead to inflation. Financial administrators must also tackle tax evasion and the growth of parallel economies.
- Investment Decisions: The financial and socio-economic appraisal of capital expenditure, or project appraisal, is essential for financial administrators. With massive investments being made in the public sector, a thorough understanding of the concepts, techniques, and methodology of project appraisal is indispensable.
- Expenditure Control: With government finances becoming increasingly inelastic, there is a pressing need for the careful utilization of resources. Both executive and legislative control are necessary to ensure the accountability of the executive to the legislature and protect the interests of individual taxpayers and the public.
- Accounting, Reporting, and Auditing: These aspects are designed to aid both executive and legislative control. In India, the Comptroller and Auditor General (C & AG) and the Indian Audit and Accounts Department ensure that accounting and audit functions are performed in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution.
In conclusion, the scope of financial administration is broad, encompassing various aspects of a government's financial management system. By adopting an integrated approach that incorporates all these core areas, financial administration can effectively contribute to economic decision-making within the government.
Components of Financial Administration
Theorists of public finance have identified three elements of public finance. They are :- Public Revenue
- Public Expenditure
- Public Debt
Since financial administration concerns itself with public finance and deals with the principles and practices pertinent to the proper and efficient administration of the state finances, the thinkers of financial administration have included the administrative aspects in the scope of financial'administration.
Some other thinkers, taking clue from Luther Gulick, have tried to project POSDCORCs view wherein:
P — Stands for Financial Planning
O — Stands for Financial Organisation such as Finance Ministry
S — Stands for Financial Personnel
D — Stands for Direction such as Financial advise
CO — Stands for Coordination of Income and Expenditure
R — Stands for Financial Reporting such as accounting
C — Stands for control which includes executive control, audit control and legislative control.
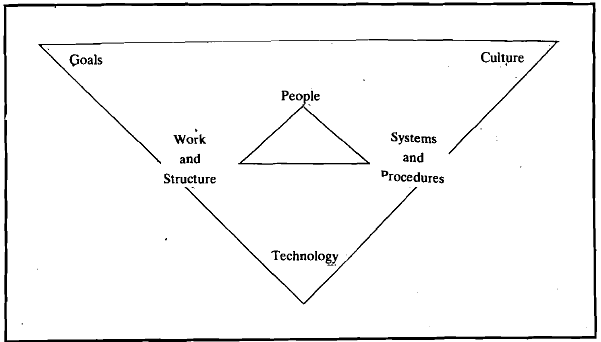
The above exposition does not reveal the exact picture related to the elements of financial administration. An organisational system consists of the following basic elements :
- The People
- Work and structure
- Systems and procedure
People represent human resources of the organisation. Work and structure represent efforts and processes concerning definition of tasks and roles, and organisation of ieporting relationships. Systems and procedures represent framework to facilitate interactions between the people and the work. These interactions result in organisational output. It is possible to identify the following elements of financial administration :
(a) Human Element
- Tax payers
- Fee Remitters
- Suppliers (Funds and materials)
- Employees (Public Officials)
- Entrepreneurs (Politicians)
- Customers & Common person
(b) Work and Structures
- The Legislature and its financial committees
- The Cabinet
- The Finance Department
- The Administrative Departments
- The Executive Departments
- The Audit Department
(c) Systems and Procedures
- Planning Systems
- Budgeting systems and procedure
- Controlling systems such as accounting and auditing
1. The human element in an organization consists of its participants, whose involvement is determined by a balance between their contributions and the rewards they receive. For example, people may be willing to contribute their money (through taxes or other means) and support a government as long as they feel they are adequately rewarded for their sacrifices and support. Public organizations cannot afford to ignore this aspect, as it plays a crucial role in determining the success and smooth functioning of the organization.
2. Work and structure refer to the organizational processes, such as divisional and integration processes, which create organizational subdivisions and allow for mutual interaction between them. Systems and procedures are the tools that connect people with the work and structure of the organization. These three components - human element, work and structure, and systems and procedures - interact with each other to produce the desired organizational outcomes.
3. However, any discussion of these administrative components would be incomplete without considering the environment that influences their content, nature, and capabilities. Financial administration is affected by two types of environments. The first one is the well-known socio-economic and political environment in which financial administration operates, also known as the suprasystem.
4. The second environment is an intermediary sub-system, which includes the goals pursued by the financial administration, the norms, values, beliefs, and behavior that make up the culture of financial administration, and the nature of the technology employed by the organization. In summary, the interaction between the human element, work and structure, systems and procedures, and the external and internal environments all contribute to the overall functioning and effectiveness of financial administration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial administration is a crucial aspect of public administration, playing a vital role in the sustenance and growth of political communities. Its importance has grown significantly since the advent of industrial revolution, welfare state, and planned development. Financial administration encompasses various aspects such as financial planning, budgeting, resource mobilization, investment decisions, expenditure control, and accounting, reporting, and auditing. It consists of three key components: human element, work and structure, and systems and procedures, all of which interact within the socio-economic and political environment. An understanding of these components is essential for effective financial management and ensuring the proper functioning of public organizations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Financial Administration - 1
What is the meaning of Financial Administration?
Financial Administration refers to the set of activities related to making money available to various branches of an organization, enabling it to carry out its objectives. It includes tasks such as financial planning, budgeting, resource mobilization, investment decisions, expenditure control, accounting, reporting, and auditing.
What is the difference between Public Finance and Private Finance?
Public finance deals with the management of financial resources by governments, while private finance deals with the management of financial resources by private individuals or corporations. Public finance focuses on taxation, public expenditure, and public debt, whereas private finance focuses on investment, savings, and borrowing.
What are the roles of Financial Administration according to the modern view?
The modern view of financial administration includes equalizing role, functional role, activating role, stabilizing role, and participatory role. These roles involve addressing wealth inequalities, ensuring the proper functioning of the economy, facilitating investment, stabilizing price levels and inflationary trends, and maximizing social welfare through state participation.
What are the core areas of Financial Administration?
The core areas of financial administration include financial planning, budgeting, resource mobilization, investment decisions, expenditure control, accounting, reporting, and auditing.
What are the components of Financial Administration?
The components of financial administration can be divided into three categories: human element, work and structures, and systems and procedures. The human element includes taxpayers, fee remitters, suppliers, employees, entrepreneurs, and customers. Work and structures consist of the legislature, cabinet, finance department, administrative departments, executive departments, and audit department. Systems and procedures include planning systems, budgeting systems and procedures, and controlling systems such as accounting and auditing.
FAQs on Financial Administration - 1 - UPSC
| 1. What is the meaning of financial administration? |  |
| 2. Why is financial administration important? |  |
| 3. What is the nature of financial administration? |  |
| 4. What are the components of financial administration? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions about financial administration? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















