Firearm Entry vs Exit wound | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Definitions
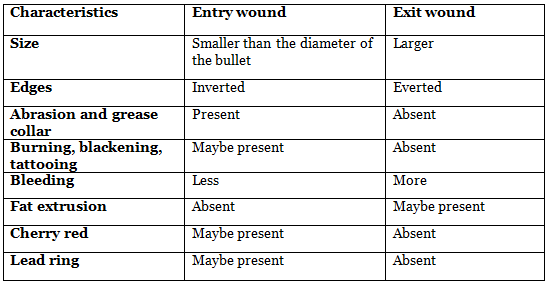
Tattooing (peppering/stippling): Tiny, distinct black specks resistant to removal, resulting from the embedding of gunpowder grains into the skin.
Blackening/Smudging/fouling: The presence of carbonaceous deposits on the skin that can be easily wiped away, originating from the accumulation of smoke on the skin.
Lead ring/Metal ring: The deposition of minute amounts of lead at the projectile's entry point, derived from bullet lubrication, gun oil, lead surface residue, and dirt carried on the bullet.
Abrasion collar: Skin abrasion surrounding a wound caused by the rotating bullet's friction against the inverted epidermis and the bullet's heat.
Contusion collar: An abraded collar exhibiting contusion, also known as a "contusion collar."
Grease collar/Dirt collar: The transportation of firearm barrel lubricant onto the projectile's surface.
Scorching, singeing (burning): Resulting from exposure to flames.
Fouling: Denotes minuscule lesions around the entry wound caused by metal fragments (from missiles or the barrel interior) expelled during discharge, resistant to wiping.
Back spatter: In contact shots, the muzzle blast and negative pressure in the barrel may draw blood, hair, tissue fragments, and cloth fibers several centimeters back into the barrel, referred to as "back spatter."
Fire arm-Entry vs Exit Wound
Estimation of Distance of Fire arm injury



Firearm Entry vs Exit wound-Repeats
- How will you differentiate an Entry Wound from an Exit Wound (1995)?
- How will you differentiate an entry wound from an exit wound in case of a firearm injury? (1999)
- Describe the features of the entry wound by a bullet fired, from a rifle. Mention the differentiating features of an entry and exit wound caused by a rifled firearm (2003).
- Describe the features of contact wound by a rifled firearm. How will you differentiate entry and exit wound in a distant fire (2007)?
- A young person ol 25 years has sustained smooth barrel shotgun firearm injury on right side of chest. How will you establish on clinical examination the entry wound and distance of fire? (2015)
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Firearm Entry vs Exit wound - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is a firearm entry vs exit wound? |  |
| 2. How can the estimation of distance of a firearm injury be determined? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of a firearm entry wound? |  |
| 4. How are firearm exit wounds different from entry wounds? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to analyze firearm entry and exit wounds in forensic investigations? |  |

















