|
Card: 1 / 32 |
Citizens in India have the right to vote in elections to the ___ and ___ legislative assemblies. |
|
Card: 3 / 32 |
True or False: Only citizens by birth are eligible for the office of President in India. |
|
Card: 4 / 32 |
False. Both citizens by birth and naturalized citizens are eligible for the office of President in India. |
|
Card: 5 / 32 |
What is the classification of aliens in India based on their country's relationship with India? |
|
Card: 7 / 32 |
The Indian Constitution provides for ___ citizenship, ensuring that all citizens owe allegiance solely to the Union. |
|
Card: 9 / 32 |
True or False: India allows for double citizenship, similar to the USA and Australia. |
|
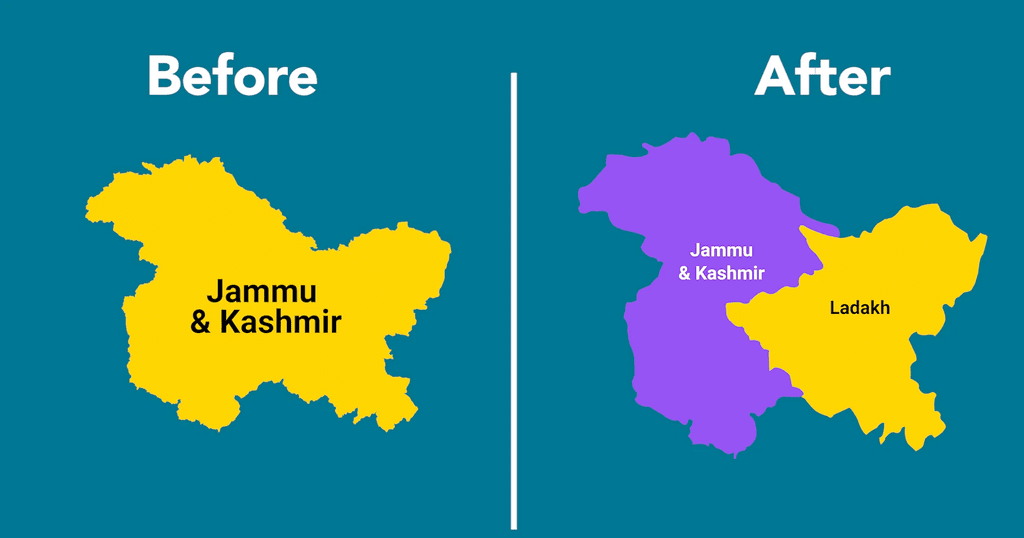
Card: 13 / 32 |
Fill in the blank: Until 2019, Jammu and Kashmir had special provisions defining permanent residents based on Article ___ . |
|
Card: 15 / 32 |
True or False: The abolition of Jammu and Kashmir's special status in 2019 has not impacted the rights of its residents. |
|
Card: 16 / 32 |
False. The abolition of special status impacted the rights and privileges of residents.  |
|
Card: 17 / 32 |
The Constitution of India provides detailed provisions for the acquisition or loss of citizenship after its commencement. True or False? |
|
Card: 18 / 32 |
False. The Constitution lacks permanent or detailed provisions regarding acquisition or loss of citizenship after its commencement. |
|
Card: 19 / 32 |
True or False: An Indian citizen can voluntarily acquire foreign citizenship while retaining their Indian citizenship. |
|
Card: 20 / 32 |
False. There is a prohibition on acquiring foreign citizenship voluntarily while remaining an Indian citizen.  |
|
Card: 21 / 32 |
What must individuals of Indian origin residing abroad do to become Indian citizens? |
|
Card: 22 / 32 |
They must register as Indian citizens through diplomatic or consular representatives. |
|
Card: 23 / 32 |
The Citizenship Act, 1955 governs the rules for acquiring and losing citizenship after the Constitution's commencement. True or False? |
|
Card: 25 / 32 |
The Central Government can register individuals for citizenship based on specific criteria such as Indian origin or marriage to an Indian citizen. True or False? |
|
Card: 29 / 32 |
True or False: A citizen of India automatically loses citizenship if they acquire citizenship of another country only during peacetime. |
|
Card: 30 / 32 |
False. Citizenship automatically terminates if a citizen voluntarily acquires citizenship of another country, with exceptions during wartime. |
|
Card: 31 / 32 |
Fill in the blank: Special provisions for migrants from Afghanistan, Bangladesh, or Pakistan allow citizenship for specified communities who entered India before ___ . |