|
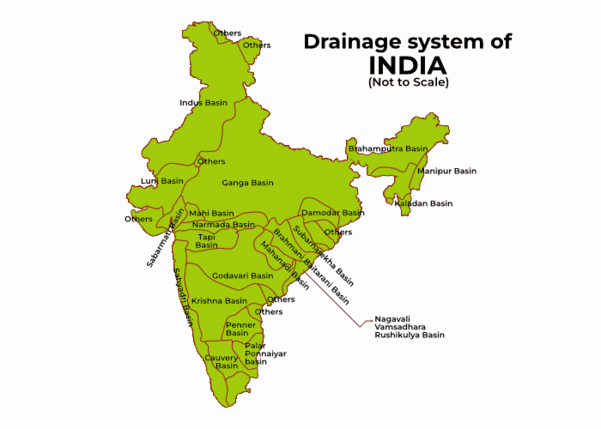
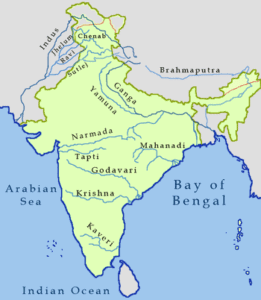
What separates the Arabian Sea drainage from the Bay of Bengal drainage in India? |
Card: 5 / 40 |
|
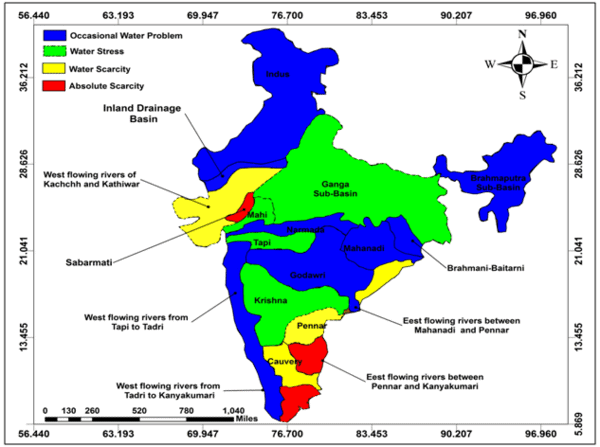
Fill in the blank: Nearly ___ percent of the drainage area in India is oriented towards the Bay of Bengal. |
Card: 7 / 40 |
|
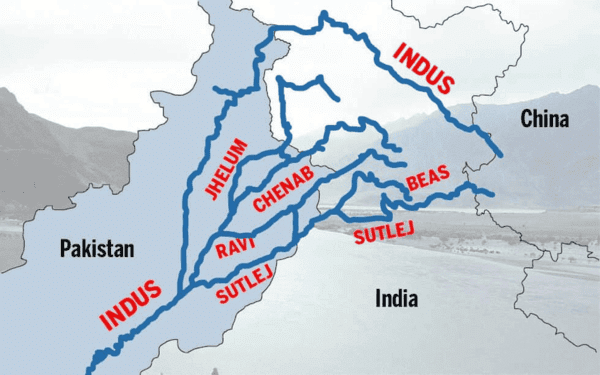
True or False: The Indus River system discharges its water into the Bay of Bengal. |
Card: 9 / 40 |
|
How are Indian drainage systems categorized based on water discharge orientation? |
Card: 11 / 40 |
|
They are categorized into the Arabian Sea drainage and the Bay of Bengal drainage.  |
Card: 12 / 40 |
|
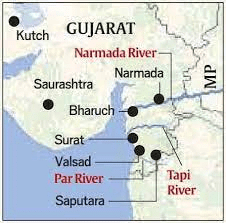
True or False: The Narmada and Tapi rivers discharge their waters into the Bay of Bengal. |
Card: 15 / 40 |
|
What are the two classifications of Indian drainage based on origin and characteristics? |
Card: 17 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The medium river basins in India have a catchment area between ___ and ___ sq. km. |
Card: 19 / 40 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
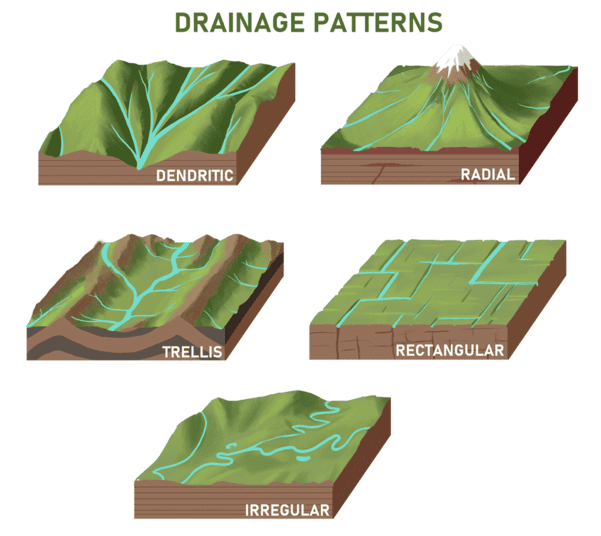
The drainage pattern resembling the branches of a tree is known as ___ and is exemplified by the rivers of the northern plain. |
Card: 23 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Himalayan drainage system is characterized by rivers that are only seasonal and not perennial. |
Card: 25 / 40 |
|
False. The Himalayan drainage system includes perennial rivers fed by melting snow and precipitation.  |
Card: 26 / 40 |
|
What are the primary features formed by rivers as they transition from the Himalayan region to the plains? |
Card: 27 / 40 |
|
The rivers form depositional features such as flat valleys, ox-bow lakes, flood plains, braided channels, and deltas near their mouths. 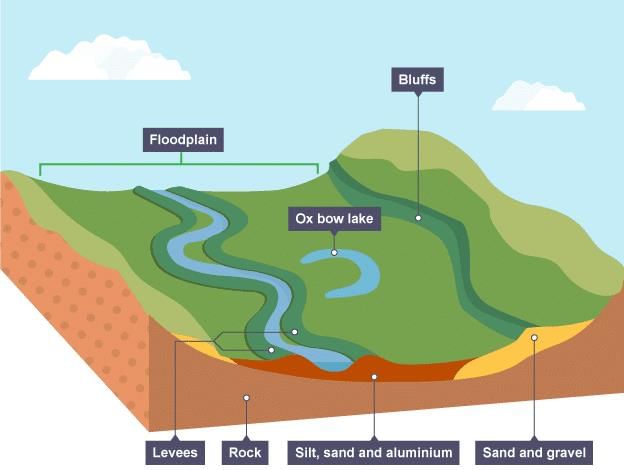 |
Card: 28 / 40 |
|
Rivers originating from the Amarkantak range illustrate which type of drainage pattern? |
Card: 29 / 40 |
|
Radial drainage pattern, where rivers flow in all directions from a central point. 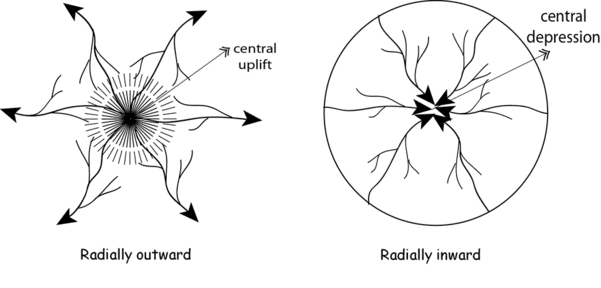 |
Card: 30 / 40 |
|
True or False: The rivers of the Himalayan drainage system pass through deep gorges and form rapids and waterfalls. |
Card: 31 / 40 |
|
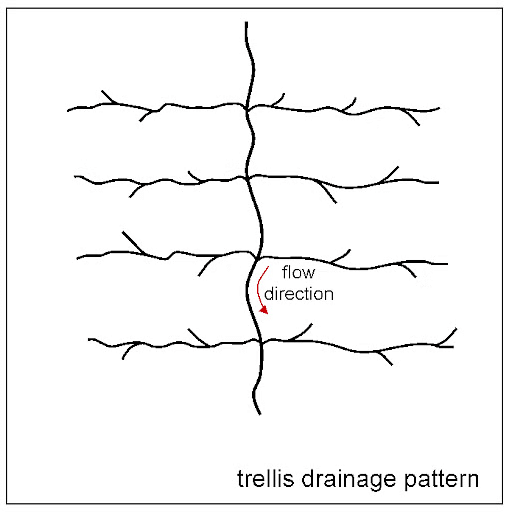
What type of drainage pattern is characterized by primary tributaries flowing parallel to each other with secondary tributaries joining at right angles? |
Card: 33 / 40 |
|
The Indo-Brahma river was thought to have traversed the entire Himalayan region during what geological period? |
Card: 35 / 40 |
|
True or False: The dismemberment of the Indo-Brahma river into separate drainage systems occurred primarily during the Holocene period. |
Card: 37 / 40 |
|
What geological feature acted as the water divide between the Indus and Ganga drainage systems? |
Card: 39 / 40 |