|
The basic structure of a constitution includes a preamble, fundamental rights, and provisions for emergencies among other elements. What is the significance of the supremacy clause? |
Card: 1 / 38 |
|
The supremacy clause ensures that the constitution is the highest law of the land, taking precedence over any conflicting laws or government actions. 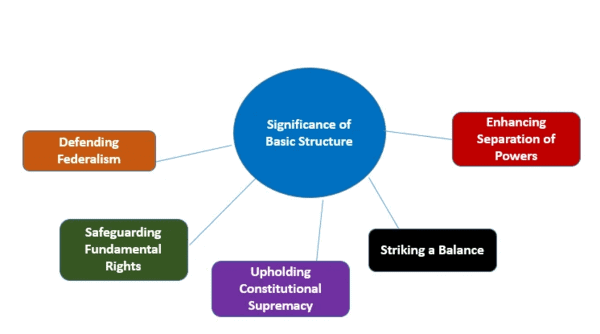 |
Card: 2 / 38 |
|
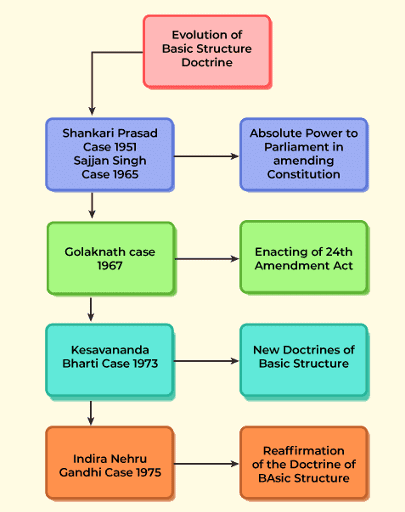
Fill in the blank: The Golak Nath Case (1967) ruled that Fundamental Rights are ___ and ___, meaning they cannot be amended by Parliament. |
Card: 3 / 38 |
|
True or False: The 24th Amendment Act (1971) affirmed that constitutional amendment acts are considered laws under Article 13. |
Card: 5 / 38 |
|
False. The 24th Amendment Act declared that such acts would not be considered laws under Article 13.  |
Card: 6 / 38 |
|
What was the primary outcome of the Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973) regarding constitutional amendments? |
Card: 7 / 38 |
|
The case established the Basic Structure Doctrine, ruling that while Parliament can amend the Constitution, it cannot alter its fundamental structure.  |
Card: 8 / 38 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Shankari Prasad Case (1951) was the first challenge to the constitutional validity of the ___ Amendment Act. |
Card: 9 / 38 |
|
The basic structure doctrine asserts that Parliament cannot alter ___ features of the Constitution. |
Card: 11 / 38 |
|
True or False: The 42nd Amendment Act declared that amendments made by Parliament cannot be questioned in court. |
Card: 13 / 38 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Supreme Court invalidated a provision of the 39th Amendment Act in the ___ case. |
Card: 15 / 38 |
|
What was the primary outcome of the Minerva Mills case regarding the 42nd Amendment? |
Card: 17 / 38 |
|
It invalidated the provision that excluded judicial review, affirming that Parliament cannot convert its limited power into an absolute one. |
Card: 18 / 38 |
|
The Waman Rao case clarified that the basic structure doctrine applies to constitutional amendments enacted after ___ date. |
Card: 19 / 38 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Fill in the blank: The Constitution of India ensures a ___ character, promoting the coexistence of multiple religions. |
Card: 23 / 38 |
|
True or False: The separation of powers in the Indian Constitution is intended to create a system of checks and balances among the legislature, executive, and judiciary. |
Card: 25 / 38 |
|
It refers to the distribution of powers between the central government and the state governments, allowing both levels of government to operate independently in their respective areas. |
Card: 28 / 38 |
|
The principle of equality in the Constitution ensures that ___ and ___ are treated equally under the law. |
Card: 29 / 38 |
|
Fill in the blank: The welfare state concept in the Constitution emphasizes ___ and ___ justice. |
Card: 31 / 38 |
|
They are meant to be harmonized to ensure that individual freedoms do not undermine the goals of socio-economic justice as laid out in the Directive Principles. |
Card: 34 / 38 |
|
Fill in the blank: The parliamentary system in India is characterized by the ___ relationship between the executive and the legislature. |
Card: 35 / 38 |
|
True or False: Free and fair elections are not guaranteed by the Constitution of India. |
Card: 37 / 38 |
|
False - Free and fair elections are a fundamental requirement and are guaranteed by the Constitution.  |
Card: 38 / 38 |