|
The Indian Constitution can be amended through a process outlined in which article? |
Card: 1 / 40 |
|
The amendment process in India requires a ___ majority in both Houses of Parliament. |
Card: 3 / 40 |
|
True or False: The President of India can withhold assent to a constitutional amendment bill. |
Card: 5 / 40 |
|
What is the significance of the 'basic structure' doctrine established by the Supreme Court? |
Card: 7 / 40 |
|
It prevents amendments from altering the fundamental framework of the Constitution. 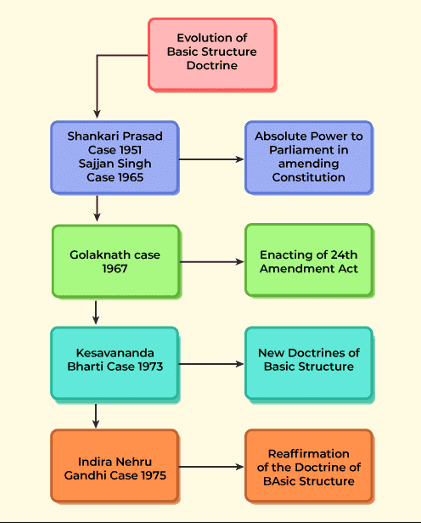 |
Card: 8 / 40 |
|
True or False: A joint sitting of Parliament is held if there is disagreement between the Houses on a constitutional amendment bill. |
Card: 9 / 40 |
|
What is required for a state legislature to ratify a constitutional amendment? |
Card: 11 / 40 |
|
True or False: A Special Majority of Parliament requires a majority of the total membership of each House and a two-thirds majority of members present and voting. |
Card: 13 / 40 |
|
What distinguishes an amendment by Special Majority of Parliament from an amendment by Simple Majority? |
Card: 15 / 40 |
|
A Special Majority requires both a majority of the total membership and a two-thirds majority of those present and voting, while a Simple Majority requires only a simple majority of those present and voting. |
Card: 16 / 40 |
|
The process of altering the areas, boundaries, or names of existing states requires a ___ majority in Parliament. |
Card: 17 / 40 |
|
True or False: To amend provisions related to Fundamental Rights, only a simple majority is required in Parliament. |
Card: 19 / 40 |
|
False. A special majority is required to amend provisions related to Fundamental Rights.  |
Card: 20 / 40 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
What is the significance of the 'total membership' concept in the context of amending the Constitution? |
Card: 21 / 40 |
|
Total membership refers to all members in the House, regardless of absence, and is used to determine the majority needed for constitutional amendments. |
Card: 22 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Fifth Schedule of the Constitution deals with the administration of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes. |
Card: 23 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The procedure for changing most parts of the Constitution requires a ___ majority at the third reading in Parliament. |
Card: 25 / 40 |
|
True or False: The consent of states is necessary for all amendments to the Constitution. |
Card: 27 / 40 |
|
False. Consent of states is only necessary for amendments related to the federal structure. 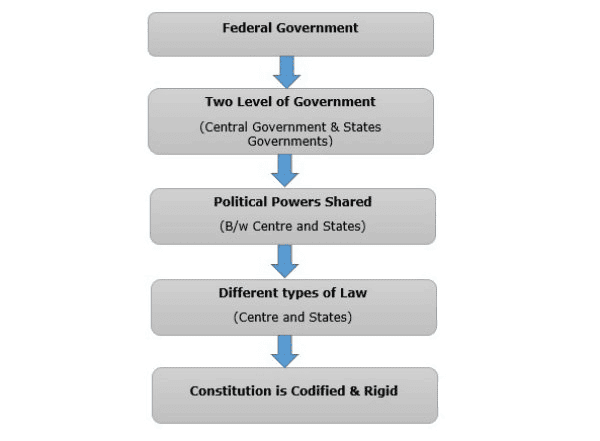 |
Card: 28 / 40 |
|
The process of amending the Constitution does not have a time limit for states to decide. True or False? |
Card: 29 / 40 |
|
What is the role of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council in relation to constitutional amendments? |
Card: 31 / 40 |
|
The GST Council decides on GST matters, which are part of the legislative powers that can be amended.  |
Card: 32 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The Seventh Schedule lists categorizing subjects for legislation include ___ and ___ powers between the Union and states. |
Card: 33 / 40 |
|
What is a key criticism of the amendment process regarding state legislature consent? |
Card: 37 / 40 |
|
There is no set time frame for state legislatures to approve or reject an amendment, and it is unclear if they can change their approval after initially consenting. |
Card: 38 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Indian Constitution provides a procedure for a joint sitting of both Houses of Parliament in case of disagreement on a constitutional amendment. |
Card: 39 / 40 |
|
False: There is no provision for a joint sitting for constitutional amendments, which differs from ordinary bills.  |
Card: 40 / 40 |
























