|
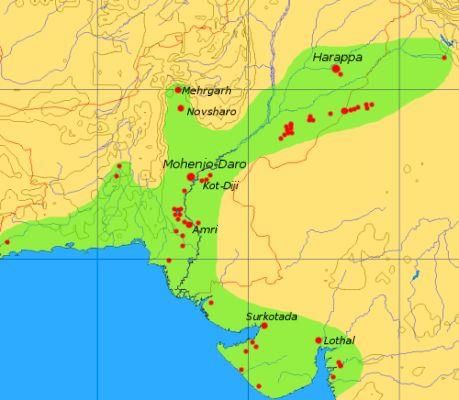
True or False: The Indus Valley Civilization was first discovered at the site of Mohenjodaro. |
Card: 3 / 38 |
|
Fill in the blank: The area of the Indus Valley Civilization extended from ___ in the north to the Narmada estuary in the south. |
Card: 5 / 38 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The Harappan civilization reached its mature phase in coastal cities like ___ and ___. |
Card: 9 / 38 |
|
What is the significance of the city of Lothal in the context of the Indus Valley Civilization? |
Card: 11 / 38 |
|
Lothal is one of the important Harappan cities located at the head of the Gulf of Cambay.  |
Card: 12 / 38 |
|
Fill in the blank: The two cultural phases identified at Banwali are ___ and ___ phases. |
Card: 13 / 38 |
|
True or False: The Harappan Civilization was discovered in 1921 at the site of Mohenjo-daro. |
Card: 15 / 38 |
|
False. The Harappan Civilization was discovered in 1921 at the site of Harappa.  |
Card: 16 / 38 |
|
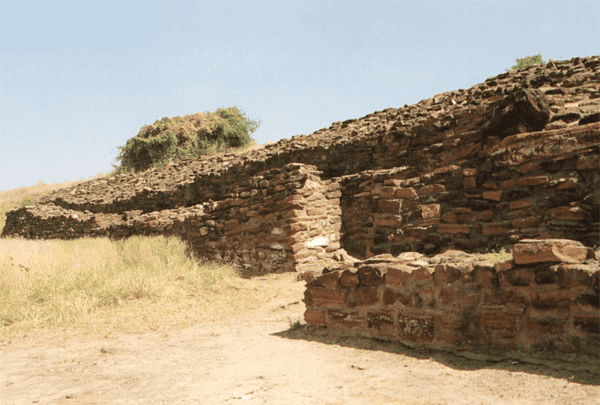
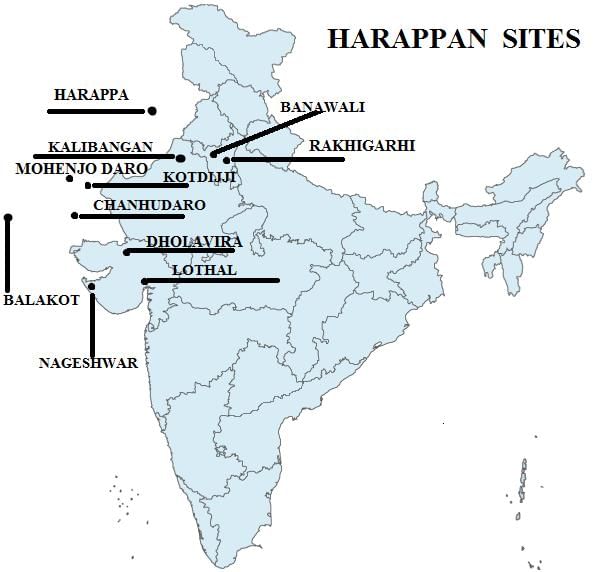
There are six major cities known to be part of the Harappan Civilization: Harappa, Mohenjo-daro, Chanhu-daro, Lothal, Kalibangan, and Banwali. 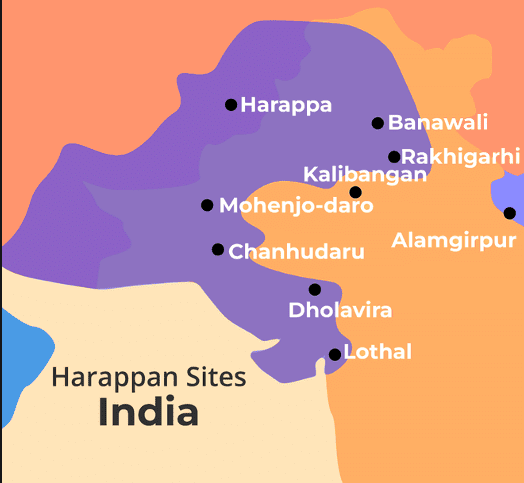 |
Card: 18 / 38 |
|
The architecture of Harappan cities is characterized by a ___ system of town planning. |
Card: 19 / 38 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
True or False: The Great Bath in Mohenjo-daro is believed to have served as a public bathing facility. |
Card: 21 / 38 |
|
What materials were primarily used in the construction of Harappan cities, setting them apart from contemporary Egyptian architecture? |
Card: 25 / 38 |
|
True or False: The granaries in Harappa were constructed without any consideration for proximity to the river. |
Card: 27 / 38 |
|
The Indus Valley Civilization was known for producing two types of ___ and ___ in significant quantities. |
Card: 29 / 38 |
|
Food grains were stored in large granaries in Mohenjo-daro and Harappa primarily for ___ and ___ during emergencies. |
Card: 33 / 38 |
|
True or False: The Indus people relied primarily on livestock for their economy. |
Card: 35 / 38 |
|
The Harappans domesticated several animals including ___, ___, and ___ for agricultural purposes. |
Card: 37 / 38 |