|
Card: 1 / 40 |
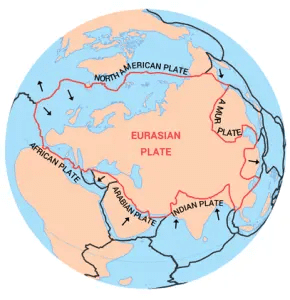
The Himalayas were formed as a result of the convergence of the Indo-Australian Plate with the ___ Plate. |
|
Card: 3 / 40 |
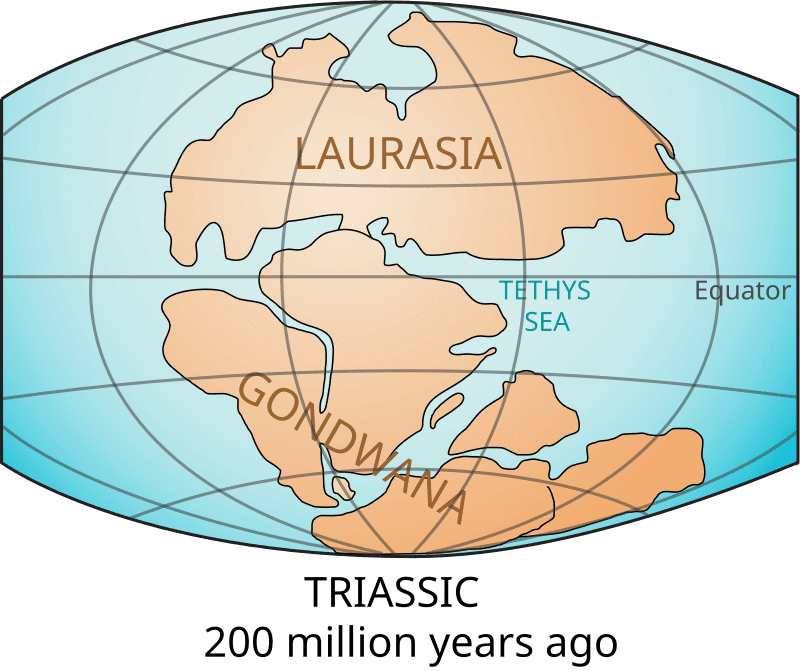
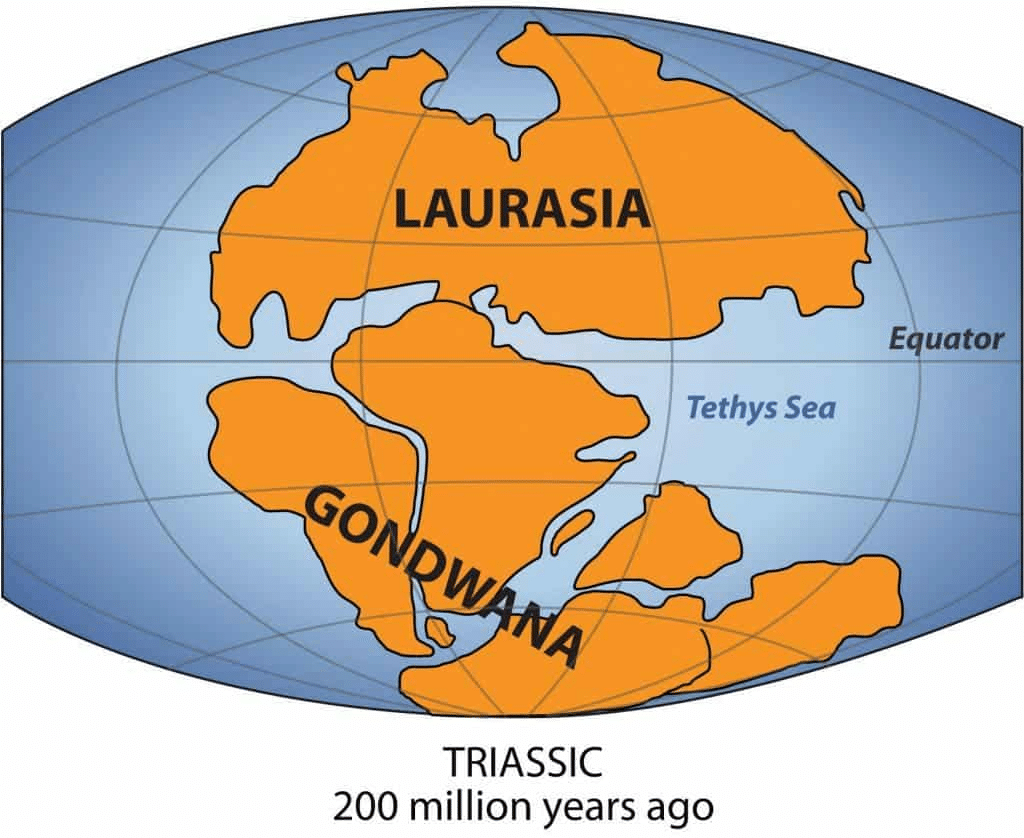
True or False: The Tethys Sea was formed after the breakup of the supercontinent Pangea. |
|
Card: 5 / 40 |
What significant geological event occurred approximately 150 million years ago that contributed to the formation of the Himalayas? |
|
Card: 9 / 40 |
The sediments deposited into the Tethys Sea came primarily from the landmasses of ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 11 / 40 |
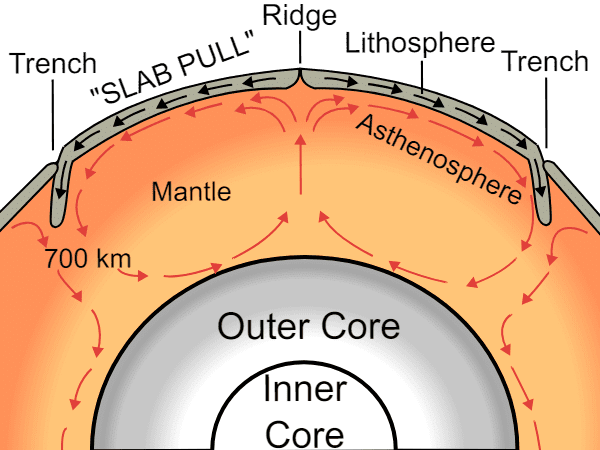
What was the primary driver behind the northward movement of the Indo-Australian Plate? |
|
Card: 15 / 40 |
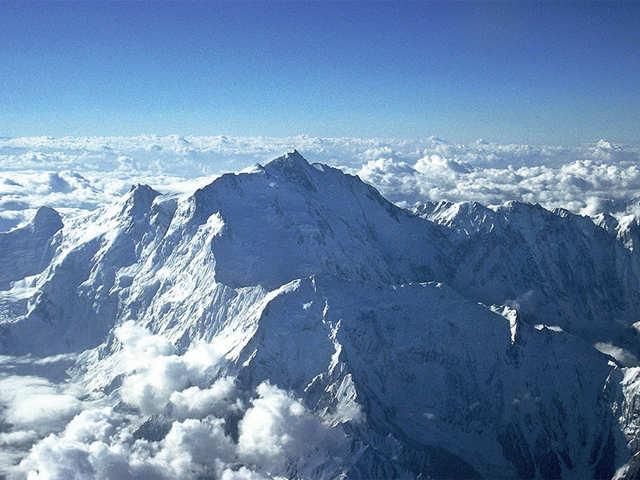
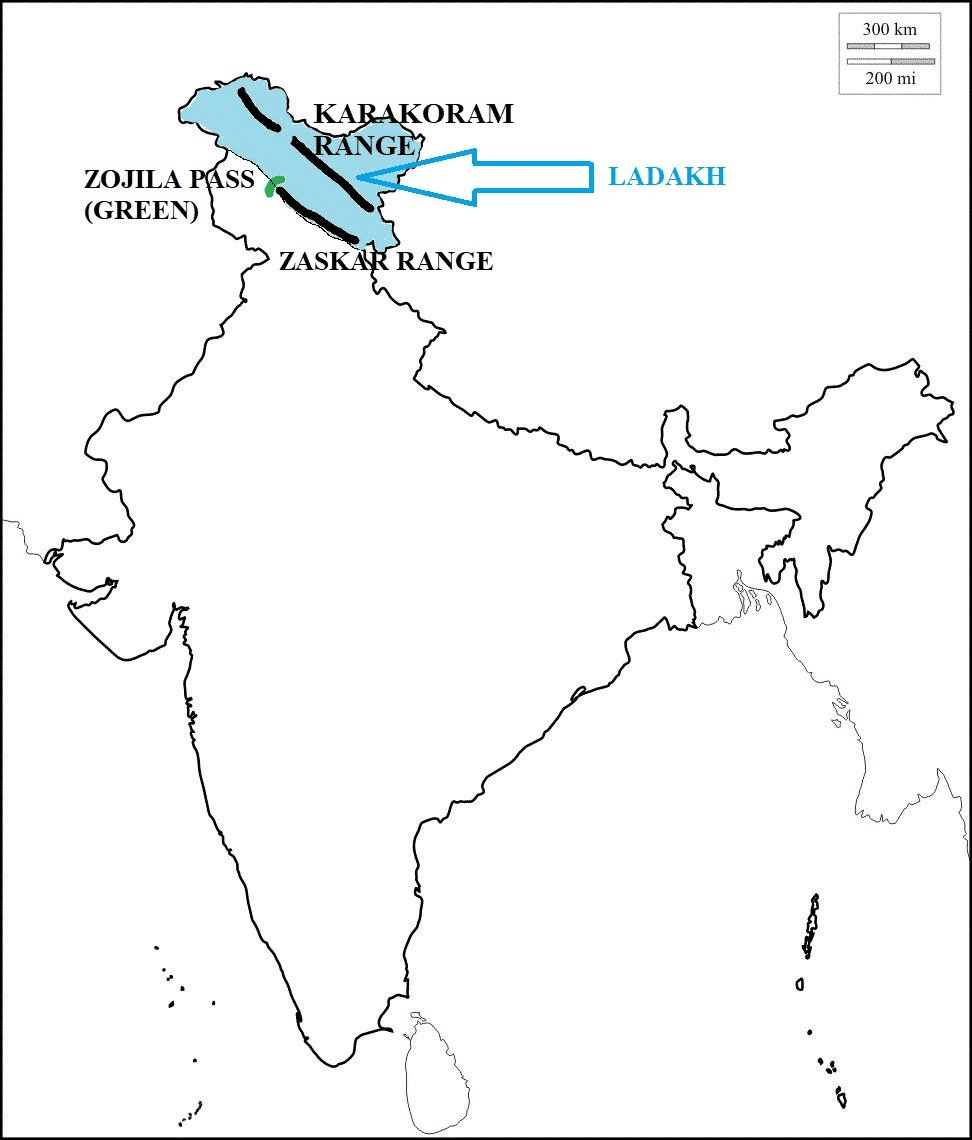
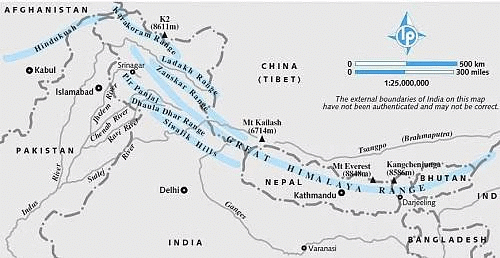
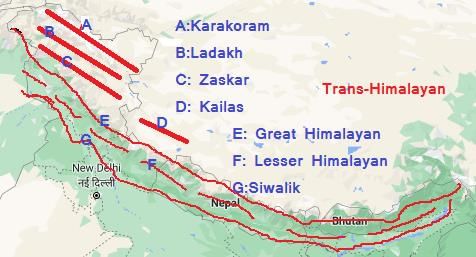
True or False: K2, located in the Karakoram Range, is the highest peak in the Trans-Himalayas. |
|
Card: 16 / 40 |
False. K2 is the second-highest peak in the world, while Mount Everest is the highest.  |
|
Card: 21 / 40 |
True or False: The Ladakh Range is considered an extension of the Great Himalayan Range. |
|
Card: 24 / 40 |
It contains K2, the world's second-highest peak, and significant glaciers like the Siachen Glacier.  |
|
Card: 27 / 40 |
True or False: The southern boundary of the Himalayan Range is clearly defined by the Indo-Gangetic Plains. |
|
Card: 29 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The Himalayan Range spans over ___ kilometers from the Indus Gorge to the Brahmaputra Gorge. |
|
Card: 35 / 40 |
The Greater Himalayas are home to the world's highest peaks including ___, ___, and ___. |