|
The Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution are more elaborate than those in the Constitution of ___ and ___. |
Card: 1 / 44 |
|
True or False: The right to property is currently listed as one of the Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution. |
Card: 3 / 44 |
|
False; it was deleted by the 44th Amendment Act, 1978 and is now a legal right under Article 300-A.  |
Card: 4 / 44 |
|
What are the six Fundamental Rights currently recognized in the Indian Constitution? |
Card: 5 / 44 |
|
Right to equality, Right to freedom, Right against exploitation, Right to freedom of religion, Cultural and educational rights, Right to constitutional remedies. 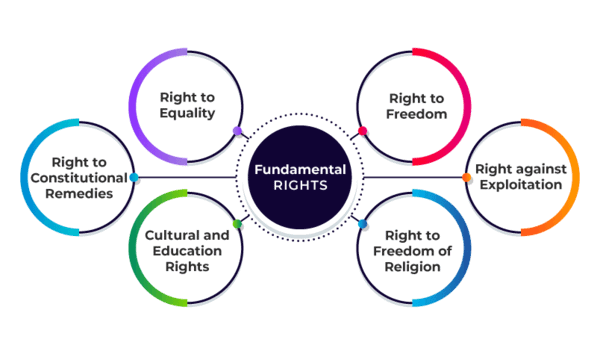 |
Card: 6 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Fundamental Rights are enshrined in Part ___ of the Indian Constitution. |
Card: 7 / 44 |
|
Which article of the Indian Constitution provides for the Right to constitutional remedies? |
Card: 9 / 44 |
|
True or False: The original Constitution of India provided for eight Fundamental Rights. |
Card: 11 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: The right against exploitation is covered under Articles ___ and ___. |
Card: 13 / 44 |
|
Article 12 of the Indian Constitution defines The State as encompassing ___, ___, and other authorities under the control of the Government of India. |
Card: 15 / 44 |
|
The Government and Parliament of India, the Government and legislatures of the states  |
Card: 16 / 44 |
|
True or False: Article 13 states that all laws inconsistent with Fundamental Rights are void only if they were enacted after the commencement of the Constitution. |
Card: 17 / 44 |
|
False. Article 13 states that all laws inconsistent with Fundamental Rights, regardless of when they were enacted, are void.  |
Card: 18 / 44 |
|
True or False: According to Article 13, a constitutional amendment can never be challenged in court. |
Card: 19 / 44 |
|
False. A constitutional amendment can be challenged if it violates a fundamental right that forms part of the basic structure of the Constitution. |
Card: 20 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Supreme Court held in the Kesavananda Bharati case that a constitutional amendment can be declared void if it violates a fundamental right that forms part of the ___ of the Constitution. |
Card: 21 / 44 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Article 14 of the Indian Constitution guarantees ___ before the law and ___ protection of the laws. |
Card: 23 / 44 |
|
True or False: The concept of 'equality before law' provides special privileges to certain individuals. |
Card: 25 / 44 |
|
True or False: Members of Parliament can be prosecuted for statements made during parliamentary sessions. |
Card: 27 / 44 |
|
False; they are protected under Article 105 for anything said or voted in Parliament.  |
Card: 28 / 44 |
|
What is the significance of 'equal protection of laws' in the context of the Indian Constitution? |
Card: 29 / 44 |
|
It ensures that every individual is treated equally by the laws of the land, preventing discrimination. 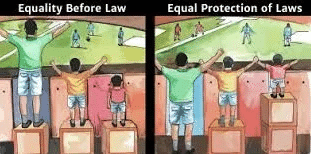 |
Card: 30 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: The concept of 'equality before law' is derived from ___ law, while 'equal protection of laws' is from ___ law. |
Card: 31 / 44 |
|
What are the exceptions to the principle of equality before law as outlined in Article 361? |
Card: 33 / 44 |
|
The President and Governor cannot be prosecuted or arrested during their term of office. |
Card: 34 / 44 |
|
True or False: The rule of equality before law is considered an absolute principle without exceptions. |
Card: 35 / 44 |
|
False; there are constitutional exceptions like those concerning the President and Governor. |
Card: 36 / 44 |
|
Article 15 prohibits discrimination against citizens on the grounds of ___, ___, ___, ___, and ___ only. |
Card: 37 / 44 |
|
Article 16 ensures equality of opportunity in public employment for all citizens except for special provisions made for ___ classes. |
Card: 39 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: Article 16 prohibits discrimination in public employment on the grounds of ___, ___, ___, ___, ___, and ___. |
Card: 41 / 44 |
|
The Protection of Civil Rights Act, 1955 punishes offenses committed on the ground of untouchability with imprisonment up to ___ months or a fine up to ___ or both. |
Card: 43 / 44 |